Found 12 results
Review
30 May 2024A Review on Design of Sustainable Advanced Materials by Using Artificial Intelligence
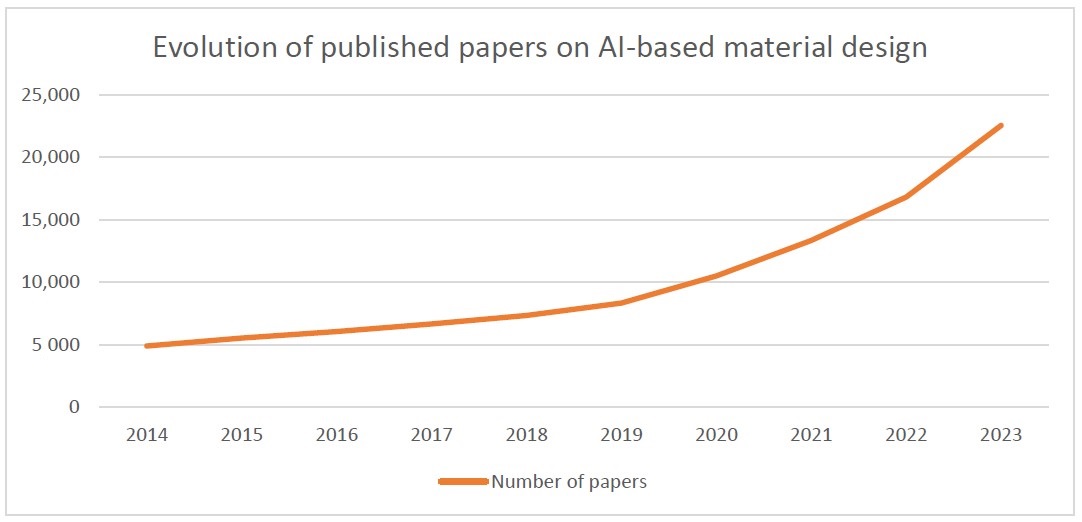
This paper gives a comprehensive review of scientific interests and current methodologies of artificial intelligence applied to advanced material design and discovery by taking into account multiple sustainable design criteria such as functionalities, costs, environmental impacts, and recyclability. The main research activities include predicting material properties, compositions, and structures with data mining, new material discovery, hybrid modeling approaches combining AI techniques and classical computational formulations based on physical and chemical laws, and multicriteria optimization of materials. Based on this review, a short analysis is provided on the perspectives of this research area in the future, aiming at creating an everything connected material life cycle with real-time traceability systems
Communication
30 May 2024A Novel Animal Model for Pulmonary Hypertension: Lung Endothelial-Specific Deletion of Egln1 in Mice
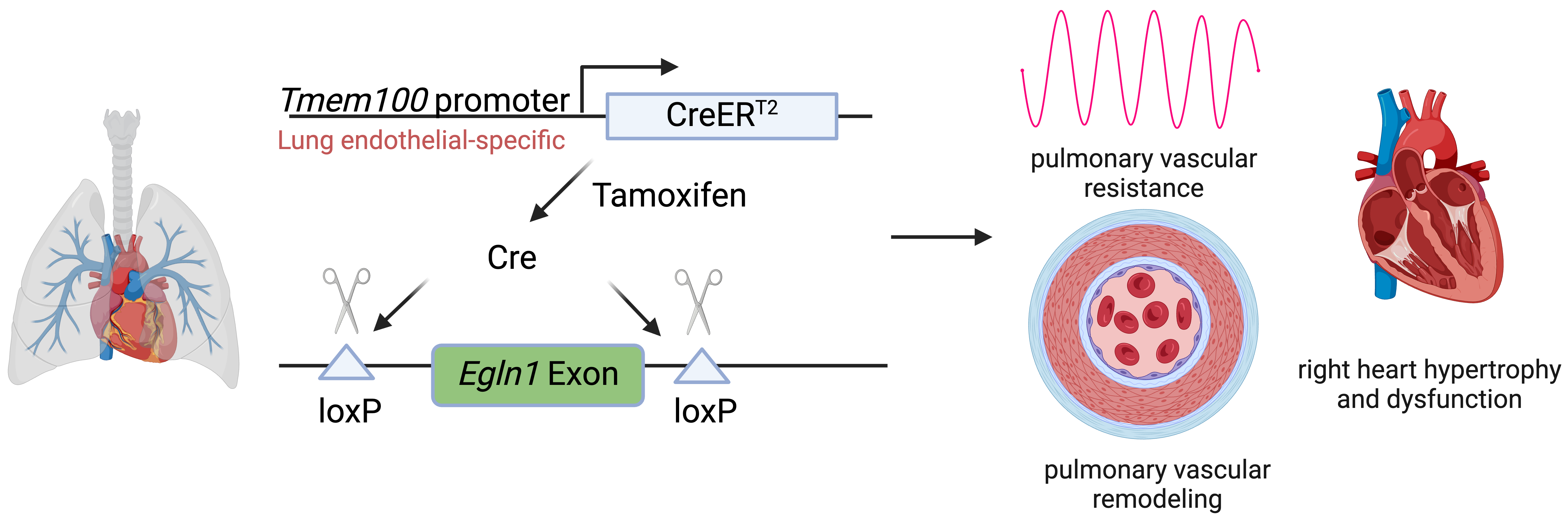
Pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH) is a devastating disease characterized by high blood pressure in the pulmonary arteries, which can potentially lead to heart failure over time. Previously, our lab found that endothelia-specific knockout of Egln1, encoding prolyl 4-hydroxylase-2 (PHD2), induced spontaneous pulmonary hypertension (PH). Recently, we elucidated that Tmem100 is a lung-specific endothelial gene using Tmem100-CreERT2 mice. We hypothesize that lung endothelial-specific deletion of Egln1 could lead to the development of PH without affecting Egln1 gene expression in other organs. Tmem100-CreERT2 mice were crossed with Egln1flox/flox mice to generate Egln1f/f;Tmem100-CreERT2 (LiCKO) mice. Western blot and immunofluorescent staining were performed to verify the knockout efficacy of Egln1 in multiple organs of LiCKO mice. PH phenotypes, including hemodynamics, right heart size and function, pulmonary vascular remodeling, were evaluated by right heart catheterization and echocardiography measurements. Tamoxifen treatment induced Egln1 deletion in the lung endothelial cells (ECs) but not in other organs of adult LiCKO mice. LiCKO mice exhibited an increase in right ventricular systolic pressure (RVSP, ~35 mmHg) and right heart hypertrophy. Echocardiography measurements showed right heart hypertrophy, as well as cardiac and pulmonary arterial dysfunction. Pulmonary vascular remodeling, including increased pulmonary wall thickness and muscularization of distal pulmonary arterials, was enhanced in LiCKO mice compared to wild-type mice. Tmem100 promoter-mediated lung endothelial knockout of Egln1 in mice leads to development of spontaneous PH. LiCKO mice could serve as a novel mouse model for PH to study lung and other organ crosstalk.
Article
14 May 2024Measurement and Structure of Common Prosperity of Urban Residents the Case of Hangzhou, China
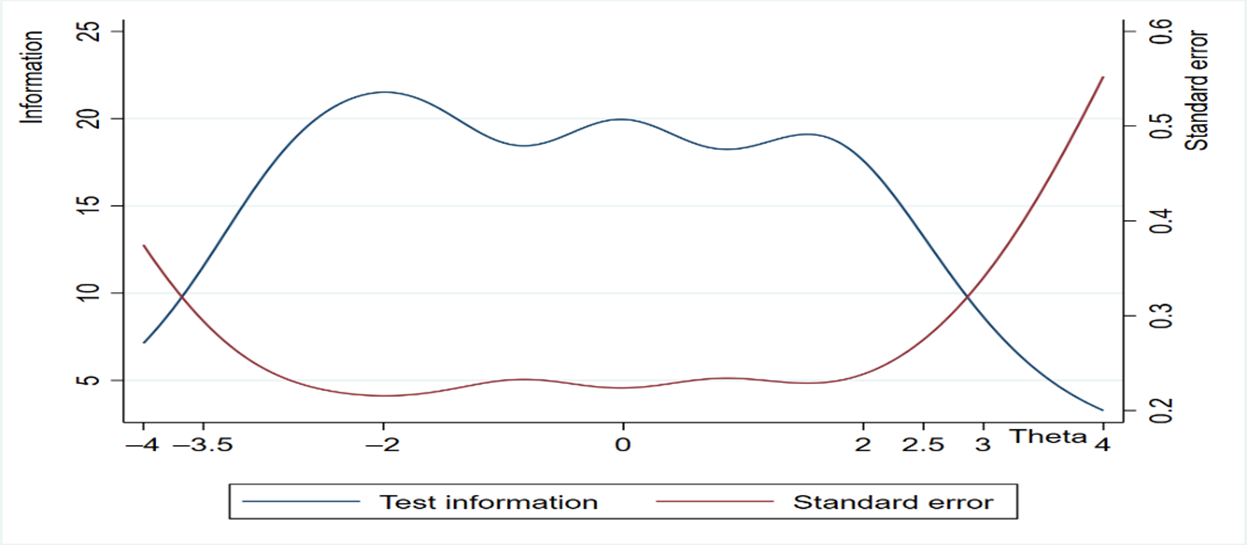
Common prosperity is an important feature of the social state that the people of the world aspire to, and an important feature of the Chinese path to modernization. Taking common prosperity as the result of income and assets does not facilitate a full understanding of people’s common prosperity, because common prosperity also includes people’s pursuit of subjective happiness such as happiness and satisfaction. From the perspective of the need for a better life in China, this study constructs a subjective evaluation system of the common prosperity of urban residents, including 5 dimensions and 25 specific indicators. It uses survey data from 460 participants and applies the graded response models to estimate parameters and predict latent variables. We find that 21 indicators are in line with the reasonable range of basic assumptions and parameters. They have a strong ability to distinguish the common prosperity of residents in different regions, but have different functional characteristics. The confirmatory factor analysis shows that the common prosperity index of residents includes four potential factors: income, education, medical care, and old-age care, and ecology, which has a good structural effect. In terms of weight, education, medical care and old-age care are the most important factors influencing common prosperity. Among them, the classification policy of high school entrance examination, the quality and fairness of primary and secondary education, the degree of medical insurance security, and the waste sorting and community security are important aspects of evaluating the Common prosperity of residents.
Article
01 April 2024Identity, Secondary Vocational Education Options and Return on Investment: Evidence from Children of Rural Chinese Families
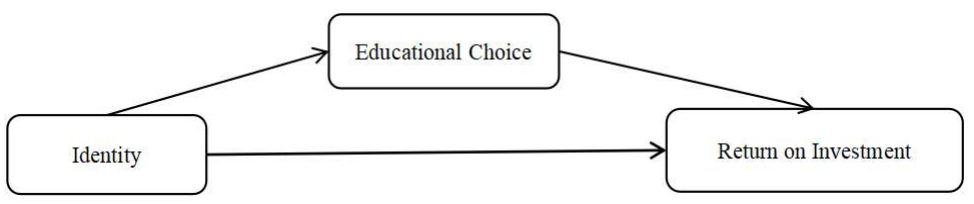
With the continuous improvement of living standards, the importance of educational choice becomes more and more prominent. Based on the data of China General Social Survey (CGSS), a simultaneous equation model of identity, secondary vocational education choice and investment return is constructed. On the basis of fully considering endogeneity and sample selection bias, this paper analyzes the influence of identity on secondary vocational education choice and investment return by means of instrumental variables and propensity score matching (PSM). It is found that class differentiation is the main factor affecting class identity. The more blurred class differentiation, the higher class identity. Class identity has a significant positive impact on identity. The higher class identity, the easier it is to form identity. Identity has a direct positive impact on personal investment return. The stronger the identity, the higher the investment return. At the same time, identity has a significant positive impact on the choice of secondary vocational education. The stronger the identity, the more inclined to choose secondary vocational education. Compared with individuals with junior high school education, individuals with secondary vocational education have a higher return on education investment. Therefore, identity can not only directly improve an individual’s return on investment, but also improve the possibility of an individual’s choice of secondary vocational education, thereby improving an individual’s return on education investment, and ultimately increasing an individual’s return on investment.
Article
25 March 2024Discussion on the Marine Protected Area on the High Seas: From the Perspective of Obligations Erga Omnes Partes
The BBNJ Agreement promotes the conservation and sustainable use of high seas marine biodiversity through the establishment of high seas protected areas. The high seas biodiversity protected by the Agreement has the nature of “obligations erga omnes partes” on an ex officio basis, but in judicial practice it is subject to a finding by the International Court of Justice that the adoption of treaty-based institutional arrangements is in the “collective interest” and that it is in the “collective interest” to adopt such arrangements. The BBNJ Agreement is currently not a “collective interest” agreement in terms of the management of the BBNJ Agreement. At present, the hybrid management model adopted in the BBNJ Agreement does not reflect the collective interest in substance, and cannot resolve the conflict between the establishment of protected areas on the high seas and other area-based management tools, so it is necessary to further harmonize the relationship between the Conference of Parties to the BBNJ and the IFB, and to strengthen the mandate of the COP.

Article
27 February 2024Knowledge-data Collaborated Digital Twin Model of Papermaking Process
The structure of the drying section in papermaking process is complex and too compacted to install sensors. In order to monitor the parameters in dynamic and manage the process practically with virtual simulations instead of physical experiments, a digital twin-based process parameter visualization model is constructed in this study. Regarding to the possible missing data in the modeling framework, it is proposed to combine industrial data, and knowledge of mechanism with intelligent algorithms to fill in the missing parameters. Upon which, a digital twin-based data visualization model is established using CADSIM Plus simulation software. Both of the knowledge -based mechanism solution model and the random forest-based parametric prediction model perform well, and the predicted parameters can support the digital twin visualization model in CADSIM Plus. Visual modeling of surface condenser in the paper drying section was realized for example, and results show that the model is capable of monitoring the dynamic changes of parameters in real time, so as to support the optimization and decision making of papermaking process such as formation, drying, et al.

Review
26 February 2024Mechanisms of Fibroblast Activation during Fibrotic Tissue Remodeling
Fibrosis can occur in almost every organ system. It can occur in single organs, such as in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF), or affect multiple organs as in systemic sclerosis (SSc). Fibrotic diseases are recognized as major cause of morbidity and mortality in modern societies due to the dysfunction or loss of function of the affected organs. This dysfunction is caused by progressive deposition of extracellular matrix proteins released by activated fibroblasts. Activation of fibroblasts and differentiation into myofibroblasts is required for physiological tissue remodeling, e.g, during wound healing. Disruption of regulatory mechanisms, however, results in chronic and uncontrolled activity of fibroblasts and myofibroblasts. Intensive research during the past years identified several core pathways of pathophysiological relevance, and described different fibroblast subsets based on their expression profile in fibrotic tissue. Herein, we discuss the molecular changes in fibroblasts leading to persistent activation during fibrotic tissue remodeling with a focus on lung fibrosis and SSc.

Article
29 January 2024A Novel High Step-up DC-DC Converter Using State Space Modelling Technique for Battery Storage Applications
This paper focuses a novel non-isolated coupled inductor based DC-DC converter with excessive VG (voltage gain) is analyzed with a state-space modeling technique. It builds up of using three diodes, three capacitors, an inductor and CI (coupled inductor). The main switch S is turn on due to body diode and voltage stress is reduced at the switch S by using diode D1 and Capacitor C1. This paper focuses on design modelling, mathematical calculations and operation principle of DC-DC converter is discussed with state-space modelling technique. The performance has been presented for two different voltages for EV applications, i.e., 12 V, 48 V as input voltages with a high step-up outputs of 66 V and 831.7 V respectively. The converter stability is studied and determined the bode plot along with simulation performance results which are carried out using MATLAB R2022B.

Article
16 January 2024The Interplay between Experimental Data and Uncertainty Analysis in Quantifying CO2 Trapping during Geological Carbon Storage
Numerical simulation is a widely used tool for studying CO2 storage in porous media. It enables the representation of trapping mechanisms and CO2 retention capacity. The complexity of the involved physicochemical phenomena necessitates multiphase flow, accurate fluid and rock property representation, and their interactions. These include CO2 solubility, diffusion, relative permeabilities, capillary pressure hysteresis, and mineralization, all crucial in CO2 trapping during carbon storage simulations. Experimental data is essential to ensure accurate quantification. However, due to the extensive data required, modeling under uncertainty is often needed to assess parameter impacts on CO2 trapping and its interaction with geological properties like porosity and permeability. This work proposes a framework combining laboratory data and stochastic parameter distribution to map uncertainty in CO2 retention over time. Published data representing solubility, residual trapping, and mineral trapping are used to calibrate prediction models. Geological property variations, like porosity and permeability, are coupled to quantify uncertainty. Results from a saline sandstone aquifer model demonstrate significant variation in CO2 trapping, ranging from 17% (P10 estimate) to 56% (P90), emphasizing the importance of considering uncertainty in CO2 storage projects. Quadratic response surfaces and Monte Carlo simulations accurately capture this uncertainty, resulting in calibrated models with an R-squared coefficient above 80%. In summary, this work provides a practical and comprehensive framework for studying CO2 retention in porous media, addressing uncertainty through stochastic parameter distributions, and highlighting its importance in CO2 storage projects.

Article
28 November 2023Translational Studies Reveal the Divergent Effects of Simtuzumab Targeting LOXL2 in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis
The composition of extracellular matrix (ECM) is altered during pathologic scarring in damaged organs including the lung. One major change in the ECM involves the cross-linking of collagen, which promotes fibroblast to myofibroblast differentiation. We examined the role of lysyl oxidase (LOX)-like 2 in lung progenitors and fibroblasts cultured from normal or IPF lung samples and in a humanized mouse model of IPF using a monoclonal antibody (Simtuzumab). Primary lung fibroblasts from normal donor lungs and IPF lung explants were examined for expression of LOXL2. Targeting LOXL2 with Simtuzumab on normal and IPF fibroblasts was examined both in vitro and in vivo for synthetic, functional, and profibrotic properties. LOXL2 was increased at transcript and protein level in IPF compared with normal lung samples. In a dose-dependent manner, Simtuzumab enhanced differentiation of fibroblasts into myofibroblasts. Inhibition of LOXL2 also enhanced fibroblast invasion and accelerated the outgrowth of fibroblasts from dissociated human lung cell preparations. Finally, preventative or delayed delivery of Simtuzumab enhanced lung fibrosis in a humanized mouse model of pulmonary fibrosis. Consistent with its failure in a Phase 2 clinical trial, Simtuzumab exhibited no therapeutic efficacy in translational in vitro and in vivo assays.
