Found 4 results
Article
07 January 2025Trace DNA Recovery: Insights from Dubai Police Casework
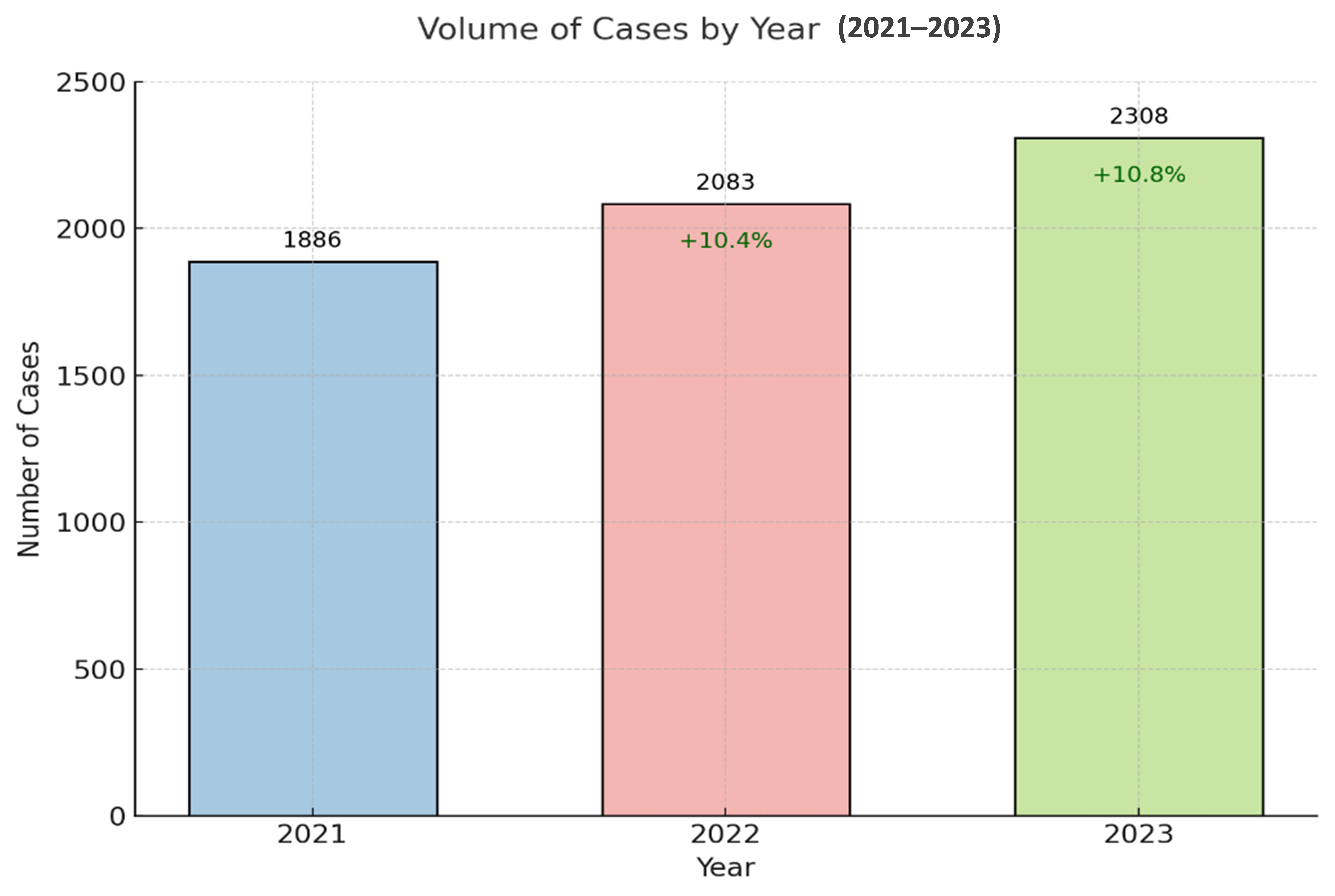
Trace DNA represents a critical form of forensic evidence, frequently recovered from a wide variety of touched or used items. Despite its evidentiary value, trace DNA analysis poses significant challenges due to the minute quantities of DNA involved, as well as the influence of factors such as surface type, collection methods, and environmental exposure. This study systematically examines the success rates and characteristics of trace DNA profiles recovered from six-item categories—tools, stolen items, wearable items, packaging materials, vehicles, and touched items—processed between 2021 and 2023 by the Biology and DNA Section of the Dubai Police Force. A total of 6277 cases were analyzed, encompassing a range of crimes, including homicide, suicide, missing persons, paternity disputes, and burglary. The results demonstrated an overall trace DNA success rate of 64%, with wearable items yielding the highest success rate at 76% and packaging materials yielding the lowest at 54%. Detailed analysis of positive DNA trace samples revealed significant variability in DNA profile types across item categories. Wearable items and touched items predominantly yielded full single (FS) DNA profiles, reflecting their reliability as sources of singular and high-quality DNA. Conversely, stolen items and packaging materials showed a greater prevalence of full mixed (FM) DNA profiles, highlighting their association with complex mixtures due to handling by multiple contributors. Tools and vehicles, meanwhile, exhibited higher rates of partial profiles, presenting unique challenges related to surface irregularities and environmental factors. This study emphasizes the importance of tailoring forensic strategies to item-specific characteristics, as well as the need for systematic mechanisms to categorize trace samples. Addressing operational challenges such as manual sorting and leveraging automation or AI-based systems can further streamline trace DNA analysis. The findings also underscore the importance of data sharing and standardization across forensic laboratories to enhance trace DNA recovery protocols and improve reliability in forensic investigations. Future research should focus on the effects of material properties, environmental exposure, and collection techniques on DNA retention, advancing the field of trace DNA profiling and its applications in forensic science.
Communication
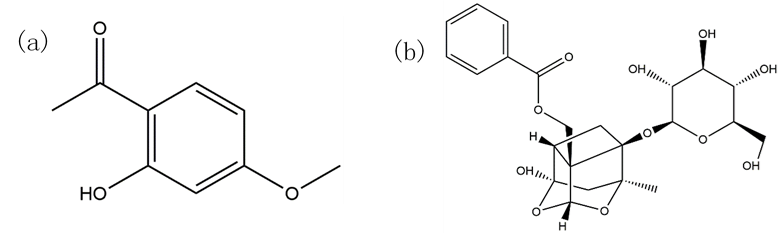
30 December 2024Magnetic Solid Phase Extraction of Paeonol and Paeonoflorin from Moutan Bark with Magnetic Graphene Oxide
Herbal medicine plays an
important role in modern medicine and separation of the active ingredients from
herbal medicine is vital for convenient and safe usage. Paeonol and
paeonoflorin are the active ingredients in the widely used herbal medicine of
moutan bark. In this study, the composite of graphene oxide-Fe3O4 nanoparticles (GO-Fe3O4) was synthesized and used as a magnetic
absorbent to extract paeonol and paeonoflorin from the herbal medicine of
moutan bark. The adsorption of paeonol and paeoniflorin on GO-Fe3O4 rapidly reached equilibrium (within 10 min) due to the high absorption
capability of GO. Thermodynamics and kinetics for the absorption process were
studied. The optimal condition for the elution of the target compound from GO-Fe3O4 was the use of 2 mL of a mixed solvent (methanol and dichloromethane, 1:1 by
volume) with 0.2% formic acid for 5 min. The GO-Fe3O4 adsorbent possesses the advantages of rapid adsorption and convenient
separation. GO-Fe3O4 can be used over 6 times without
losing absorbing capacity. This method is efficient, convenient and rapid, thus
possesses a high potential for the separation of active ingredients from herbal
medicine.
Article
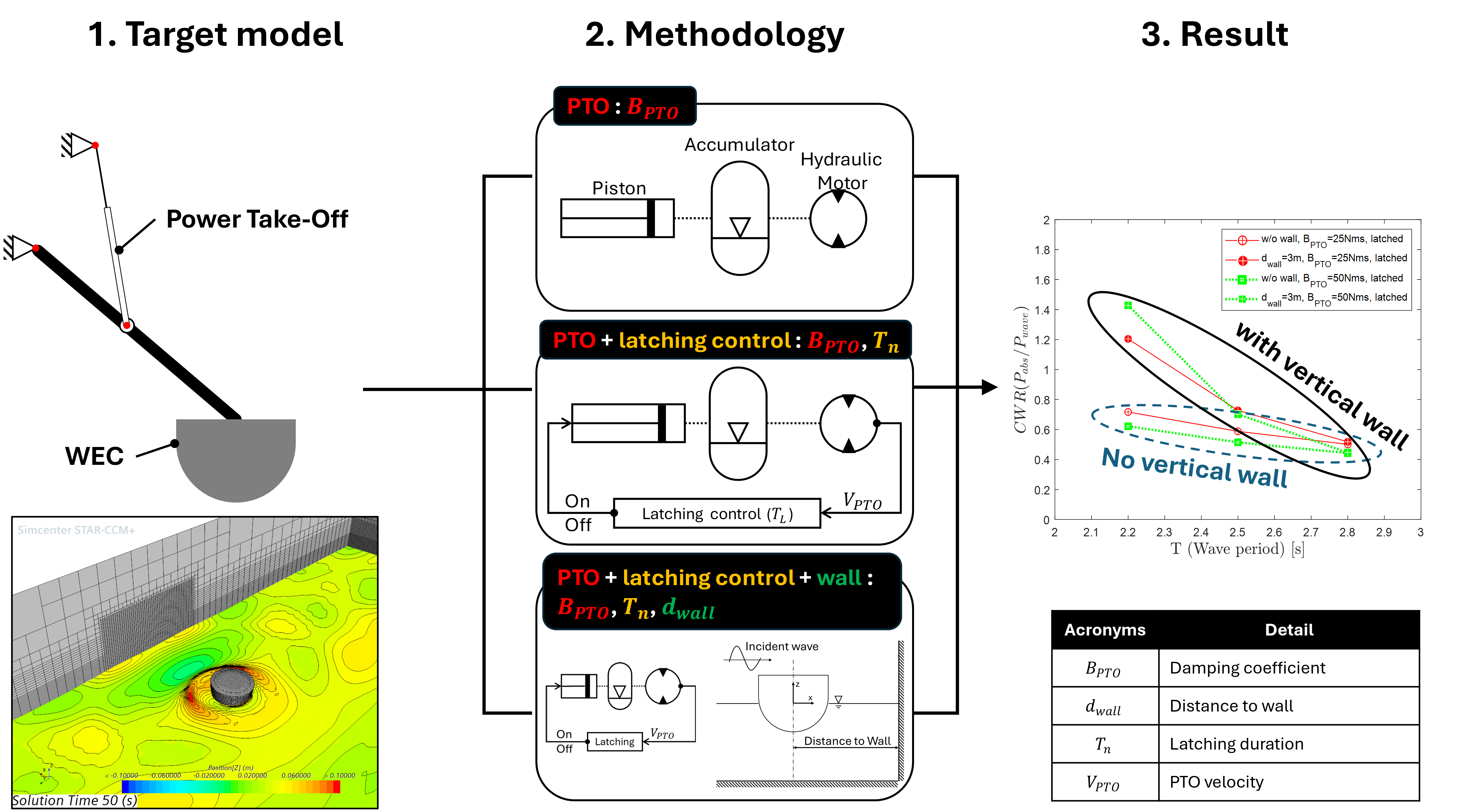
27 September 2024Numerical Investigation of a Point Absorber Wave Energy Converter Integrated with Vertical Wall and Latching Control for Enhanced Power Extraction
This study presents a numerical investigation of a point absorber wave energy converter (WEC) with a focus on improving its performance through the utilization of a vertical wall and latching control in the power take-off (PTO) system. Prior to numerical evaluations, experimental data incorporating PTO considerations and numerical simulation results were examined to validate the accuracy of the numerical methodology employed in this research. This study introduces a numerical PTO model and latching control for a further investigation. Comparative analyses were carried out on the displacement, velocity, and force of the PTO, absorbed power, and capture width ratio (CWR), considering the incorporation of a vertical wall and latching control. The results confirm that the introduction of both vertical wall and latching control significantly improves the CWR of the WEC, showing the effectiveness of incorporating a vertical wall and latching control in enhancing power extraction.
Article
12 August 2024Comparative Study: Biodegradable Chelating Agents vs. Aqua Regia for Extraction of Indispensable Elements from Pyrite Ore of Bagrot, Gilgit Baltistan
This study investigates the optimization of metal extraction from Bagrot pyrite ore, with a focus on gold recovery. Initial characterization using X-ray fluorescence (XRF) provided a comprehensive elemental profile of the ore. Fire assaying was employed to establish a baseline gold concentration. Systematic leaching experiments were conducted, varying parameters such as reaction time, temperature, and stirring speed, and the results were analyzed using Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometry (ICP-MS). Among the chelating agents tested Ethylenediamine N-N′ disuccinic acid (EDDS), Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA), and Diethylenetriaminepentaacetic acid (DTPA) only limited efficacy in gold extraction was observed. In contrast, ammonium thiosulfate demonstrated substantial potential for effective gold recovery. Mercaptobenzothiazole (MBT) and N,N-Dimethylglycine (DMG) were determined to be ineffective for metal leaching under the tested conditions. This research highlights the critical role of reagent selection and parameter optimization in enhancing the efficiency and sustainability of gold extraction processes, positioning ammonium thiosulfate as a promising alternative to traditional cyanide-based methods.
