Found 2 results
Article
21 January 2025Machining Characteristics of Graphene Oxide-Based Nanosuspensions in Abrasive Machining of Single-Crystal Si and SiC
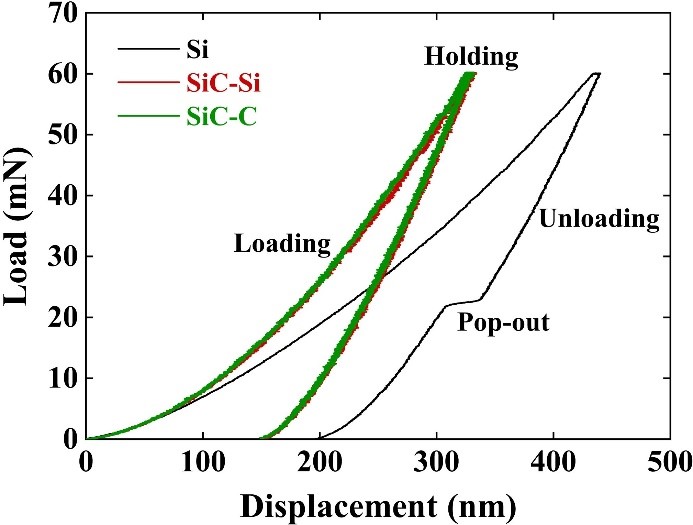
Single-crystal silicon (Si) and silicon carbide (SiC) are core semiconductor materials in communication, lighting, power generation, and transportation. However, their high hardness and wear resistance combined with low fracture toughness have posed significant challenges for high-efficiency and low-damage machining. Aqueous suspensions containing nanoparticle additives have recently been developed for sustainable manufacturing due to their satisfactory tribological performance and environmentally friendly nature. In this work, nanoadditives, including two-dimensional (2D) graphene oxide (GO) nanosheets and zero-dimensional (0D) diamond nanoparticles, were ultrasonically dispersed in water to formulate different GO-based nanosuspensions for achieving high-efficiency and low-damage abrasive machining. The experimental results indicated that GO nanosuspension was a suitable coolant for grinding Si, generating a ground surface of 32 nm in Ra, owing to its great lubricity and excellent resistance against mechanical abrasion. Diamond-GO hybrid nanosuspension demonstrated a synergistic effect in abrasion, lubrication and oxidation, which was thus appropriate for polishing SiC single crystals, leading to approximate 60% and 30% improvements in removal and roughness respectively, in comparison to a commercially available diamond suspension.
Communication
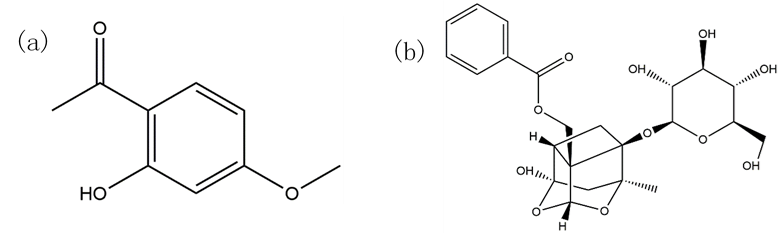
30 December 2024Magnetic Solid Phase Extraction of Paeonol and Paeonoflorin from Moutan Bark with Magnetic Graphene Oxide
Herbal medicine plays an
important role in modern medicine and separation of the active ingredients from
herbal medicine is vital for convenient and safe usage. Paeonol and
paeonoflorin are the active ingredients in the widely used herbal medicine of
moutan bark. In this study, the composite of graphene oxide-Fe3O4 nanoparticles (GO-Fe3O4) was synthesized and used as a magnetic
absorbent to extract paeonol and paeonoflorin from the herbal medicine of
moutan bark. The adsorption of paeonol and paeoniflorin on GO-Fe3O4 rapidly reached equilibrium (within 10 min) due to the high absorption
capability of GO. Thermodynamics and kinetics for the absorption process were
studied. The optimal condition for the elution of the target compound from GO-Fe3O4 was the use of 2 mL of a mixed solvent (methanol and dichloromethane, 1:1 by
volume) with 0.2% formic acid for 5 min. The GO-Fe3O4 adsorbent possesses the advantages of rapid adsorption and convenient
separation. GO-Fe3O4 can be used over 6 times without
losing absorbing capacity. This method is efficient, convenient and rapid, thus
possesses a high potential for the separation of active ingredients from herbal
medicine.