Found 2 results
Article
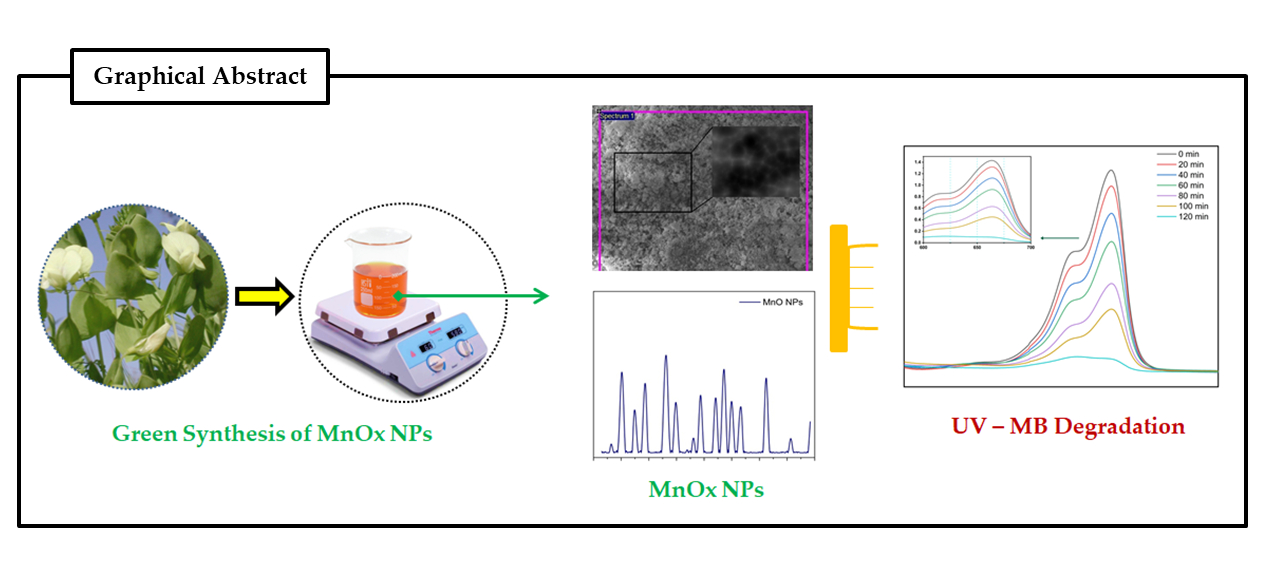
11 June 2024Lathyrus aphaca Extract MnO Nanoparticles: Synthesis, Characterization, and Photocatalytic Degradation of Methylene Blue Dye
Our environment has been impacted by man-made pollutants mainly industries make substantial use of synthetic dyes which exhibit cytotoxicity and have significant environmental consequences. Effective photocatalyst-based approaches for degrading synthetic dyes into less toxic chemical are of great interest. Synthesizing nanoparticles (NPs) using biological approaches, particularly plant-based approaches offer advantages, decreasing the risk of NPs losing biocompatibility during synthesis, cost-effectiveness, and eco-friendliness. In this study, we employed a green synthesis method to produce manganese oxide nanoparticles (MnO NPs) utilizing leaf extract from the Lathyrus aphaca plant. The synthesized MnOx NPs were characterized through various techniques; X-ray diffraction (XRD), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDX), Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), and UV–visible spectroscopy. XRD analysis showed distinct peaks, indicated the presence crystallographic planes within the MnO2 nanoparticles, thus confirming their crystalline structure. FTIR, showed the presence of the O-O stretching mode at a frequency of 719 cm−1, the presence of MnO6 oxides of manganese, and peak at 548 cm−1 corresponded to the Mn-O stretching mode. Furthermore, the green-synthesized manganese oxide nanoparticles exhibited promising photocatalytic and adsorption capabilities against Methylene Blue (MB) dye, leading to approximately 93% degradation of MB when treated with the green-synthesized MnO nanoparticles derived from plant extract. This highlights the efficacy and potential of these nanoparticles in environmental remediation applications, particularly in the degradation of methylene blue contaminants.
Article
08 March 2024Green Synthesis of Gold Nanoparticles for Catalytic Reduction of 4-Nitrophenol and Methylene Blue for Sustainable Development
Unique structural features and wide applications of gold nanoparticles (GNPs) are inspiring researchers to develop biocompatible, reliable and cost-effective methods for their synthesis. Herein, a clean, eco-friendly and non-toxic method to obtain GNPs was developed by reducing and capping the liquid extract of stem of Lilium longiflorum and highlights the catalytic reduction of 4-nitrophenol (4-NP) and methylene blue (MB). The formation of GNPs was confirmed through the absorption peak at 535 nm in the UV-Vis spectra. TEM and HRTEM analyses reveal GNPs spherical morphology with an average size of 4.97 nm. SEM and EDX analyses further elucidate the spherical nature of GNPs and elemental composition. FTIR spectroscopy analysis demonstrates that the GNPs were coated with organic compounds, which prevent the nanoparticle from aggregation. GNPs exhibit remarkable efficiency in reducing 4-NP and MB. The catalytic efficacy of the synthesized GNPs was demonstrated through the enhanced reduction rates of 4-NP and MB, with rate constants of 1.50 min−1 and 1.29 min−1, respectively. This study develops a novel and eco-friendly technique for the synthesis of gold nanoparticles and opens possibilities for the green synthesis of other metal nanoparticles. The confirmed catalytic activity holds promise for a range of industrial applications and environmental sustainability.
