Found 297 results
Article
01 November 2024Energy Consumption and Economic Growth: Evidence from Electricity and Petroleum in Eastern Africa Region
This study investigates the distinct impacts of electricity and petroleum consumption on economic growth in Eastern Africa. Using a Panel Autoregressive Distributed Lag Model and data for a period spanning 2000 to 2021, the study examines both the short-run and long-run effects of these energy sources on Gross Domestic Product. The findings reveal that petroleum consumption has a statistically significant and positive impact on GDP in both the short run and long run. In contrast, while electricity consumption shows a positive but statistically insignificant effect on GDP in the short run, it exhibits a negative and statistically significant impact in the long run. These results suggest that policymakers in Eastern Africa should prioritize sustainable petroleum management to maximize its economic benefits while mitigating potential environmental risks. While the negative coefficient of electricity implies a corrective response of the variables to long-run equilibrium in the face of short-term shocks. As a result, it is recommended that economic shocks caused by energy consumption be considered in terms of their relationship to economic growth, whether positive or negative in the long or short term, as decision makers need to address their impact and limit such shocks on economic growth.

Book Review
31 October 2024The Shennong’s Herbal Canon for Health Management of Herbal Foods
The Shennong’s Herbal Canon lays the foundation for the basic theory of herbal combination in traditional Chinese medicine (TCM). However, after the Tang dynasty, the text of this book was nearly entirely lost, with only a short preface and a catalogue of 365 herbs remaining. In Interpretation of Shennong’s Herb Canon and Catalogue of Herbal Foods, molecular anthropologist Hui Li systematically elaborated on the philosophical basis and practical application by starting from the TCM perspective and integrating multi-disciplinary scientific evidence. This book provides scholars with numerous empirical and logically-based scientific hypotheses and offers insights for daily health maintenance.
Article
29 October 2024Experimental Study on Cold Plasma Jet (CPJ) Assisted Micro-Milling of 30CrMnSiNi2A
As a typical high-performance alloy, the excellent mechanical properties and stringent processing requirements of 30CrMnSiNi2A high-strength steel pose great challenges to high-quality and efficient processing. Currently, researchers have proposed methods such as improving cutting tool performance, minimal quantity lubrication (MQL), and applying external energy field to assist processing. However, due to the unregulated material properties, the further improvement of surface quality is limited, and there are problems of phase change and thermal damage in laser processing. Cold plasma jet (CPJ) is rich in active particles and has a low macroscopic temperature. It can effectively regulate material properties without causing serious surface damage. Therefore, a new 30CrMnSiNi2A machining approach adopting CPJ is proposed to improve the cutting process. The mechanism of its action on material properties and cutting process is revealed based on single-grain diamond scratching tests and micro-milling tests. The results show that CPJ can promote material fracture and improve material removal efficiency. The material removal efficiency R at 400 mN is increased from 0.433 before treatment to 0.895. Under the optimal processing parameters (feed speed Vf = 800 μm/s, spindle speed n = 40,000 rpm, and milling depth ap = 5 μm), compared with dry micro-milling, the cutting forces Fz, Fx and Fy in CPJ-assisted micro-milling are reduced by 26.5%, 24.8% and 31.3%, respectively. The surface roughness Sa is reduced by 19.3%, and the phenomena of plastic flow and burr are suppressed. The CPJ-assisted machining process proposed in this paper can regulate the material properties to improve the cutting process without causing serious damage to the material, providing a new approach for achieving high-quality and efficient processing of 30CrMnSiNi2A.

Article
29 October 2024Postmortem Blood Metal Levels: Establishing Updated Reference Ranges Using ICP-OES
Postmortem testing for metals is crucial in forensic toxicology to determine whether metal exposure contributed to an individual’s death. However, current reference ranges for metal concentrations, primarily based on living individuals, fail to account for postmortem physiological changes. This study addresses this gap by analyzing thelevels of zinc and iron postmortem blood levels over various postmortem intervals (PMI) using Inductively Coupled Plasma Optical Emission Spectroscopy (ICP-OES). Fifty samples were analyzed, revealing a significant increase in metal concentrations over time, with zinc levels rising from 181 μg/dL to 24,935 μg/dL and iron levels from 155 μg/dL to 11,421 μg/dL across a 40-month PMI. These changes are attributed to the redistribution of metals from tissues into the bloodstream and decomposition processes. The study proposes postmortem-specific reference ranges, emphasizing the need for forensic pathologists and toxicologists to consider PMI in their assessments to avoid misinterpretation and inaccurate cause-of-death determinations. This research underscores the necessity of updating reference ranges for postmortem analysis, ultimately improving the accuracy of forensic toxicology reports and contributing to more reliable determinations of cause of death.

Article
28 October 2024Challenges and Solutions: China’s Illegal Hunting Crime from the Perspective of Ecological Civilization Development
In recent years, the number of crimes involving illegal hunting in China’s judicial system has steadily increased, giving rise to numerous disputes. The root of these disputes lies in the fact that China’s Criminal Law lags in terms of animal protection legislation, failing to strike a balance between wildlife protection and human rights. This disconnection is particularly evident in the legislation and judicial practice regarding illegal hunting crimes and the value principles of ecological civilization strongly advocated by China. Moreover, China’s legal framework and judicial practices concerning illegal hunting crimes suffer from low thresholds for conviction and a lack of comprehensive investigations into the subjective intentions of offenders. Chinese legislators and judges should consider international experiences in combating illegal hunting crimes, elucidate the right to defend oneself against wildlife in certain dangerous situations, and thoroughly revise legal provisions, including the definition of illegal hunting and related judicial interpretations. Additionally, greater efforts should be made to disseminate public legal knowledge regarding illegal hunting crimes.

Review
28 October 2024Acute Exacerbations of Interstitial Lung Disease: Evolving Perspectives on Diagnosis and Management
Interstitial lung diseases (ILDs) are a heterogeneous group of chronic lung diseases caused by several potential etiologies but for many, the cause of a given ILD remains unknown. Accurate epidemiologic data are hard to find because of varying definitions, overlapping characteristics once thought to be unique to specific diseases, and ongoing changes in how ILDs are diagnosed and managed. In addition, there are significant variations in prevalence among different geographic populations, likely reflecting a combination of genetic and environmental differences. Certain risk factors, including exposure to cigarette smoke or environmental toxicants (asbestos, silica, fracking, coal dust, and air pollution), genetic mutations, and single nucleotide polymorphisms, have all been associated with developing interstitial lung disease. Due to the availability of high-resolution computed tomography (CT) scans, earlier and broader recognition of subtle imaging changes, and an aging worldwide population, the incidence and prevalence of ILDs are increasing. While a given cause of particular interstitial lung disease may vary, patients often experience breathlessness and a non-productive cough due to impaired alveolar gas exchange. Patients with ILD are prone to the development of acute exacerbations, marked by acute or chronic respiratory failure because of an acute exacerbation of the underlying lung disease. In this review, we discuss the definition of an acute exacerbation and comment on what is known about the underlying pathophysiology in exacerbations of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis and other ILDs. We also emphasize the similarities in the clinical presentation of the acute exacerbations regardless of the underlying ILD, highlight key prognostic features of the diagnosis, and underscore the importance of interdisciplinary management of acute interstitial lung disease exacerbations.

Communication
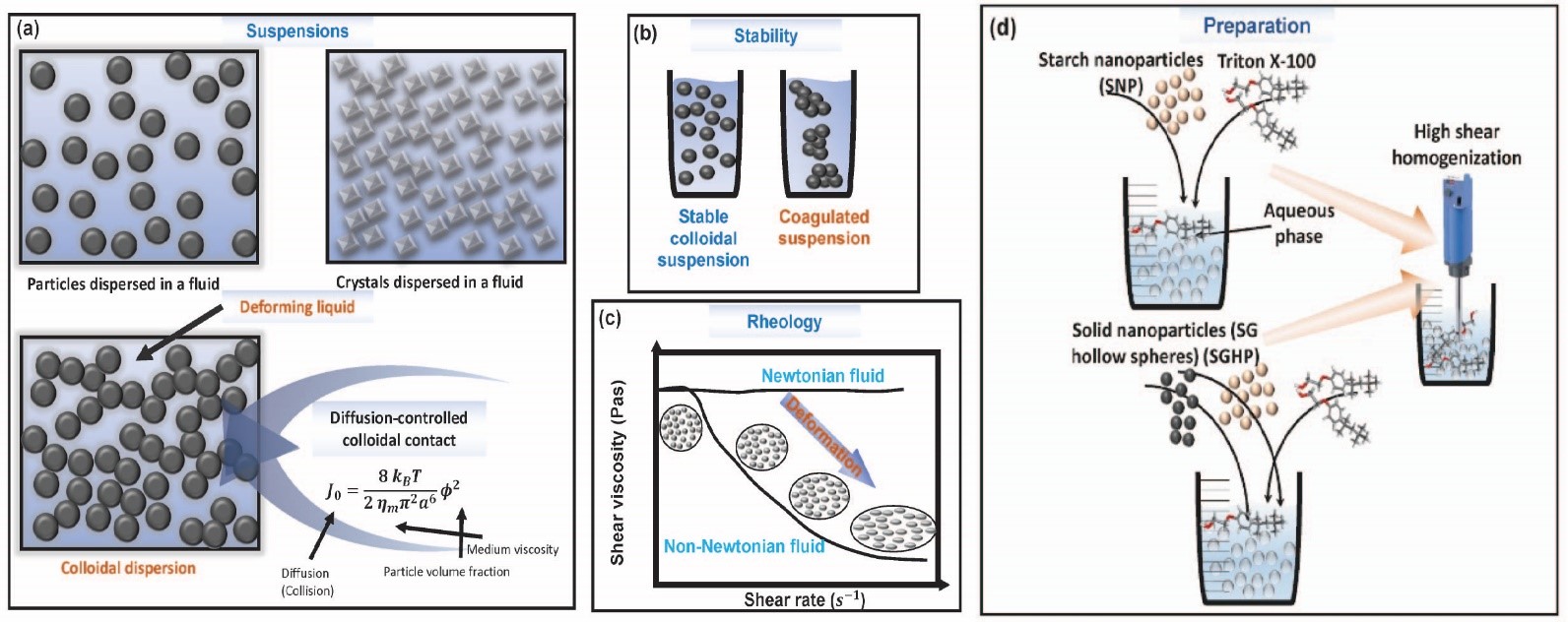
23 October 2024Modeling Viscosity in Starch-Polymer Suspensions: A Comparative Analysis of Swarm Algorithm-Aided ANN Optimization
The analysis of rheological properties of suspensions requires the use of models such as Einstein’s formulation for viscosity in dilute conditions, but its effectiveness diminishes in the context of concentrated suspensions. This study investigates the rheology of suspensions containing solid particles in aqueous media thickened with starch nanoparticles (SNP). The goal is to model the viscosity of these mixtures across a range of shear rates and varying amounts of SNP and SG hollow spheres (SGHP). Artificial neural networks (ANN) combined with swarm intelligence algorithms were used for viscosity modeling, utilizing 1104 data points. Key features include SNP proportion, SGHP content, log-transformed shear rate (LogSR), and log-transformed viscosity (LogViscosity) as an output. Three swarm algorithms—AntLion Optimizer (ALO), Particle Swarm Optimizer (PSO), and Dragonfly Algorithm (DA)—were evaluated for optimizing ANN hyperparameters. The ALO algorithm proved most effective, demonstrating strong convergence, exploration, and exploitation. Comparative analysis of ANN models revealed the superior performance of ANN-ALO, with an R2 of 0.9861, mean absolute error (MAE) of 0.1013, root mean absolute error (RMSE) of 0.1356, and mean absolute percentage error (MAPE) of 3.198%. While all models showed high predictive accuracy, the ANN-PSO model had more limitations. These findings enhance understanding of starch suspension rheology, offering potential applications in materials science.
Review
23 October 2024The Notch3 Pathway in Organ Fibrosis
Fibrosis occurs in many organs, including the lung, heart, skin, liver or kidney, and is characterized by progressive tissue scarring in response to repetitive or chronic non-resolving injury, ultimately leading to organ failure and death. It is, in fact, a major cause of morbidity and mortality worldwide, being estimated to account for 45% of deaths in the world. Despite this fact, little progress has been made therapeutically, and fibrosis remains a major clinical and therapeutic challenge. Although significant advances in our understanding of cellular and molecular mechanisms driving tissue fibrosis have been made, the lack of an efficient treatment reflects the limited insight into the pathophysiological mechanisms underlying the initiation and progression of the fibrotic process. Thus, there is an urgent need for better understanding of tissue fibrosis and repair mechanisms that later lead to the development of new therapeutic approaches to fight fibrosis. The Notch pathway is a highly conserved signaling pathway that has been linked to tissue fibrosis in many organs and promises to open new therapeutic opportunities. This manuscript reviews the relevance of Notch signaling in the development and progression of tissue fibrosis in several organs with a special focus on the Notch3 pathway due to the unique features of this receptor.

Review
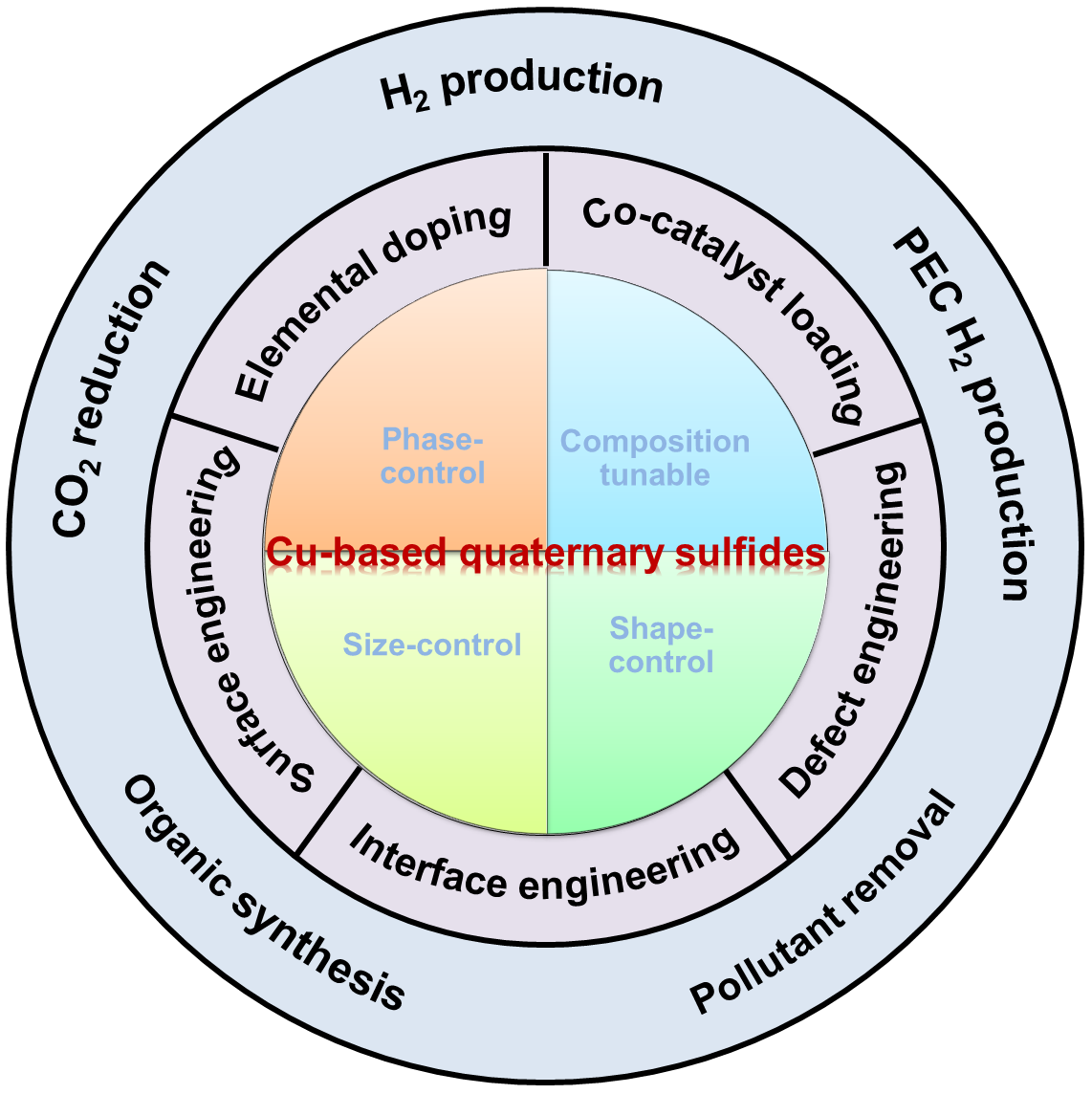
22 October 2024Engineering of Cu-Based Quaternary Sulfide Nanomaterials for Photocatalytic Applications
Semiconductor nanomaterials have been widely used as light-responsive photocatalysts for solar-to-fuel conversion over the past decade. However, the wide band gap of the most reported photocatalysts stems from light absorption in the visible region and results in low solar conversion efficiency. Therefore, it is necessary to develop new semiconductor nanomaterials with high absorption coefficients over the visible region as photocatalysts. The most promising candidates include Cu-based quaternary sulfide nanomaterials (CQSNs), such as Cu-II-III-S (e.g., CuZnInS, CuZnGaS), Cu-II-IV-S (e.g., Cu2ZnSnS4, Cu2ZnGeS4), and I-III-IV-S (e.g., CuInSnS4, Cu3GaSnS5). This review provides a comprehensive overview of the recent progress in developing CQSNs for various photocatalytic applications. Firstly, we present an overview of the synthesis of CQSNs with precise control over crystal phase, composition, size, and shape using solution-based methods. Then, the enhancement of photocatalytic performance was presented via the engineering of CQSNs, which included surface engineering, elemental doping, cocatalyst loading, vacancy engineering, and interface engineering. Subsequently, we further introduce the photocatalytic applications in the fields of photocatalytic and photoelectrochemical hydrogen conversion, CO2 reduction, organic synthesis, and pollutant degradation. Lastly, this review ends with views on the current challenges and opportunities of CQSNs in future studies.