Found 297 results
Article
26 August 2024Delivery of Novel Replicating Vectors to Synechococcus sp. PCC 7002 Via Natural Transformation of Plasmid Multimers
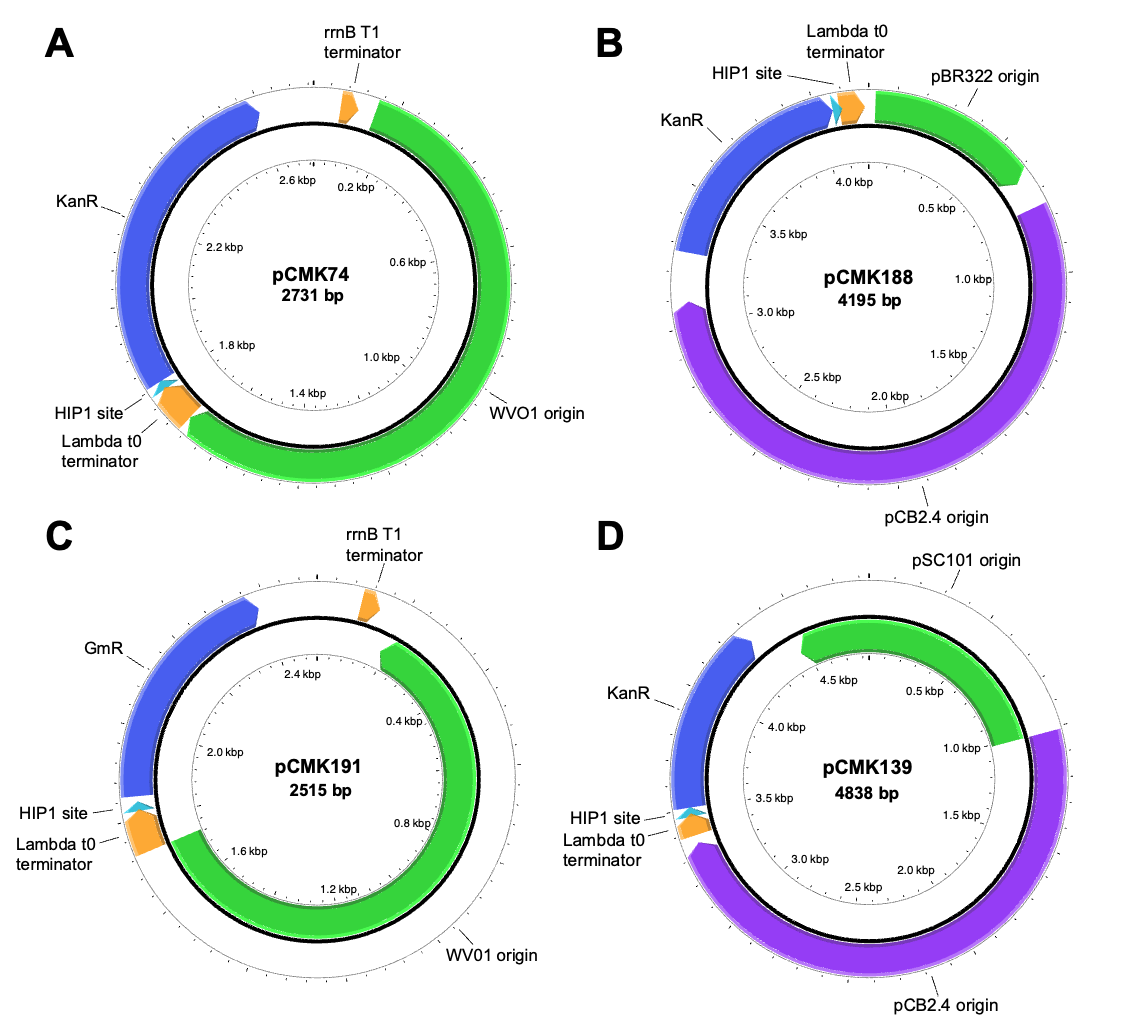
In most cyanobacteria, genetic engineering efforts currently rely upon chromosomal integration; a time-consuming process due to their polyploid nature. To enhance strain construction, here we develop and characterize two novel replicating plasmids for use in Synechococcus sp. PCC 7002. Following an initial screen of plasmids comprising seven different origins of replication, two were found capable of replication: one based on the WVO1 broad host range plasmid and the other a shuttle vector derived from pCB2.4 from Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803. These were then used to construct a set of new replicating plasmids, which were shown to be both co-transformable and stably maintained in PCC 7002 at copy numbers between 7–16 and 0.6–1.4, respectively. Lastly, we demonstrate the importance of using multimeric plasmids during natural transformation of PCC 7002, with higher order multimers providing a 30-fold increase in transformation efficiency relative to monomeric plasmids. Useful considerations and methods for enhancing multimer content in plasmid samples are also presented.
Communication
22 August 2024Mixed Matrix Membranes Produced from a Fluorinated MOF and Pebax for CO2/H2 Separation
Hydrogen (H2) emerges as a promising clean energy source, but its efficient purification from various sources needs advanced separation technologies. This study explores the use of CO2-selective membranes, especially mixed matrix membranes (MMM) incorporating KAUST-7 metal-organic framework (MOF), for hydrogen purification. The MMM was fabricated with various KAUST-7 content in a polymer matrix (Pebax 1657) and characterized via Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), thermogravimetric analysis (TGA), X-ray diffraction (XRD), and gas permeation tests. The XRD analysis confirms the incorporation of KAUST-7 into the MMM, while SEM reveals a homogeneous particle distribution at low content (below 10%) but agglomeration at higher ones (above 10%). FTIR confirms good interfacial interactions between the MOF and polymer matrix. TGA results show that the MMM thermal stability slightly decreases with increasing MOF content. Gas permeation results reveal improved CO2 permeability (79%) and CO2/H2 selectivity (19%) for MMM compared to neat Pebax membranes, with an optimal performance observed at 10 wt.% KAUST-7. Beyond this threshold, the performance deteriorates, possibly due to polymer rigidity and MOF agglomeration. Overall, the study highlights the potential of KAUST-7/Pebax MMM for enhanced hydrogen purification.

Review
22 August 2024Current Application of Modeling and Cell-Free System for Synthetic Gene Circuit Design
The desire to harness nature’s capability of precise gene expression regulation has motivated the pursuit of synthetic gene circuits. However, designing and building novel synthetic gene circuits with predictable dynamics is nontrivial. To facilitate the design, cell-free systems have emerged as an effective alternative testbed to living biological systems in characterizing and prototyping synthetic gene regulatory networks, given its relative simplicity and designability in terms of cellular contents. Meanwhile, as parameterizing and analyzing first principle-based models can shed light on the required kinetic parameter values, thus the specific regulatory components, for the desired dynamics, coupling mathematical modeling with cell-free experiments has become an effective approach in exploring novel synthetic gene circuits. In this mini-review, we provide an overview of current progress on using deterministic first principle-based mathematical modeling in conjunction with cell-free systems, in designing and characterizing novel gene circuits, as well as the standing challenges and issues with this approach.

Article
19 August 2024Maturity Model for the Manufacturing Industry with Case Experiences
This manuscript describes the research path when extending a maturity model. The initial model—ManuMaturity—was for manufacturing companies aiming beyond Industry 4.0. The extended OSME model covers data sharing within a supply chain, an open innovation ecosystem and sustainable manufacturing. The OSME maturity model has five maturity levels: traditional factory, modern factory, agile factory, agile cognitive factory and agile cognitive industry and seven dimensions (such as infrastructure, data, customer, business model, employee, sustainability and processes). The tool was experimented with in manufacturing companies on two occasions: with a set of manufacturing companies and a group of companies. In both cases, feedback was gathered from the respondents. The article follows the maturity assessment development phases such as scope, design, populate, test, deploy and maintain, and reports the software implementation of the maturity tool. With the help of the developed maturity model and the tool, it was possible to make assessments in case companies, where the tool and its results were commented mostly positively. The tool can be applied in various ways. For example, a group of people can jointly submit their common understanding and have a thorough discussion or a group of company representatives submit their responses and the variation is discussed afterwards.

Article
15 August 2024Hazardous Gas Monitoring with IoT Enabled Drone in Underground Tunnels and Cavities
Considering the healthiness of the atmosphere in mining activities (e.g., tunnelling), two of the most important parameters to be monitored are the concentration of oxygen and the presence of harmful gases such as CO2. Traditional methods for their measurement are fixed platforms and portable gas detectors carried by miners; they are incapable of recognizing sudden or short-term pollution events or correctly accounting for the spatial scarcity of gases. A UAV (Unmanned Aerial Vehicle) device capable of guaranteeing the measurement and continuous monitoring of concentrations has been designed. By using innovative technologies, it promotes digitization in the mining sector. This approach replaces current methods that, while effective at detecting and measuring environmental parameters, are slow, routine, and heavily reliant on human input. It saves productive expenses in the sector since it reduces costs compared to hiring a field technician for activities such as analysis of environmental conditions. This saving is about 110 euros daily, representing a 32% saving per working day for each mining technical responsible for environmental control. It also obtains a 3D spatial distribution of contaminants, a high sample resolution and a high sample resolution.. It reduces inspection time in mining works and the data collection time by more than 50%. The ECODRONE project constitutes a contribution to the MINE THE GAP challenge is a project financed with European funds whose line of desire aims to combine the innovation and development of SMEs or business groups from different regions of the mining, raw materials and materials sector. This program is aimed at strengthening the existing value chains and developing new industrial ones while designing new procedures, automated technologies, information and communication flows, which increase efficiency in the consumption of resources. All of the above implies integration with a circular economy and respect for European and global efficiency policies aimed at sustainability, industrial modernization, human health and the environment.

Article
12 August 2024Comparative Study: Biodegradable Chelating Agents vs. Aqua Regia for Extraction of Indispensable Elements from Pyrite Ore of Bagrot, Gilgit Baltistan
This study investigates the optimization of metal extraction from Bagrot pyrite ore, with a focus on gold recovery. Initial characterization using X-ray fluorescence (XRF) provided a comprehensive elemental profile of the ore. Fire assaying was employed to establish a baseline gold concentration. Systematic leaching experiments were conducted, varying parameters such as reaction time, temperature, and stirring speed, and the results were analyzed using Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometry (ICP-MS). Among the chelating agents tested Ethylenediamine N-N′ disuccinic acid (EDDS), Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA), and Diethylenetriaminepentaacetic acid (DTPA) only limited efficacy in gold extraction was observed. In contrast, ammonium thiosulfate demonstrated substantial potential for effective gold recovery. Mercaptobenzothiazole (MBT) and N,N-Dimethylglycine (DMG) were determined to be ineffective for metal leaching under the tested conditions. This research highlights the critical role of reagent selection and parameter optimization in enhancing the efficiency and sustainability of gold extraction processes, positioning ammonium thiosulfate as a promising alternative to traditional cyanide-based methods.

Article
09 August 2024Interstage Growth Failure May Adversely Affect Clinical Outcomes in Hypoplastic Left Heart Syndrome: Results from a Single Center Ten-Year Review
Infants with Hypoplastic left heart syndrome (HLHS) are particularly vulnerable during their interstage period which is the time between Stage 1 palliation (S1P) and Stage 2 palliation (S2P). Interstage Monitoring Program (IMP) was established to reduce mortality after discharge following S1P and consists of close monitoring of certain key parameters including hypoxia, growth failure and occurrence of major events. As somatic growth is a potentially modifiable determinant of interstage mortality, we aimed to study the incidence and risk factors of growth failure among infants followed by our IMP over the last 10 years. We included HLHS infants who were enrolled in institutional IMP following discharge after S1P from May 2009 to April 2019. Growth failure was defined as per the NPC-QIC criterion as failure to achieve target interstage weight of 20–30 g per day and risk factors for growth failure were explored. A total of 87 patients were enrolled during the study period, of whom 72 (n = 83%) underwent S2P. About one third (23 patients) failed to achieve the target growth rate despite close monitoring through a robust IMP. Growth failure significantly delayed the time to more stable S2P circulation (median IS duration: 131 days vs 86 days, p = 0.002). Patients with growth failure had a significantly higher incidence of death/transplant prior to Stage 3 (Fontan) completion (39% vs 16%, p = 0.03). Interstage growth failure was significantly associated with a “Hybrid-type” of repair during S1P (p = 0.03); and with the need for opioids at discharge (p = 0.04). This study highlights that growth failure is common in HLHS patients, despite active intervention through an IMP program. These patients appear to have significantly worse transplant-free survival rates compared to their counterparts. Pre-interstage risk factors including use of opioids may need to be addressed to assist adequate somatic growth during interstage.

Article
08 August 2024Rural Nonfarm Enterprise and Its Impact on Household Livelihood in Ethiopia: Evidence from Gurage Zone
In Ethiopia, until recently, less attention has been given to rural entrepreneurship, while the rural economy has accounted for the lion’s share of employment, export earnings, and national income. This study scrutinized the factors influencing rural household participation in nonfarm enterprise and its impact on household livelihood in the Gurage zone. Data was collected from 352 households using questionnaires, and Key-Informant Interviews and Focus Group Discussions were used. The factors influencing household participation in nonfarm enterprises were estimated using a logit model, while Propensity Score Matching (PSM) was employed to assess the impact on household livelihoods. Women, single-headed households, households with larger family sizes, and households with secondary and primary education are more likely to participate in nonfarm enterprises. In addition, access to extension services, training, market, transport, credit, and being a member of cooperatives have increased the probability of household participation in nonfarm enterprise. Participation in nonfarm enterprises improved the livelihood of rural households. Rural nonfarm enterprises should be integrated into national policy as a means of economic empowerment, focusing on creating employment opportunities for women and youth and reducing poverty. Rural infrastructure expansion, access to credit, and entrepreneurship training should be prioritized and the sector should be enhanced as an alternative livelihood strategy.

Article
07 August 2024Land-Tenure Shifts in the Maa Landscapes, Kenya, and the Impacts on Social-Cultural Relations, Structural Power and Social Economic Differentiation
In recent years, the expansive pastoralist landscapes in southern Kenya have undergone rapid transformation, the key being a change in the land-tenure system from communal to individual ownership. However, little is known about the complexities influencing these changes and how the changes impact the local people. This study employed qualitative inductive approaches and ethnographic methods, such as participant observation and in-depth interviews. It examined how local and international formal and informal institutions have impacted land tenure changes among the Maa pastoralists living near Chyulu and Tsavo-West national parks. Despite the expected benefits of individual land ownership, the changes have not addressed significant social barriers. These include norms and power structures that disadvantage the poor in the community, as well as women and youth within households. People with higher levels of poverty and fewer or no political connections are marginalized during land adjudication at the community level. At the same time, traditions and customs deny women and youth entitlement to property at the household level. Such groups thus experience land privatisation differently. This article argues that expropriation and unequal abilities to control, access and benefit from land profoundly impact social differentiation among pastoralists. Further, the article illuminates a more-than-human achievement, with wildlife shaping people’s lives through conservation-induced land expropriation, and a more-than-human vulnerability that livestock and wildlife face in the wake of land fragmentation and fencing that restrict their free movement. The article contributes to more significant debates on pastoralist land tenure, property relations, ongoing changes in land control processes, and more-than-human achievements and vulnerabilities.