Found 297 results
Article
07 August 2024Airway Serous Cells: A Comparative Study of Spatial Distribution and Abundance among Species
The conducting airways of the respiratory system play a crucial role in filtering, humidifying, and directing air into the lungs. Among the specialized cell types within these airways, airway serous cells are notable for their secretion of watery, protein-rich fluids and enzymes, which contribute to maintaining airway surface liquid homeostasis and defending against pathogens. However, the distribution and abundance of serous cells across different species in the conducting airways remain poorly understood. In this study, we addressed this gap by investigating the spatial distribution of the airway serous cell-specific marker BPI fold containing family A member 1 (BPIFA1) in humans, pigs, and mice. Our findings demonstrate significant variations in the distribution and abundance of serous cells among these species, potentially reflecting their different respiratory anatomy and evolutionary adaptations to diverse environmental challenges and respiratory demands. In humans and pigs, airway serous cells are predominantly found in the submucosal glands of the trachea and segmental bronchi, frequently overlapping with lysozyme-positive secretory cells. In contrast, rodents like mice exhibit a distinct pattern where serous cells are scarce in submucosal glands. Instead, rodent serous cells are primarily located at the epithelial surface from the trachea to the main bronchi, where many co-express the Club cell-specific protein SCGB1A1. The abundance of serous cells diminishes progressively in the intrapulmonary airways. Given that rodent models are widely utilized in respiratory research, understanding anatomical and cellular differences in airway serous cells is critical for interpreting experimental outcomes and translating findings to human respiratory diseases and therapeutic strategies. This comparative analysis enhances our understanding of airway biology across species and informs the selection and interpretation of animal models in respiratory studies.

Article
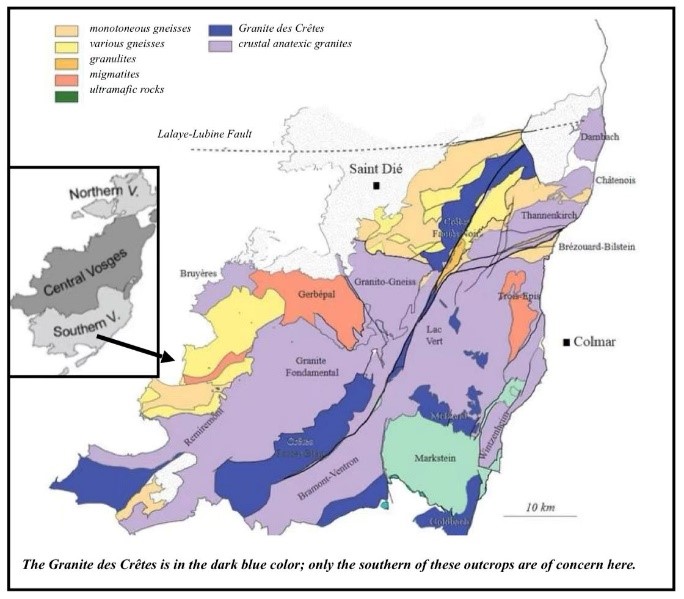
06 August 2024Evaluation of a Present-Day Thermal Activity on the Constitutive Minerals of a Granite and of Its Impact on the Whole-Rock Sealing Potentials
Mineralogical and chemical analyses of the major constitutive minerals from granite des Crêtes collected near the thermal site of Plombières-les-Bains (Vosges Mountains, eastern France) clearly show that recently circulating thermal waters up to 90 °C do not impact them. Even the constitutive minerals smaller than 2 microns are not affected. As a result, all minerals reflect the entire complex tectonic-thermal history of the granitic massif rather than just the recent thermal impact. Only the open faults and natural drains contain calcite from recent thermal waters. This is confirmed by similar calcite deposits with the same elemental contents sampled in the pipes of thermal installations. As a complementary conclusion, storage of containers of nuclear waste that diffuse an overall temperature up to 100 °C will not alter the potential sealing properties of a plutonic host massif, of course, without any recent thermal drainage that could potentially spread radioactive waste. This conclusion was already obtained on a moderately faulted sedimentary environment after a one-year in-situ heating experiment at about 100 °C. Calcium is a key indicator of low thermal impact. After an initial decrease, its levels rose significantly in the most "altered" granite samples, inducing calcite precipitation, even in the water pipes at the thermal site. The negligible impact of a hydro-thermal activity at a maximum of about 100 °C in a granitic material represents, indeed, a piece of useful information, as deep sites for nuclear waste in plutonic host rocks appear to act, also, as potential isolated host systems.
Review
06 August 2024Considerations for Unmanned Aerial System (UAS) Beyond Visual Line of Sight (BVLOS) Operations
This paper, intended for expert and non-expert audiences, evaluates the technical and regulatory requirements for Unmanned Aerial Systems (UAS) to operate beyond visual line of sight (BVLOS) services. UAS BVLOS operations have the potential to unlock value for the industry. However, the regulatory requirements and process can be complex and challenging for UAS operators. The work explored the BVLOS regulatory regime in the UK, Europe and the US and found similarities in process and requirements covering themes like Detect and Avoid (DAA), Remote identification and Reliable Connectivity. A unifying goal across these jurisdictions is to operate BVLOS safely and securely in non-segregated airspace. However, operating BVLOS in segregated airspace as the default or routine mode could accelerate approval and adoption. The paper reviewed existing challenges, highlighting Coverage, Capacity and Redundancy as critical for UAS BVLOS Operations. The work also highlighted the crucial role of Non-terrestrial Network (NTN) assets like Satellites and HAPS (High Altitude Platform Station) since terrestrial networks (not optimised for aerial platform coverage) may not be reliable for BVLOS connectivity.
Article
05 August 2024Promoting Ecological Civilization through Religious Prophetic Communication: An Interreligious Framework
This paper explores the transformative potential of religious prophetic communication in advancing an ecological civilization. Drawing upon diverse religious traditions—Christianity, Islam, Buddhism, and Confucianism—it argues that religious teachings offer profound insights and ethical frameworks essential for addressing contemporary ecological challenges. A key aspect of ecological civilization is the presence of a pervasive ecological ethos. The paper contends that religious prophetic communication plays a crucial role in cultivating such an ethos by promoting a heightened ecological conscience and consciousness among individuals and communities. Through prophetic communication, faith actors and communicators articulate moral imperatives rooted in religious principles contextualized to the present ecological situation. The paper delineates five components that make up religious prophetic communication: (1) Communicating from the position of faith; (2) Communicating in a contextually relevant manner; (3) Communicating to energize; (4) Communicating to criticize; and (5) Communicating beyond words. Applied to the ecological context, religious prophetic communication aims to affirm, stimulate imagination, clarify misunderstandings, inspire action, and confront unjust realities. By carrying out its prophetic role, religious communicators can help bring about an ecological ethos and promote the realization of ecological civilization.

Article
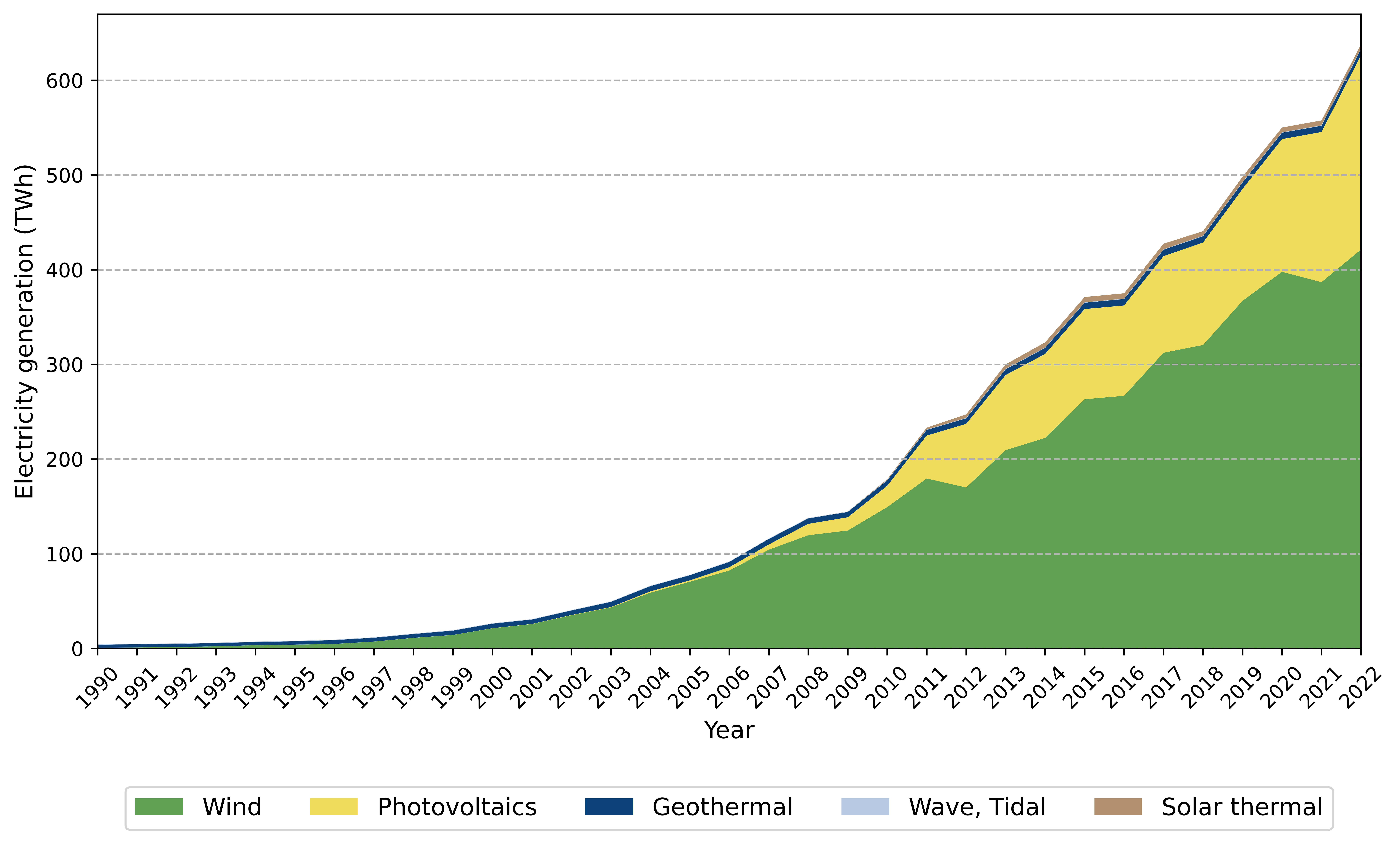
26 July 2024Current and Future Costs of Storage for Electricity in a Decarbonized Electricity System
As power systems globally are transitioning from fossil fuels to renewable sources, integrating energy storage becomes imperative to balance variable renewable electricity generation. The core objective of this paper is to conduct a comprehensive cost assessment of selected energy storage technologies from 2023 to 2050, focusing on the Austrian electricity market. Our method combines techno-economic assessment with the technological learning method to integrate various storage technologies into a renewable electricity system, using scenarios that account for decarbonization goals. Results indicate that pumped storage hydro exhibits none or negative learning effects, while lithium-ion batteries demonstrate significant investment cost decreases. Despite investment cost reductions, underground hydrogen storage continues to incur high total costs per kWh discharged due to low roundtrip efficiency, suggesting its future outlook depends on seasonal storage needs in fossil-free power systems. An important finding of this analysis underscores the importance of optimizing the ratio of electricity demand, renewable generation expansion and storage deployment for cost-effectiveness. Excessive storage deployment leads to lower utilization and higher costs, emphasizing the necessity of at least 1500 full-load hours for profitable operation across all storage systems. Strategic planning for optimal storage deployment is emphasized to optimize utilization and minimize costs.
Communication
26 July 2024The Project of Constructive Anthropology in Russian Empiriocriticism
The article analyzes the main provisions of constructive anthropology developed in Russian empirio-criticism in the first quarter of the 20th century. The justification of non-metaphysical philosophy, which developed the “problematic” approach to cognition, made the new understanding of man possible. From this point of view, the essence of man is not a metaphysical constant, but is modeled on the basis of an appropriate organization of experience; the essence of man is determined by his existence and is constantly changing; the essence of man can be consciously adapted by directing his development and giving him the necessary characteristics; man as an essence is always man’s project, or scientific and philosophical concept; only by understanding man as a dynamic project can we justify free will and man’s capacity for creation. The project of constructive anthropology is fundamentally different from the philosophical anthropology developed in Germany in the 20th century by Max Scheler and Helmuth Plessner, since the latter is essentially an attempt to preserve the traditional metaphysical interpretation of man.

Article
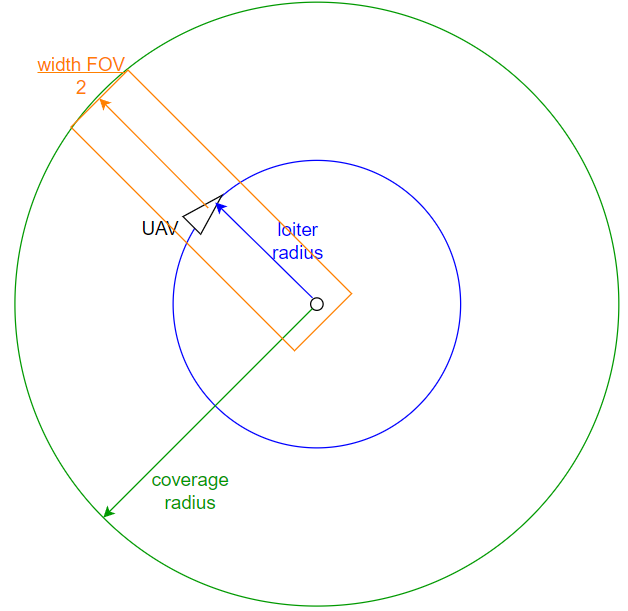
25 July 2024A Distributed Framework for Persistent Wildfire Monitoring with Fixed Wing UAVs
Wildfires have proven to be a significantly exigent issue over the past decades. An increasing amount of research has recently been focused on the use of Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs) and multi-UAV systems for wildfire monitoring. This work focuses on the development of a decentralized framework for the purpose of monitoring active wildfires and their surrounding areas with fixed wing UAVs. It proposes a distributed fire data update methodology, a new formation algorithm based on virtual forces, fine-tuned by a Genetic Algorithm (GA), to arrange virtual agents into the monitoring area, and a control strategy to safely and efficiently guide fixed wing UAVs to loiter over the structured virtual agents. The system is tested in Software In The Loop (SITL) simulation with up to eight UAVs. The simulation results demonstrate the effectiveness of the system in monitoring the fire in a persistent manner and providing updated situational awareness data. The experiments show that the proposed framework is able to achieve and maintain coverage up to 100% over the area of interest, and very accurate fire representation. However, the performance is decreased for the experiments with low UAV numbers and large fire sizes.
Review
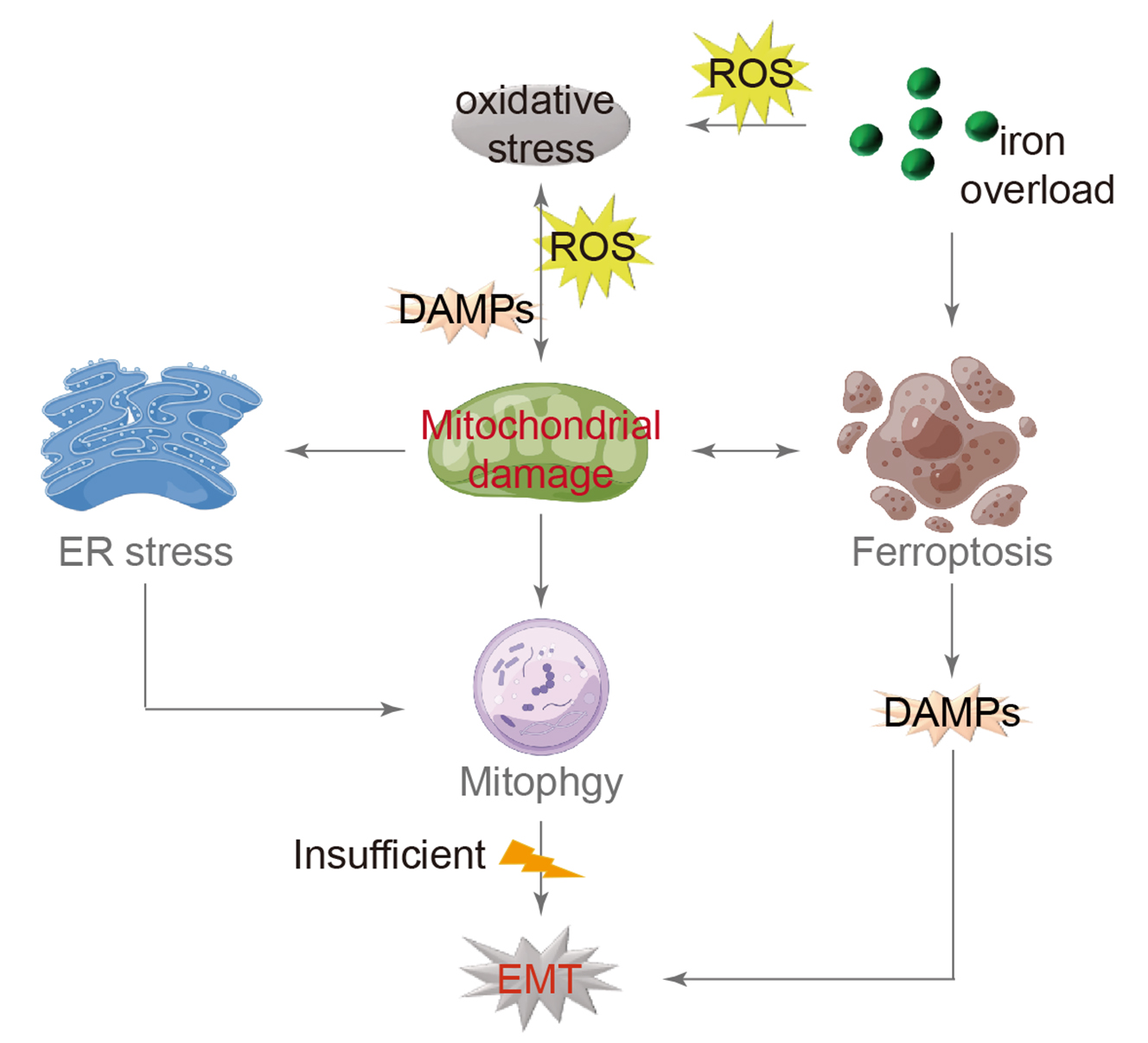
16 July 2024Mitochondrial Damage and Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition as Major Triggers of the Development of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis
Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) is a type of interstitial pneumonia with an unknown cause that progresses gradually, primarily affecting the elderly. The presence of fibrosis has significant implications for individuals with reduced lung compliance, resulting in decreased quality of life and limited survival. Although the exact mechanism remains unclear, researchers have investigated various factors, such as senescent telomerase replication and abnormal lung stem cell differentiation, to understand the root cause. Extensive research has consistently shown that IPF is closely linked to the dysfunction of alveolar epithelial cells. Current scientific studies on IPF cover a range of aspects including oxidative stress, endoplasmic reticulum stress, mitochondrial damage, and iron-induced apoptosis. By examining these mechanisms, a comprehensive model has been developed that explains the process of IPF. Oxidative stress is identified as the primary trigger, followed by mitochondrial damage as a central component, leading to the mesenchymal transformation of alveolar epithelial cells as the ultimate outcome. This model is expected to serve as a valuable reference for understanding the mechanism of IPF and guiding future drug development efforts.
Review
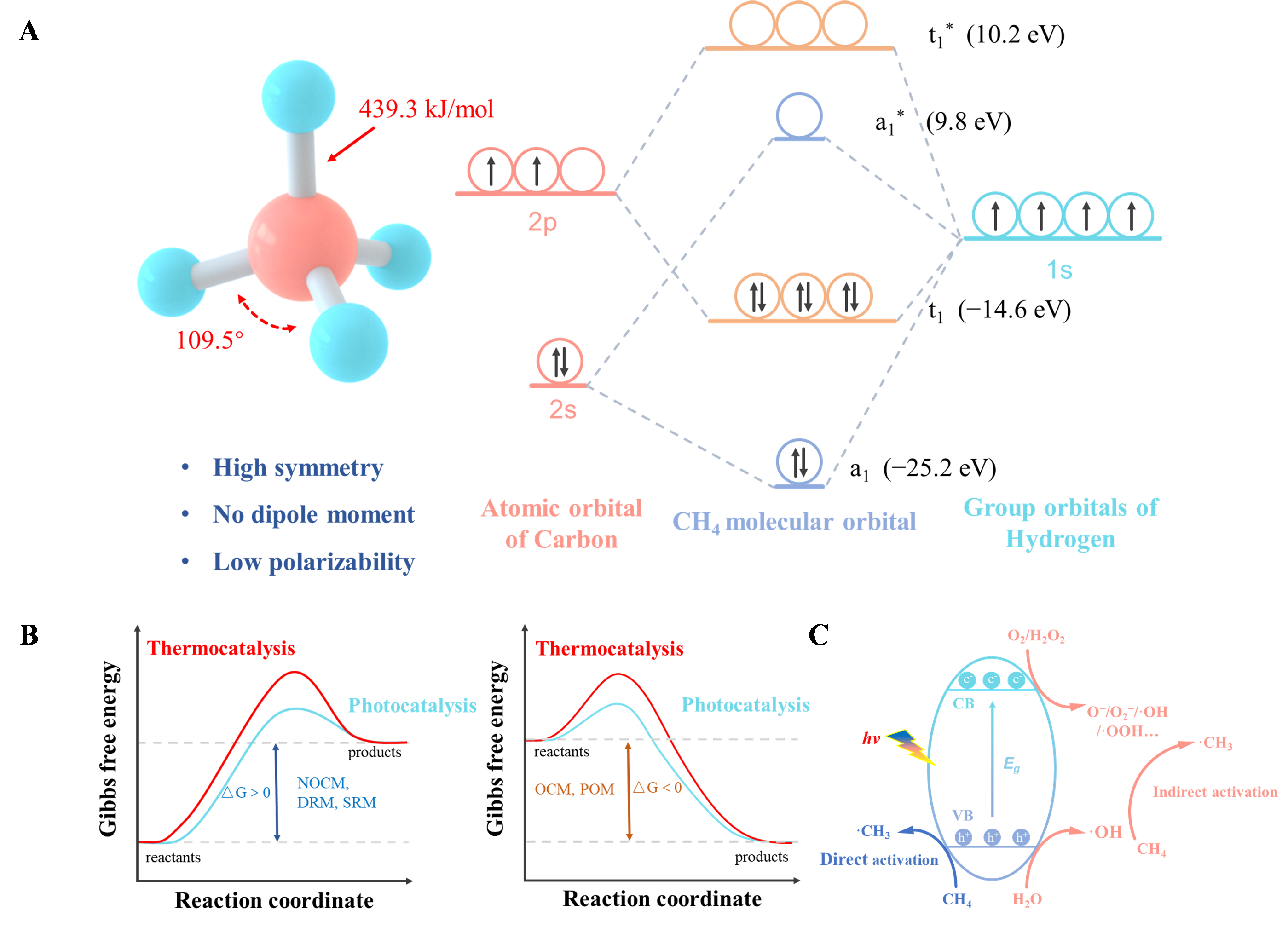
11 July 2024Photocatalytic Aerobic Conversion of Methane
The direct conversion of methane into high-value chemicals has been a persistent research focus in the fields of chemical engineering and energy. Photocatalysis, as an innovative technology, not only circumvents the issues of catalyst sintering and carbon deposition associated with traditional thermal catalysis but also transcends thermodynamic limitations by providing new reaction pathways. Utilizing molecular oxygen as an oxidant generates various reactive oxygen species, offering unique thermodynamic advantages for methane conversion. This review summarizes the advancements in photocatalytic partial oxidation (PPOM) and oxidative coupling of methane (POCM) using oxygen as an oxidant. It discusses the activation mechanisms and reaction pathways of methane and oxygen in different systems, as well as the application of photochemical cycling strategies in methane conversion. Finally, it addresses the challenges in this field, proposes potential solutions, and offers perspectives on the future development of photocatalytic systems.
Communication
10 July 2024Return Their Names to Forgotten Bones: Memory Process about Spanish Civil War in Ponferrada (León)
For more than 80 years, Spain has had a human rights problem. Since the 18th of July 1936, when military personnel and fascists staged a coup d’état against the democratic government of the Second Republic, thousands of victims remain missing. We will examine how the victims have been treated by the State and how civil society has led the process of recovering democratic memory. We will focus on its impact in the Bierzo region, in the northwest of the Iberian Peninsula, and its importance in this process. We will also look at how scientific efforts continue to search for missing persons. History, archaeology, physical anthropology, and genetics join forces to repair the victims of the Spanish Civil War and Franco’s dictatorship.
