Found 297 results
Article
04 June 2024Investigating and Analyzing the Impact of a Bidirectional Multiport Power Electronic Transformer Interface on the Power Quality and Stability of Interconnected Microgrids
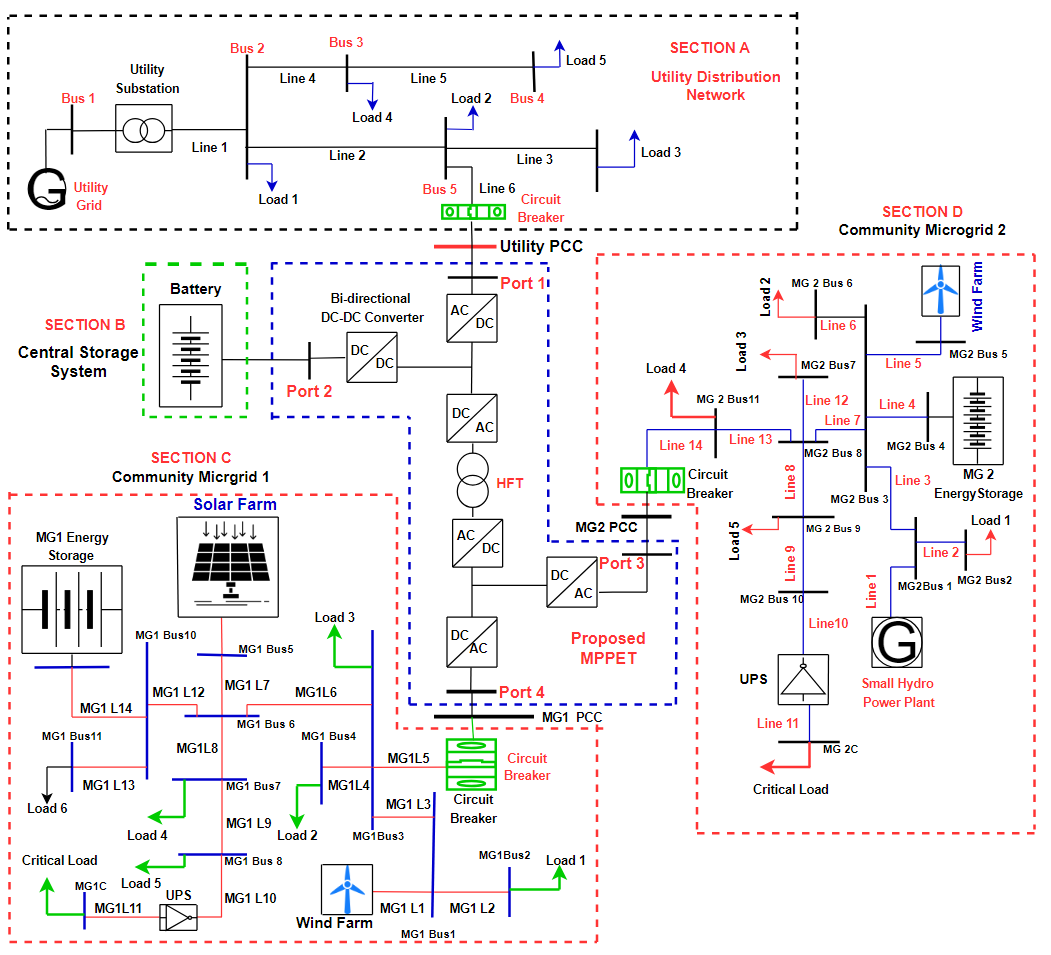
This paper investigates the potential benefits of a bidirectional multi-port power electronic transformer (MPPET) to interface multiple microgrids with utility distribution networks in terms of power quality and stability. The main concept is based on the interaction between the utility grid, the connected microgrids, and the MPPET in controlling the disturbances that lead to grid instability and power quality issues. The proposed MPPET does not require any serious communication infrastructure for operation. In addition, the MPPET can respond to reverse power flow caused by excess power generation on the grid. Due to the intermittent nature of the renewable energy sources and the different stages involved in the design of the proposed MPPET, the system is liable to internal DC voltage fluctuation, causing grid instability; thus, an energy storage system (ESS) is incorporated to avert the challenges. The networks under investigation and the proposed MPPET are designed and simulated using MATLAB and Simulink software. The electrical isolation capability of the proposed bidirectional MPPET is verified through simulation. Several case studies have been carried out to evaluate the behavior of the system under different operating conditions and to check the feasibility of MPPET for power quality improvements. It was observed that the MPPET is proficient in regulating power quality issues, thus enhancing grid stability. It is also varied that the proposed MPPET prevents the escalation of the impact of faults or disturbances all over the grid. At the same time, it is verified that the proposed bidirectional energy storage systems enhance energy transfer between the utility grid and microgrids, which improves the system’s stability.
Article
04 June 2024Initial Stages of Development of an Automated Measurement Technique on Incisors
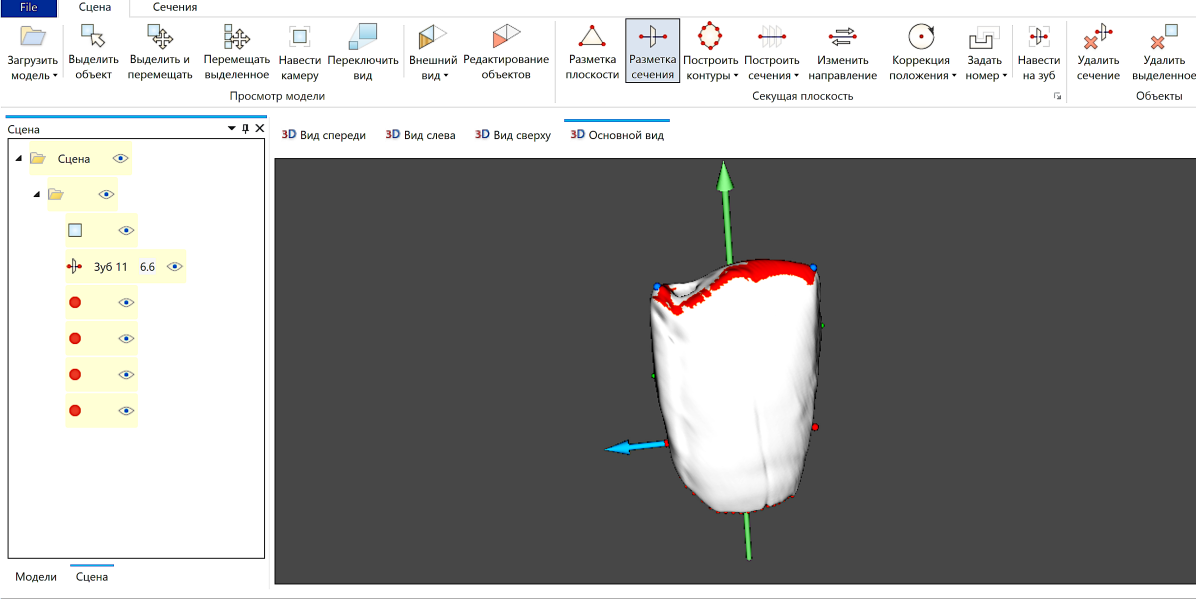
Teeth are an important object of studies in many scientific disciplines and, among various study techniques, measurements have one of the most promising prospects for further improvements supported by progress in computer sciences, imaging and image processing. Our recent work on automated odontometric algorithms for premolars and molars has gradually come to develop similar methods for another group of teeth—incisors. Using 3D reconstructions of teeth obtained through micro-focus tomographic scanning, we propose landmarks, which correspond to main morphological features of incisors and enable their formal description. In this article we present an orientation and measurement technique, based on an interpretation of incisor morphology, as a system which is able to perform in a fully automated mode. Since the primary objective of the current paper is to introduce methodological improvements, data on measurements and their results are shown at the most basic level.
Article
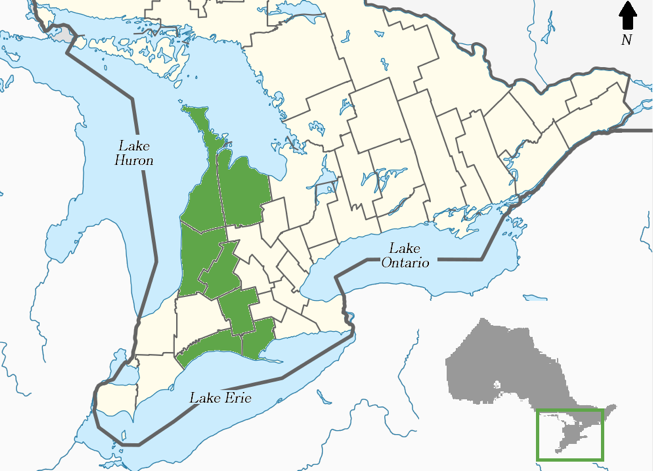
31 May 2024Advancing Green Infrastructure Solutions in Rural Regions: Economic Impacts and Capacity Challenges in Southwest Ontario, Canada
Green infrastructure (GI) is a growing topic in urban planning, asset management, and climate change adaptation. However, rural regions have been under-represented in the discourse. This paper explores the benefits and challenges associated with the implementation and management of GI through a regional study of rural communities in southwestern Ontario. Our focus concerns the inter-relationships between GI, economic resilience, and the development of rural places. Findings show rural communities benefit from GI initiatives like natural stormwater management, park naturalization, and natural heritage restoration, which provide low-cost municipal services, conserve agricultural soils, and contribute to the amenity appeal of rural places. Challenges surrounding awareness, organizational capacity, and environmental regulation have slowed the uptake of GI and led to inconsistencies across jurisdictions. A mix of supportive policies, funding of demonstration projects with economic monitoring, and training to build professional capacity will advance the use and efficacy of GI across rural regions.
Article
31 May 2024Solid Waste Recycling in Textile Processing Industries: A Case Study of India’s Clothing Hubs
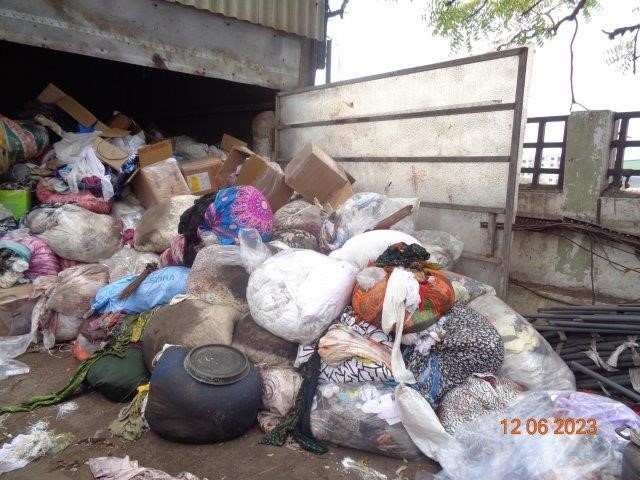
This study investigated the type and amount of solid waste generation from textile wet processing industries and analyzed the disposal and recycling strategies implemented for its utilization. The method involved industrial interactions with textile processing mills. Data was gathered based on a field survey of manufacturing units and their compliance management teams. The solid waste generated in textile processing stages against input raw materials and fuel sources was recorded. The challenges in recycling solid waste are identified and further scope for its valorization is suggested. The results indicate that significant solid waste produced during the wet processing of textiles arises from waste fabric cuttings, combustion of fuels used in processing stages, and sludge generated from the post-effluent treatment. Around 80% of solid waste generated during the wet processing of textiles can find applications in the construction industry. Effective management of solid waste and its potential applications in construction are elaborated in detail.

Review
30 May 2024A Review on Design of Sustainable Advanced Materials by Using Artificial Intelligence
This paper gives a comprehensive review of scientific interests and current methodologies of artificial intelligence applied to advanced material design and discovery by taking into account multiple sustainable design criteria such as functionalities, costs, environmental impacts, and recyclability. The main research activities include predicting material properties, compositions, and structures with data mining, new material discovery, hybrid modeling approaches combining AI techniques and classical computational formulations based on physical and chemical laws, and multicriteria optimization of materials. Based on this review, a short analysis is provided on the perspectives of this research area in the future, aiming at creating an everything connected material life cycle with real-time traceability systems
Article
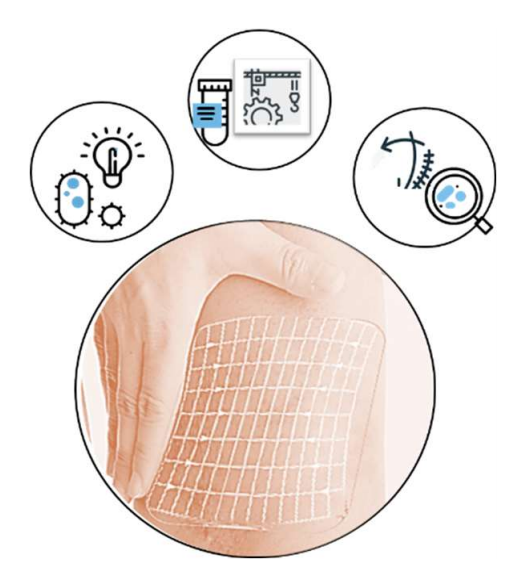
28 May 2024Efficacy and Cytocompatibility of a Pressure Garment—Silicone Composite Dressing Material for Scar Healing
Pressure garment therapy (PGT) and silicone gel sheeting (SGS) predominate non-invasive interventions for burn injuries, but the market lacks a composite solution combining pressure garment fabric (PGF) and medical-grade silicone (e.g. Biopor®AB) for multi-therapeutic efficacy. To address this gap, a versatile composite dressing of PGF-Biopor®AB was developed. PGF-Biopor®AB incorporates dual PGF-SGS therapy, mechanotherapy, and active moisture management, to facilitate recovery of hypertrophic subsidiary structures. The PGF structure enables the application of PGT, while the Biopor®AB silicone characteristics enforce silicone gel therapy (SGT). The PGF-SGS efficacy optimization not only reduces tension but also facilitates water vapor and oxygen penetration, along with hydration of the stratum corneum. Mechanotherapy, involving tension-shielding and pressure redistribution, promotes the reorganization of the collagen-fiber network. For active moisture management, the incorporation of a microchannel structure with active nylon absorbency facilitates effective moisture control through water absorption, retention, and cellular pathways of transport. In this study, the microscale features in the structure were further investigated. Under ISO 10993-5 standard, an over 70% cell viability in 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide (MTT) assay containing the L929 cell line verified the enhanced cell growth and inhibited proliferation, endorsing the safe usage of PGF-Biopor®AB. Patient studies of one-month efficacy in both high and low-cell-density samples and an early scarless healed wound suggest that over 70% cell viability is sufficient for optimal scar therapeutics. The multifaceted scar repair roles are fulfilled by addressing persistent inflammation, insufficient oxygenation, low levels of perfusion, and scar-healing tension, hence realising the multi-therapeutic efficacy of the composite dressing.
Article
23 May 2024Proposal for A Systemic Human Ecological Turn for Health Science and Medicine
Industrial development processes, accompanied by extreme growth processes, regards world population, pollution, food production and the exploitation of natural resources have caused severe ecological problems. This has been well known since 1972 through the study ‘The Limits to Growth’, in which humanity and the world society was called upon to make an ecological turn and to change its consumption model and the type of economic development that was not suited to finite natural resources (or a finite planet). However, the relationships between the state of the environment and human health have hardly been considered, although an ecological view of health was already proposed by Hippocrates, and as in the meantime, the technical terms “Environmental Health” and “Environmental Medicine” have become established at universities. It is only in recent times that global terms such as climate medicine, One Health, Eco Health, etc. have become powerful pragmatic and action-oriented initiatives. They can be understood as calls for a worldwide health-related ‘ecologization’ of (health) culture. Regarding these approaches we highlight theoretical and metatheoretical aspects, since in general, any real action is only as good as the analytical quality of the plan that serves as a guide for that action. From this point of view, we find that these approaches exhibit striking weaknesses. These are, among other things: the neglect of epistemological challenges combined with inconsistent conceptualizations of the category environment, the very superficial models of human beings, weaknesses of ecological frameworks in relation to the macro-, meso- and micro-eco-social levels of the targeted topics, and a vague notion of systems methodology. Following on from this, we call for an explicit social-/human-ecological framework (New Viennese School, Australian School) for environmental health issues as it has been established for decades in the field of environmental, sustainability and transformation sciences.

Review
20 May 2024
Advancements in the Bio-degradation of Plastic Waste into Value-added Chemicals: A
Recent Perspective
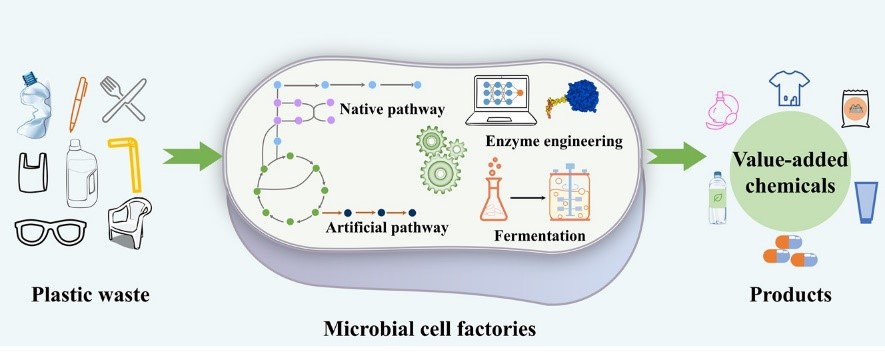
Plastics are an essential component of modern life, but the plastic waste has caused significant environmental pollution and economic losses. The effective solution to these problems is the biodegradation and high-value conversion of plastic waste. After biodegradation, plastic waste is broken into smaller molecules and eventually transformed into innocuous substances like water, carbon dioxide and biomass. High-value conversion enables plastic waste to be converted into products with higher economic value and environmental friendliness. Based on this, we summarize the biodegradation methods of bioplastics and analyze the shortage of these methods. Subsequently, we summarize the progress of converting the degradation products into value-added chemicals, comprehensively analyze the advantages and disadvantages of these bioconversion process, and propose some strategies to address these disadvantages. Finally, we analyze the significance of establishing a microbial-based conversion process that integrates the degradation and the conversion, and propose some potential strategies.
Review
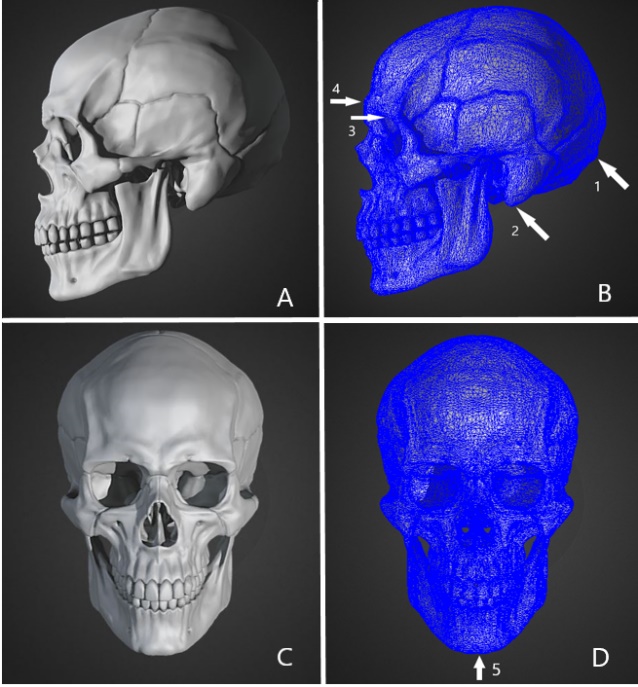
16 May 2024The Application of Forensic Imaging to Sex Estimation: Focus on Skull and Pelvic Structures
Forensic imaging is recognized as a vital tool in forensic practice mostly reflected by the wide use of post-mortem imaging in death investigations. With the surge of forensic imaging applications and research in recent years, many forensic subdisciplines have adopted this tool as a scientific investigation method, including forensic anthropology. Sex estimation is one of the key assignments in forensic anthropology along with age, ancestry and stature estimation. Traditionally, this assignment is done with non-metric macroscopic examination and metric analysis performed by forensic anthropologists. Today, forensic imaging serves as an auxiliary tool that adds to traditional methods and brings sex estimation to a dynamic era. The purpose of this article is to review forensic imaging methods in forensic anthropology sex estimation with a focus on skull and pelvic structures, aiming to provide insights into the best practices and prospective research directions.