Found 1 results
Article
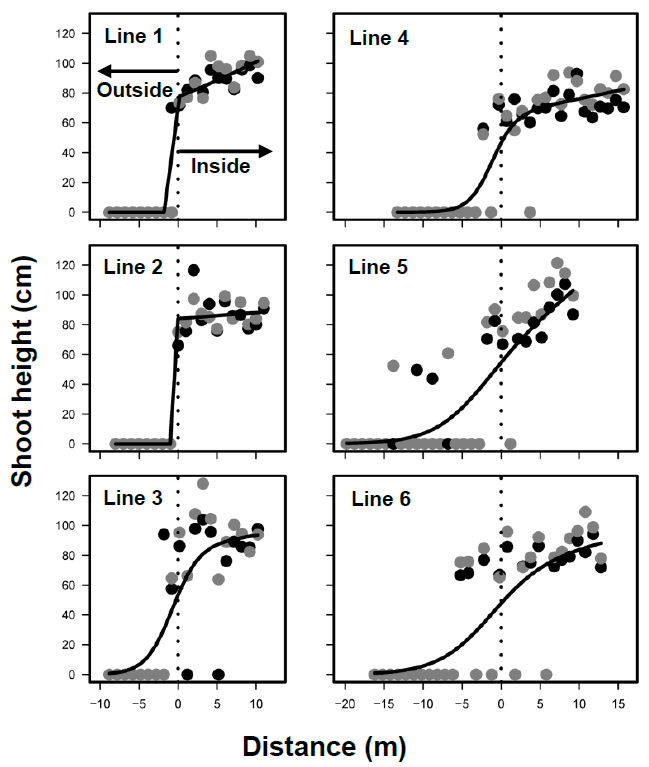
15 October 2024Stable Boundaries of Phragmites australis Marsh Development after Peat Mining in a Northern Japan Bog
Since Phragmites australis often develop marshes soon after human disturbances, such as peat mining in bogs, the establishment patterns should be clarified for restoration purposes. The inside and outside boundaries of P. australis marshes were investigated following peat mining in Sarobetsu mire, northern Japan, in 2016 and 2017. The boundaries of marshes did not move during the two years, due mostly to the slow expansion of shoots. Various vegetation types developed outside of the marsh. P. australis coexisted with neither ericaceous nor carnivorous plants, which favor Sphagnum bogs. The succession in the marsh did not progress the original bogs. P. australis dispersed seeds mostly within the marshes, suggesting limited dispersal, and developed transient seed bank. Therefore, seed dispersal (sexual reproduction) and rhizomes (vegetative reproduction) contributed to population maintenance rather than population enlargement during the studied period. Peat moisture was higher in the marsh, whereas photosynthetic active radiation was lower. Water levels did not differ between inside and outside the marshes. Chemical properties in peat water were not different between inside and outside the marshes. Therefore, water chemistry and levels did not adequately explain the marsh development. These results suggest that, for wetland restoration, environmental manipulation is ineffective in reducing P. australis and unpredictable or stochastic events alter the dynamics of P. australis marshes.