Found 5 results
Review
20 January 2025Adsorption and High-Value Transformation of Volatile Fatty Acids from Microbial Fermentation Products: A Review
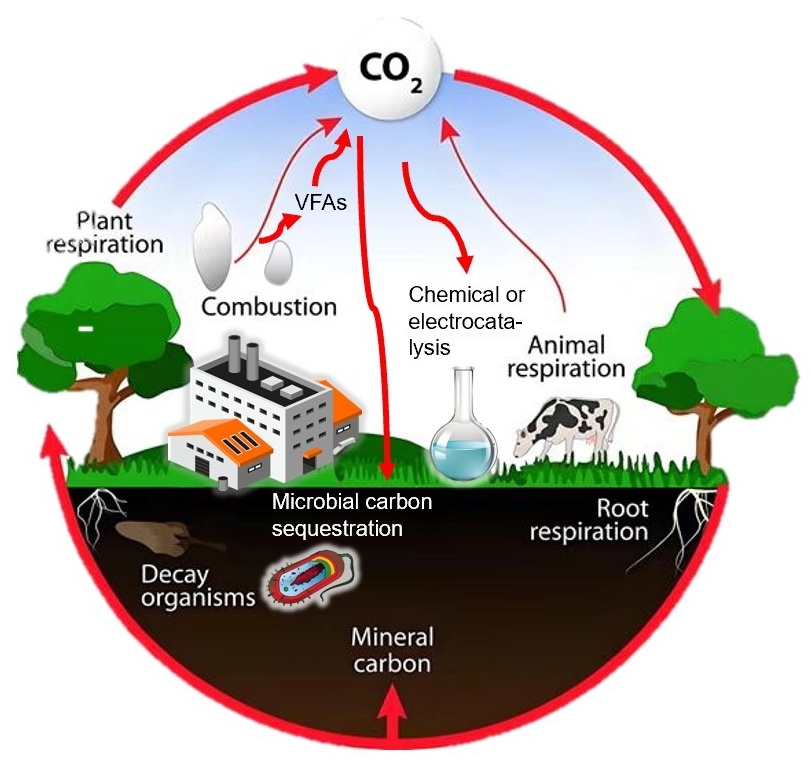
To mitigate the aforementioned global environmental issues, the concept of carbon capture and storage is crucial in addressing the necessity for carbon peaking and carbon neutrality. The buildup of volatile fatty acids during anaerobic fermentation is a primary factor contributing to the suboptimal performance or outright failure of anaerobic digestion systems. In response to the pressing demand for volatile organic acid recovery and high-value conversion, we primarily outlined the sources, recovery techniques, adsorption materials, and methods for high-value conversion of volatile fatty acids. The methods of adsorbing volatile acetic acid were presented, encompassing adsorption materials, mechanisms, and interfacial modifications of the adsorbent. Furthermore, drawing from recent research advancements, we have synthesized the high-value conversion techniques for volatile fatty acids and evaluated the research challenges and future prospects in this domain.
Article
12 October 2024Production and Destruction of Plant Organic Matter in Bog Ecosystems in the South of Western Siberia
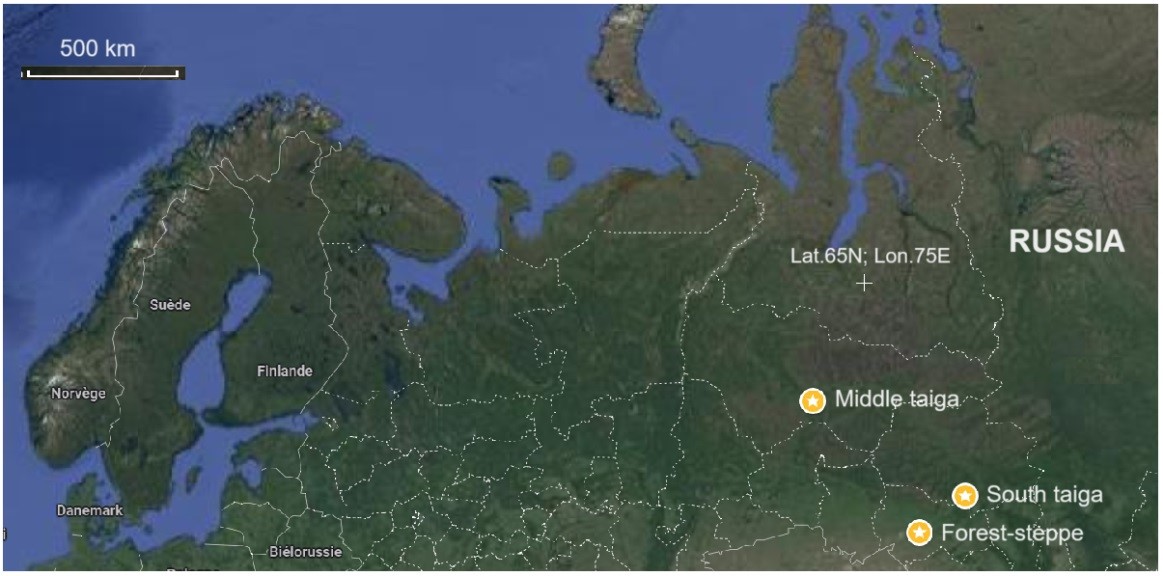
There are still many gaps in studies of the carbon cycle in northern ecosystems. It is challenging also in the context of climate change. This new study focuses on providing the state of the art data on the dynamics of plant organic matter, namely, the live plant biomass (phytomass), the dead biomass (mortmass), the Net Primary Production (NPP), as well as the rate of decomposition of plant organic matter of the major plant species, contributed to peat deposits. The study was conducted via direct in–situ measurements of different fractions of plant organic matter at a few test sites of oligotrophic pine–dwarf shrub–Sphagnum bogs at a wide geographic gradient (from the middle taiga to the forest-steppe regions in Western Siberia) based on an original methodology of measurements developed by the authors. In general, the five groups of plant species were distinguished in terms of productivity and decomposition rates. The study revealed a strong correlation between the net primary production (NPP) and the rate of decomposition of plant organic matter in pristine northern peatlands: an increase in productivity (NPPs) was basically leading to an increase in rates of decomposition in all plant materials collected in bog ecosystems. The study contributes to a global understanding of patterns and main drivers related to basic set of carbon cycle components in the northern wetland (peatland) ecosystems, their diversity and their spatial distribution.
Article
18 September 2024Direct-Ink-Writing Printing of Shape Memory Cross-Linked Networks from Biomass-Derived Small Molecules
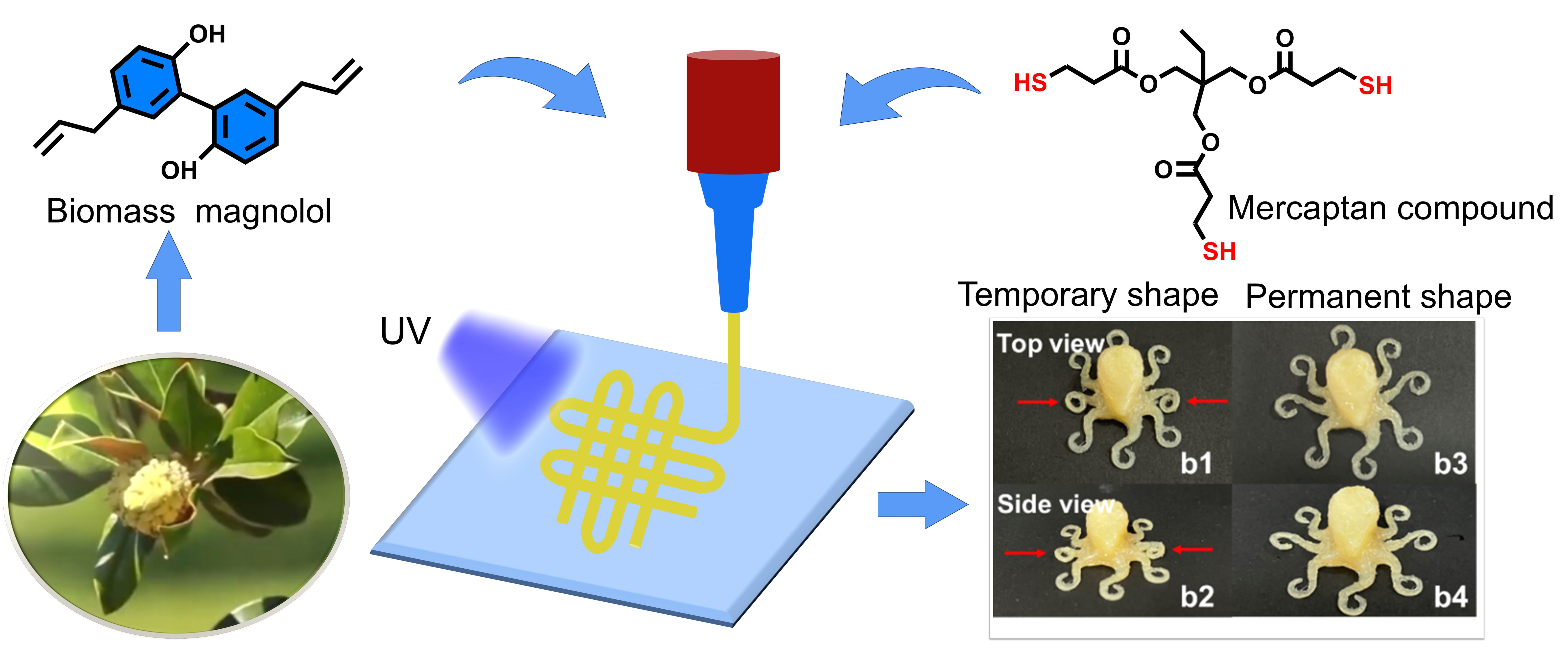
The rapid development of 3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing, has opened up new opportunities for applying shape memory polymers (SMPs) in various fields. The use of abundant, inexpensive, and easily accessible biomass materials as printing raw materials not only facilitates the creation of more intricate SMPs but also aligns with the principles of low-carbon, green, and sustainable development. Here, we successfully printed a shape memory cross-linked network (NW-MO-TTMP) in a single step by direct-ink-writing printing and an in-situ thiol-ene click reaction with magnolol and trimethylolpropane tris(3-mercaptopropionate) as raw materials. The resulting NW-MO-TTMP network exhibited high mechanical properties and a tensile strength (σ) of up to 2.7 MPa when the thiol-ene ratio was 1.0:1, and the photo-initiator content was 1.5%. To improve printability, ethyl cellulose (EC) derived from biomass was incorporated to enhance the viscosity of the printing precursor fluid, resulting in a significant increase in the σ of the NW-MO-TTMP/EC network, reaching 20.6 MPa. Moreover, the successful printing of intricate models, such as the ‘whale’ and ‘octopus,’ demonstrated excellent shape memory effects. This approach highlights the potential of combining biomass-derived materials with advanced 3D printing techniques to develop sustainable and high-performance SMPs.
Review
14 June 2024Biobased Vitrimers: A Sustainable Future
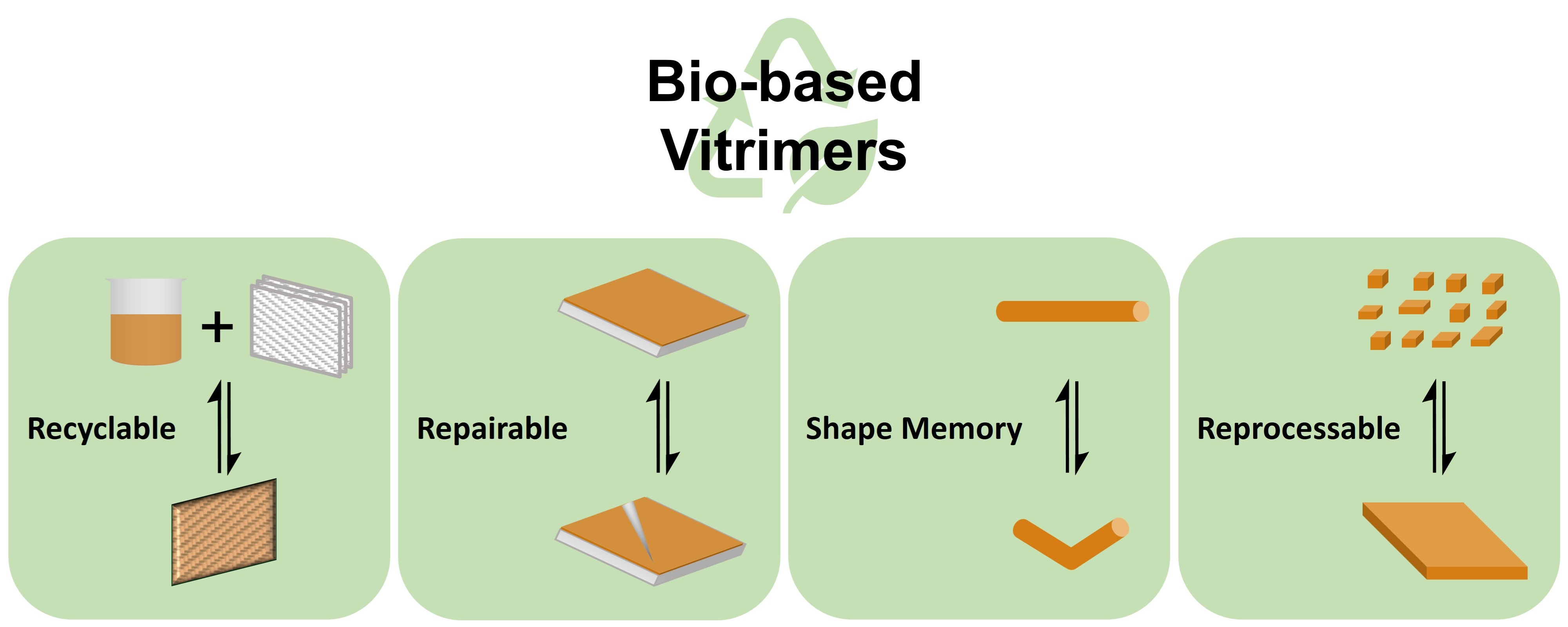
Vitrimers are crosslinked polymers containing dynamic covalent linkages. Because of their crosslinked structure, they are stable as thermosets at their service temperatures. At high enough temperatures, dynamic exchange reactions occur and rearrange the polymer network, thus vitrimers become malleable and reprocessable like thermoplastics. The dynamic covalent bonds can also undergo dissociative cleavage reactions under specific conditions, so vitrimers are inherently degradable. To achieve a sustainable future, various biomass resources have been used as raw materials in vitrimer preparation. This review summarizes recent developments in biobased vitrimers and highlights their preparation methods. The limitations of current biobased vitrimers are also discussed.
Article
06 May 2024Assessing Energy Emissions and Environmental Impact of Wool Processing: A Case Study of an Indian Textile Mill
The objective of this study is to investigate and analyze the effect of varying sources of energy inputs and their impact on carbon emissions during wool fiber processing. The method involved industrial visits to the textile wool processing mill and interaction with the manufacturing as well as commercial sourcing teams to gather relevant data. The results and outcome of this analysis indicate that wool wet processing is responsible for a significant carbon emission of about 0.031 tCO2e/unit of production. Coal as a source of energy has the highest carbon emission 0.066 tCO2e/product, while the use of biomass and Pressurized Natural Gas (PNG) had significantly lower CO2 emissions. Further, this study evaluated the scope 1 and scope 2 category emissions produced at the wool processing stage which accounted for 56303.2 tCO2e and 1817.10 tCO2e respectively.
