Found 25 results
Review
07 March 2025Mechanisms and Therapeutic Potential of Myofibroblast Transformation in Pulmonary Fibrosis
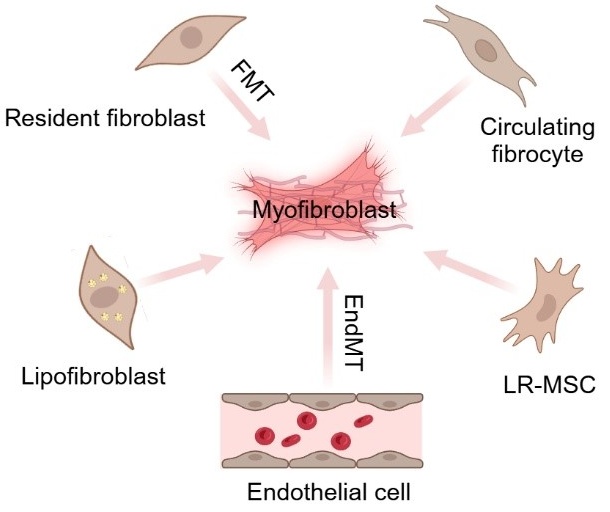
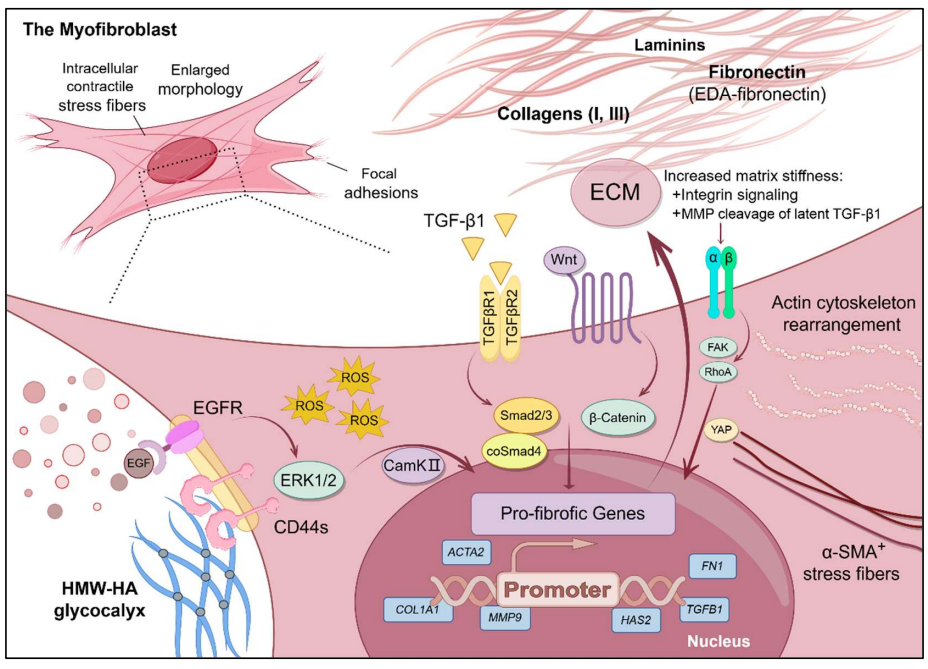
Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) is a progressive, irreversible, and fatal disease with an increasing incidence and limited therapeutic options. It is characterized by the formation and deposition of excess extracellular matrix proteins resulting in the gradual replacement of normal lung architecture by fibrous tissue. The cellular and molecular mechanism of IPF has not been fully understood. A hallmark in IPF is pulmonary fibroblast to myofibroblast transformation (FMT). During excessive lung repair upon exposure to harmful stimuli, lung fibroblasts transform into myofibroblasts under stimulation of cytokines, chemokines, and vesicles from various cells. These mediators interact with lung fibroblasts, initiating multiple signaling cascades, such as TGFβ1, MAPK, Wnt/β-catenin, NF-κB, AMPK, endoplasmic reticulum stress, and autophagy, contributing to lung FMT. Furthermore, single-cell transcriptomic analysis has revealed significant heterogeneity among lung myofibroblasts, which arise from various cell types and are adapted to the altered microenvironment during pathological lung repair. This review provides an overview of recent research on the origins of lung myofibroblasts and the molecular pathways driving their formation, with a focus on the interactions between lung fibroblasts and epithelial cells, endothelial cells, and macrophages in the context of lung fibrosis. Based on these molecular insights, targeting the lung FMT could offer promising avenues for the treatment of IPF.
Review
18 February 2025The Intersection between Immune System and Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis—A Concise Review
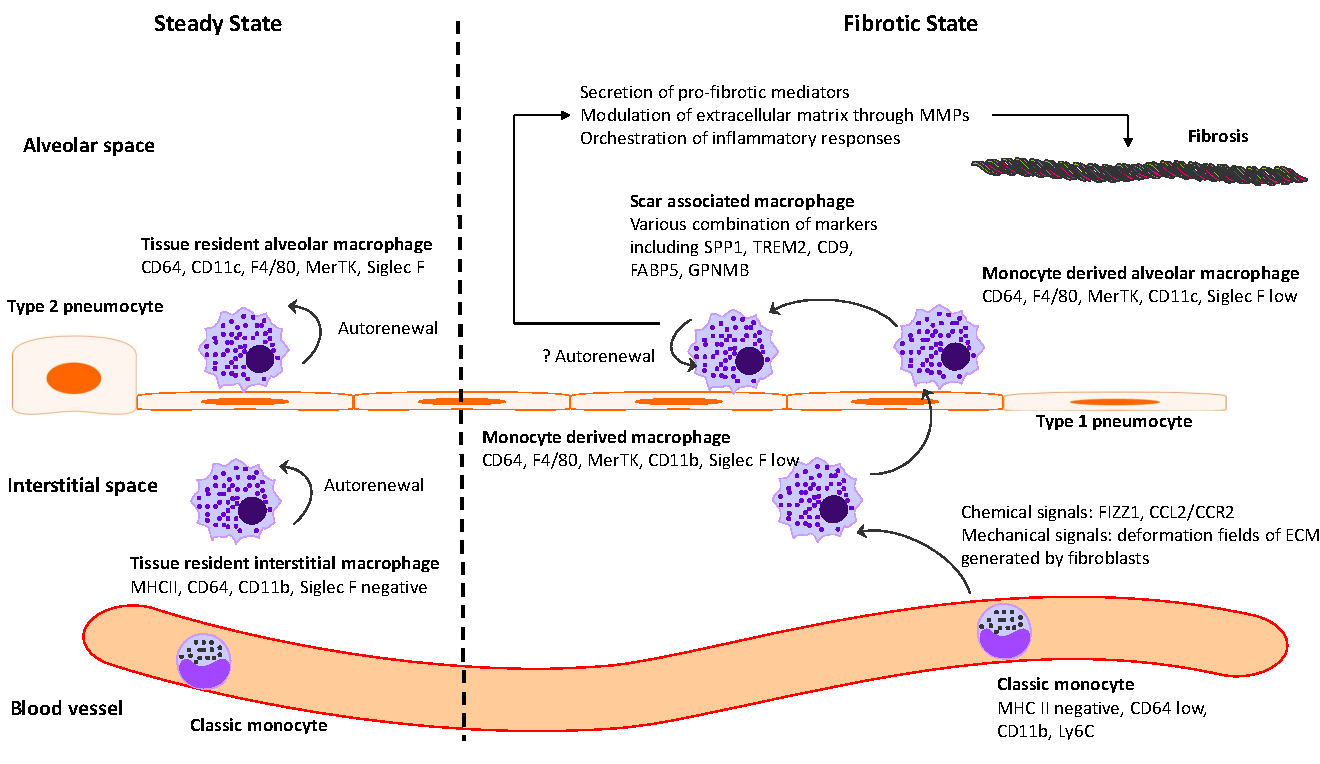
Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) is marked by progressive alveolar destruction, impaired tissue regeneration, and relentless fibrogenesis, culminating in respiratory failure and death. A diverse array of resident and non-resident cells within the lung contribute to disease pathogenesis. Notably, immune cells, both resident and recruited, respond to cues from sites of lung injury by undergoing phenotypic transitions and producing a wide range of mediators that influence, initiate, or dictate the function, or dysfunction, of key effector cells in IPF pathology, such as alveolar epithelial cells, lung fibroblasts, and capillary endothelial cells. The role of the immune system in IPF has undergone an interesting evolution, oscillating from initial enthusiasm to skepticism, and now to a renewed focus. This shift reflects both the past failures of immune-targeting therapies for IPF and the unprecedented insights into immune cell heterogeneity provided by emerging technologies. In this article, we review the historical evolution of perspectives on the immune system’s role in IPF pathogenesis and examine the lessons learned from previous therapeutic failures targeting immune responses. We discuss the major immune cell types implicated in IPF progression, highlighting their phenotypic transitions and mechanisms of action. Finally, we identify key knowledge gaps and propose future directions for research on the immune system in IPF.
Review
08 February 2025Mechanics and Synergistic Signaling of Fibronectin, Integrins, and TGF-β Isoforms
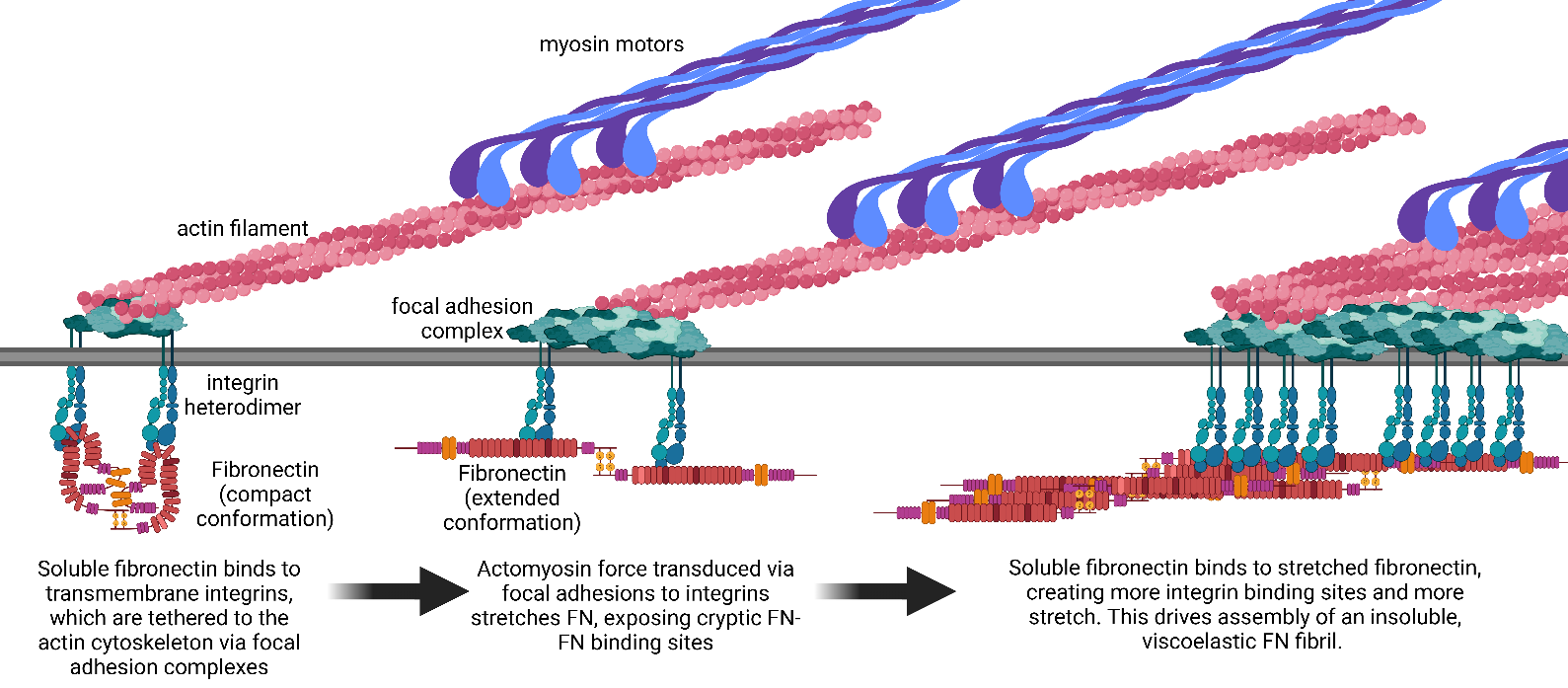
Fibrotic diseases such as pulmonary fibrosis, hepatic fibrosis, chronic kidney disease, and cancer are marked by an excess accumulation of extracellular matrix (ECM). This process involves the assembly of the ECM protein fibronectin (FN) into insoluble fibrils. FN fibril assembly is highly linked with integrin signaling, TGF-β1 signaling, and cellular contractility. This linkage consists of four stages: (i) Integrin binding and contractile forces facilitate the assembly of FN into insoluble fibrils; (ii) assembled FN fibrils bind the large latent complex of TGF-β1; (iii) activation of TGF-β1 from the latent complex requires integrin binding and contractile forces; and (iv) active TGF-β1 increases contractility, integrin expression, and FN assembly. The significance of integrin signaling and TGF-β1 signaling in fibrotic diseases is well-appreciated, as numerous clinical trials targeting integrins or TGF-β1 have been reported. However, despite a clear effort to target integrins and TGF-β1 clinically, the vast majority of these trials have failed or have been terminated. These suggest a potentially incomplete understanding of the synergistic effects of these pathways. Here we present a review of both FN fibrillogenesis and TGF-β1 signaling, as well as current opinions of under-explored areas of crosstalk related to these pathways that may explain why these have not been successfully targeted in many disease states including fibrosis.
Review
05 February 2025Perspectives of Drug Therapy for Non-Alcoholic Steatohepatitis-Related Liver Fibrosis
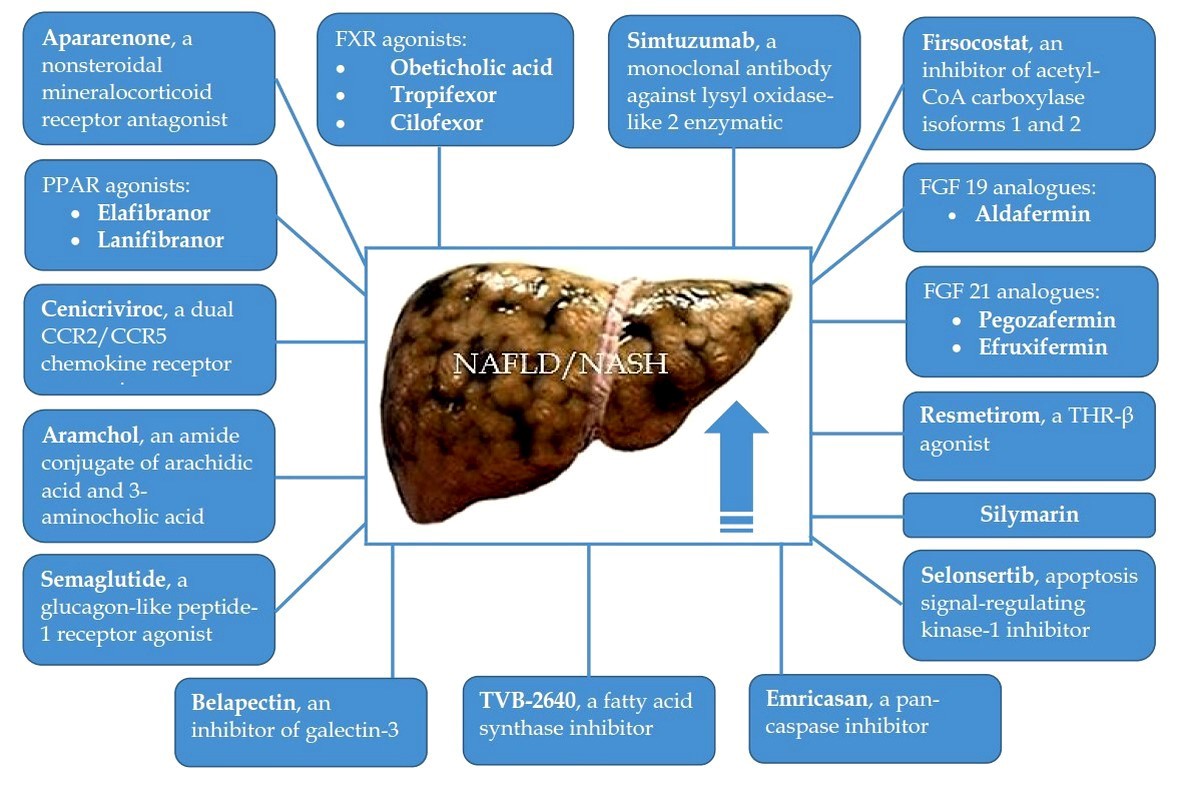
Liver fibrosis (LF) is an adverse event of the natural course of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) since its progression leads to the development of liver cirrhosis, which is associated with poor prognosis. In addition, there is evidence that the presence of advanced LF may be a strong independent predictor and risk factor for cardiovascular disease in NASH patients, which is the main cause of their death. Based on the severity of the problem, the study and implementation of drugs for the treatment of NASH-related LF is extremely necessary. The purpose of this review was to describe phase II and III randomized controlled trials (RCTs) evaluating the efficacy and safety of drug therapy for NASH-related LF. To date, the possibilities for pharmacological treatment of NASH-related LF are very limited. However, in recent years, several drugs have been evaluated in NASH patients with LF (F2–3), and in some cases with compensated liver cirrhosis, in large phase II and III RCTs, and they have shown promise. It can be assumed that drugs that have shown efficacy and safety in phase II and III RCTs will be recommended for testing and confirming practical benefits in phase IV RCTs. Besides, an in-depth study of the cellular and molecular mechanisms of NASH-related LF will contribute to the development of new medications, the introduction of which will expand the possibilities of its drug therapy.
Review
13 January 2025Comparative Analysis of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis and Progressive Pulmonary Fibrosis: Epidemiology, Pathophysiology, Clinical Features, Diagnosis and Treatment
Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) is a chronic fibrosing interstitial disease of unknown origin, characterized by radiological and histological features consistent with usual interstitial pneumonia (UIP). It is marked by a progressive worsening of dyspnea and a decline in lung function. Both IPF and PPF are comparable because they have poor prognoses with a median survival time from diagnosis of around 2–4 years without antifibrotic therapy. This review shows the main specific characteristics and differences of epidemiology, pathophysiology, clinical and radiological features, treatment, and prognosis of IPF and PPF.
Commentary
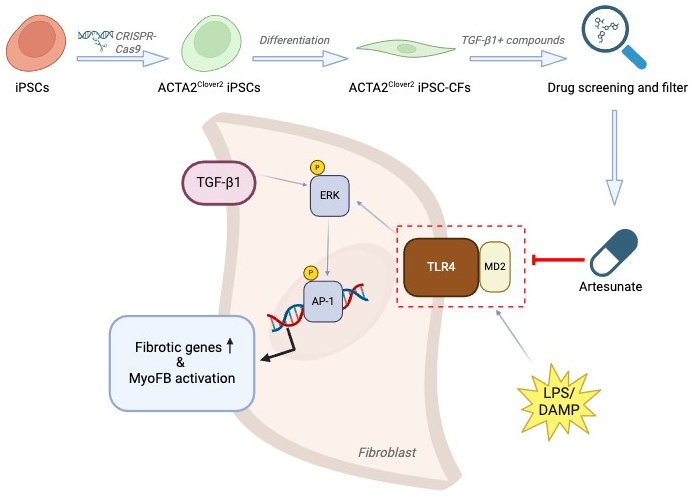
16 December 2024State of the ART: Drug Screening Reveals Artesunate as a Promising Anti-Fibrosis Therapy
Fibrosis is a progressive pathological process that severely impairs normal organ function. Current treatments for fibrosis are extremely limited, with no curative approaches available. In a recent article published in Cell, Zhang and colleagues employed drug screening using ACTA2 reporter iPSC-derived cardiac fibroblasts and identified artesunate as a potent antifibrotic drug by targeting MD2/TLR4 signaling. This study provides new insights into strategies for exploiting existing drugs to treat fibrosis.
Meeting Report
04 December 2024Progress and Gaps in Respiratory Disease Research and Treatment: Highlights of the IRM 2024 in Shanghai
Respiratory diseases pose a major public health challenge globally, necessitating collaborative efforts between basic researchers and clinicians for effective solutions. China, which is heavily impacted by a broad spectrum of respiratory disorders, has made notable strides in both research and clinical management of these diseases. The International Respiratory Medicine (IRM) meeting was organized with the primary goal of facilitating the exchange of recent research developments and promoting collaboration between Chinese and American scientists in both basic and clinical research fields. This article summarizes key insights from IRM2024, held in Shanghai, where a wide range of topics were discussed, including lung tissue development, disease mechanisms, and innovative therapeutic strategies. By integrating perspectives from basic, translational, and clinical research, IRM2024 highlighted recent advancements, addressed persistent challenges, and explored future directions in respiratory science and clinical practice. The insights gained from IRM2024 are poised to be pivotal in shaping future research and therapeutic approaches, further reinforcing the global commitment to enhancing respiratory health and improving patient outcomes.
Review
22 November 2024Dermal Fibrosis and the Current Scope of Hydrogel Strategies for Scarless Wound Healing
Dermal fibrosis poses a significant challenge in wound healing, affecting both the appearance and functionality of the scarred skin tissue. Beyond aesthetic implications, fibrosis can lead to pruritus, chronic pain, loss of mechanical flexibility, and impeded restoration of skin appendages, blood vessels, and nerves. Therefore, scar prevention remains a priority in wound management, and hydrogels, with their hydrophilic three-dimensional network and extracellular matrix-mimicking properties, have emerged as promising biomaterials for achieving scarless wound regeneration. In this review, we explore advancements in various hydrogel strategies designed to regulate myofibroblast differentiation, control the wound microenvironment, and mitigate dermal fibrosis. We provide an overview of dermal fibrosis, the scar-forming cells involved, and the various types of dermal scars. We then summarise advancements made in antifibrotic hydrogel formulations, emphasizing their practical applications in scarless skin wound healing. By reviewing the current research landscape and highlighting key hydrogel-based biomaterial strategies employed in this field, we aim to offer insights into design principles and underlying mechanisms of action. We intend for this review to serve as a valuable resource for researchers and clinicians interested in entering this field or exploring the potential of hydrogels to promote scarless wound healing.
Article
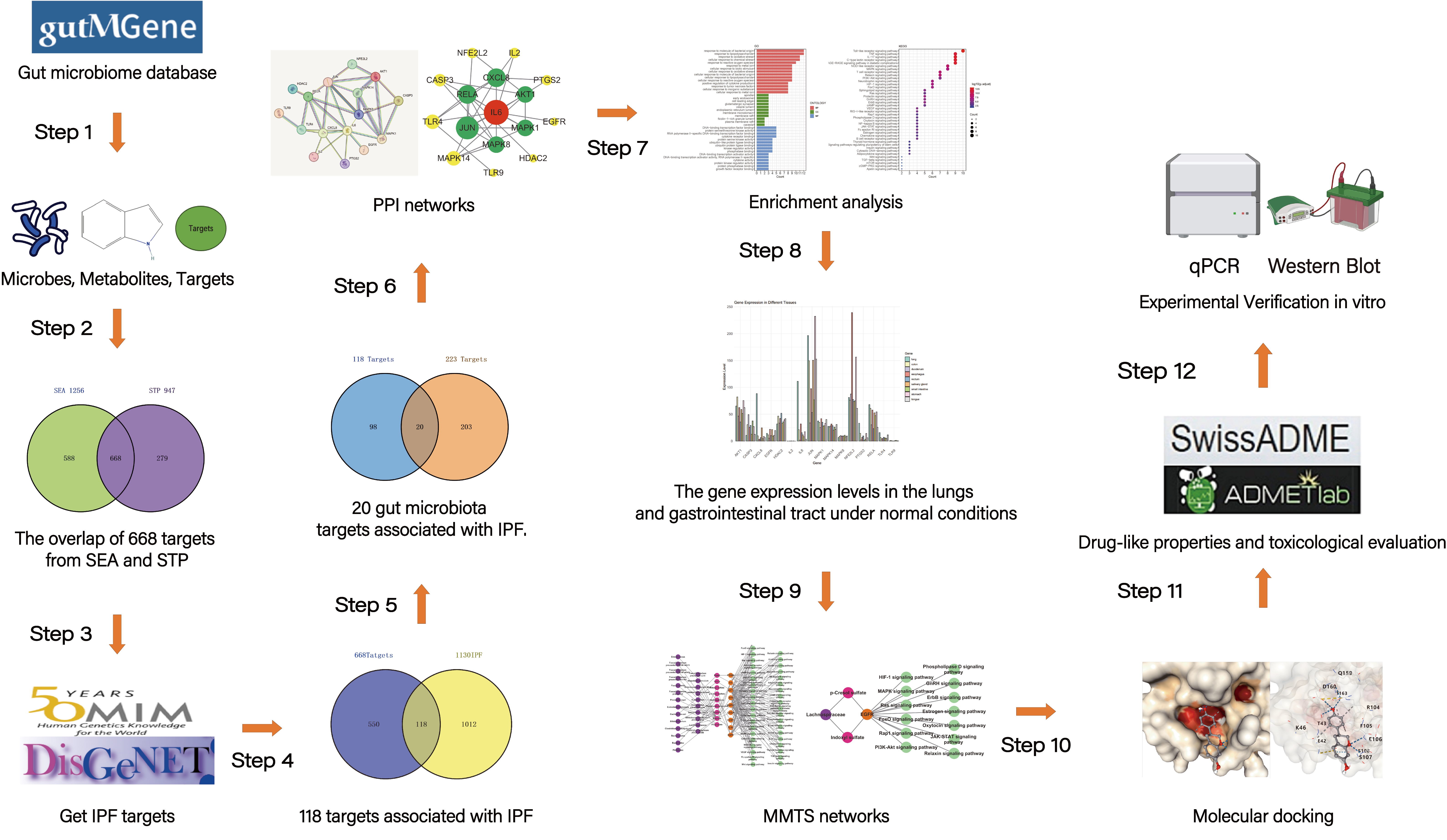
04 November 2024Exploring the Potential Relationship between Gut Microbiome Metabolites and Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis via Network Pharmacology Study
Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) is a chronic, progressive fibrotic lung disease with a poor prognosis. Previous research has revealed that the gut microbiota is associated with human health and immunity, and it interacts with the lung through the “gut-lung axis”. This study explores the potential relationship between Gut Microbiome Metabolites and Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis via Network Pharmacology Study. The metabolites from gut microbiota were retrieved from the gutMGene database, and gene targets for these metabolites were obtained from previous studies. Gene targets of IPF were obtained from public databases (DisGeNET, OMIM). Subsequently, following the identification of shared targets, IL6 was determined as the core target through protein-protein interaction analysis. Then, a microbiota-metabolite-target-signaling pathway network (MMTS) was constructed using Cytoscape 3.10, and targets with low expression in the lungs and intestines were deleted. The MMTS network revealed that three short-chain fatty acids—acetate, butyrate, propionate, and a flavonoid compound called equol—are IL6-related metabolites. Then, we performed a molecular docking test (MDT) using CB-Dock2 to validate the affinity between core targets and metabolites. MDT confirmed that equol produced by the conversion of isoflavones from Lactobacillus paracasei JS1 was more stable in binding to IL6 than the other three short-chain fatty acids, thereby affecting multiple signaling pathways and influencing the progression of IPF. Finally, we validated this hypothesis through in vitro cell culture experiments, further confirming the effect of Equol.
Review
28 October 2024Acute Exacerbations of Interstitial Lung Disease: Evolving Perspectives on Diagnosis and Management
Interstitial lung diseases (ILDs) are a heterogeneous group of chronic lung diseases caused by several potential etiologies but for many, the cause of a given ILD remains unknown. Accurate epidemiologic data are hard to find because of varying definitions, overlapping characteristics once thought to be unique to specific diseases, and ongoing changes in how ILDs are diagnosed and managed. In addition, there are significant variations in prevalence among different geographic populations, likely reflecting a combination of genetic and environmental differences. Certain risk factors, including exposure to cigarette smoke or environmental toxicants (asbestos, silica, fracking, coal dust, and air pollution), genetic mutations, and single nucleotide polymorphisms, have all been associated with developing interstitial lung disease. Due to the availability of high-resolution computed tomography (CT) scans, earlier and broader recognition of subtle imaging changes, and an aging worldwide population, the incidence and prevalence of ILDs are increasing. While a given cause of particular interstitial lung disease may vary, patients often experience breathlessness and a non-productive cough due to impaired alveolar gas exchange. Patients with ILD are prone to the development of acute exacerbations, marked by acute or chronic respiratory failure because of an acute exacerbation of the underlying lung disease. In this review, we discuss the definition of an acute exacerbation and comment on what is known about the underlying pathophysiology in exacerbations of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis and other ILDs. We also emphasize the similarities in the clinical presentation of the acute exacerbations regardless of the underlying ILD, highlight key prognostic features of the diagnosis, and underscore the importance of interdisciplinary management of acute interstitial lung disease exacerbations.
