Found 5 results
Article
15 October 2024Stable Boundaries of Phragmites australis Marsh Development after Peat Mining in a Northern Japan Bog
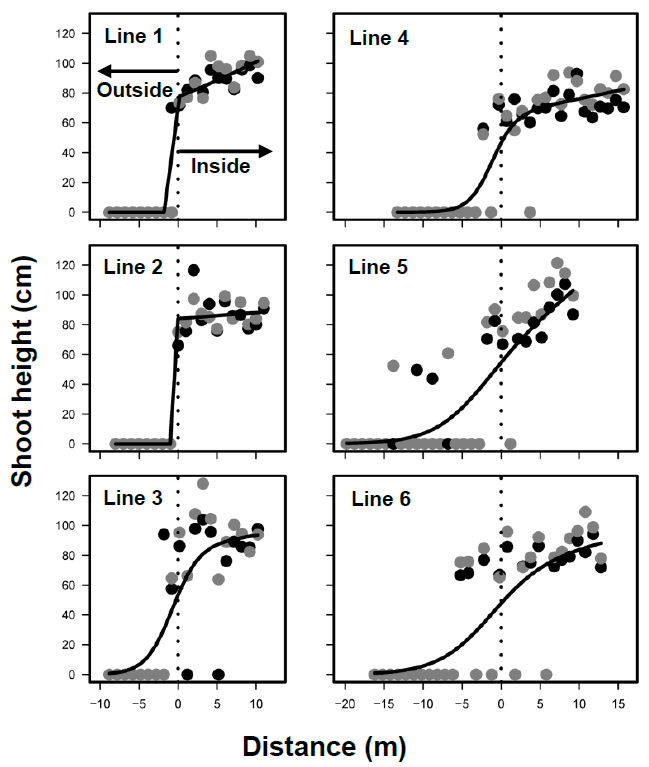
Since Phragmites australis often develop marshes soon after human disturbances, such as peat mining in bogs, the establishment patterns should be clarified for restoration purposes. The inside and outside boundaries of P. australis marshes were investigated following peat mining in Sarobetsu mire, northern Japan, in 2016 and 2017. The boundaries of marshes did not move during the two years, due mostly to the slow expansion of shoots. Various vegetation types developed outside of the marsh. P. australis coexisted with neither ericaceous nor carnivorous plants, which favor Sphagnum bogs. The succession in the marsh did not progress the original bogs. P. australis dispersed seeds mostly within the marshes, suggesting limited dispersal, and developed transient seed bank. Therefore, seed dispersal (sexual reproduction) and rhizomes (vegetative reproduction) contributed to population maintenance rather than population enlargement during the studied period. Peat moisture was higher in the marsh, whereas photosynthetic active radiation was lower. Water levels did not differ between inside and outside the marshes. Chemical properties in peat water were not different between inside and outside the marshes. Therefore, water chemistry and levels did not adequately explain the marsh development. These results suggest that, for wetland restoration, environmental manipulation is ineffective in reducing P. australis and unpredictable or stochastic events alter the dynamics of P. australis marshes.
Article
09 January 2024Climate Change Adaptation Strategies for Grape Cultivation in Yamanashi Prefecture of Japan
Climate change impacts agricultural production, especially fruits. Amongst fruits, the grape is economically valuable and highly affected by climate change. Therefore, climate adaptation strategies are essential in overcoming the detrimental effects of climate change on grape cultivation. The study summarises adaptation strategies for grape cultivation in general and focuses on climate change. The Yamanashi prefecture in Japan is taken for the case study. Our findings indicate a decline in grape production in Japan and Yamanashi prefecture. This is attributed to the effects of climate change. Following this, various support measures (adaptative, mitigation, others) provided by the Yamanashi government towards grape cultivation are summarised and analyzed. The study concludes by offering recommendations by drawing lessons from the literature review on adaptation strategies for grape cultivation, focusing on overcoming climate change impact in the context of Yamanashi prefecture.

Article
15 November 2023Local Production, Consumption, and Innovation: Enhancing Sustainability through SMEs in Japan
The study focuses on the process of business development with the use of food tech and open innovation by Small and Medium-sized Enterprises (SMEs) in Japan to create a sustainable ecosystem in the regional economy. Production of alternative food materials is introduced in the new business of SMEs with the hope to reduce carbon footprint. SMEs need to create an SME ecosystem that integrates consumers as vital partners in the process of introducing new alternative food items to the market as agents of change. Innovative ways of inventing new food products involve the processes of sourcing ingredients, creating new recipes for alternative food products, and incorporating local food culture and methods of food preparation. Therefore, it is crucial for SMEs to involve local producers as well as consumers as stakeholders in innovation. Some case examples of SMEs producing plant-based alternative meats in Japan are reviewed in this study to highlight key factors impacting the outcome of innovation in the products and processes of SMEs seeking sustainable solutions. The significance of the study lies in acknowledging catalytic roles of SMEs in regional settings and interactive roles of consumers as product buyers as well as active players who consciously opt for certain products and modes of consumption driven by their inclination to support sustainability. Based on the findings of the study, some policy suggestions are also made for enhancing sustainability and revitalizing the local economy through SMEs.

Article
21 August 2023Role of Youth in Implementing SDGs Future City in Tosacho, Kochi, Japan
The “SDG Future Cities” established by the SDG (Sustainable Development Goals) Promotion Headquarters of Cabinet Office of Government of Japan, are being expanded to all municipalities in Japan through government support for the efforts of leading municipalities. Tosa town is a small town with less than 4000 people with high aging population and surrounded by mountains in Kochi Prefecture. The town was selected as one of the SDG Future City in 2020. In this paper, through a literature review, interviews with the Tosa Town Office, and a questionnaire survey and interview with residents of Tosa town, we considered what young people need to do to achieve SDG-11. Although Tosa Town has a variety of local government initiatives, the definition of a town where young people can continue to live, as revealed in the literature review, was found to be insufficient in terms of “economic resources,” “decision-making,” “data,” and “knowledge”. However, it was found that “community leaders,” “nature/topography,” and “community/people” are the most important factors for creating a town where people can continue to live. As for future issues, it is necessary to take measures for “decision-making,” “data,” and “knowledge,” as well as to solve issues specific to Tosa town.

Article
03 March 2023Spatial Characteristics and Influencing Factors of Migration in Kanagawa, Japan
In the context of “Tokyo centralization”, population migration has become an important factor affecting Kanagawa's economic growth, living standards, and employment status. On the other hand, with the development of the declining birth rate and aging society, migration for any purpose has an impact on social development. The government has released many policies to attract people from other cities to Kanagawa. This study analyzes the factors influencing the spatial pattern of population migration in Kanagawa based on the current spatial characteristics of population migration in Kanagawa from 2016~2020 and previous population migra-tion research theories. the influencing factors are analyzed empirically by selecting a total of 9 economic, social, and environmental indicators that may affect the spatial pattern of population migration in Kanagawa. The result showed that, when only the economic factor was considered, gross prefectural product, job opportunities, and consumer price index significantly influenced migration; When only environmental factors are considered, the number of pollution complaints successfully handled had a significant positive effect on population migration; When only the social environment is considered, the level of education becomes the main consid-eration for people. Furthermore, when the economic factors, environmental factors, and social factors are analyzed together, the gross prefectural domestic product, job opportunities, consumer price index, and the number of pollution complaints successfully handled all have an impact on migration in Kanagawa and the gross prefectural product is the common influencing factor.
