Found 1 results
Review
30 December 2024
Mini Review on the Photocatalytic Removal of Gaseous Ammonia: Current Status
and Challenges
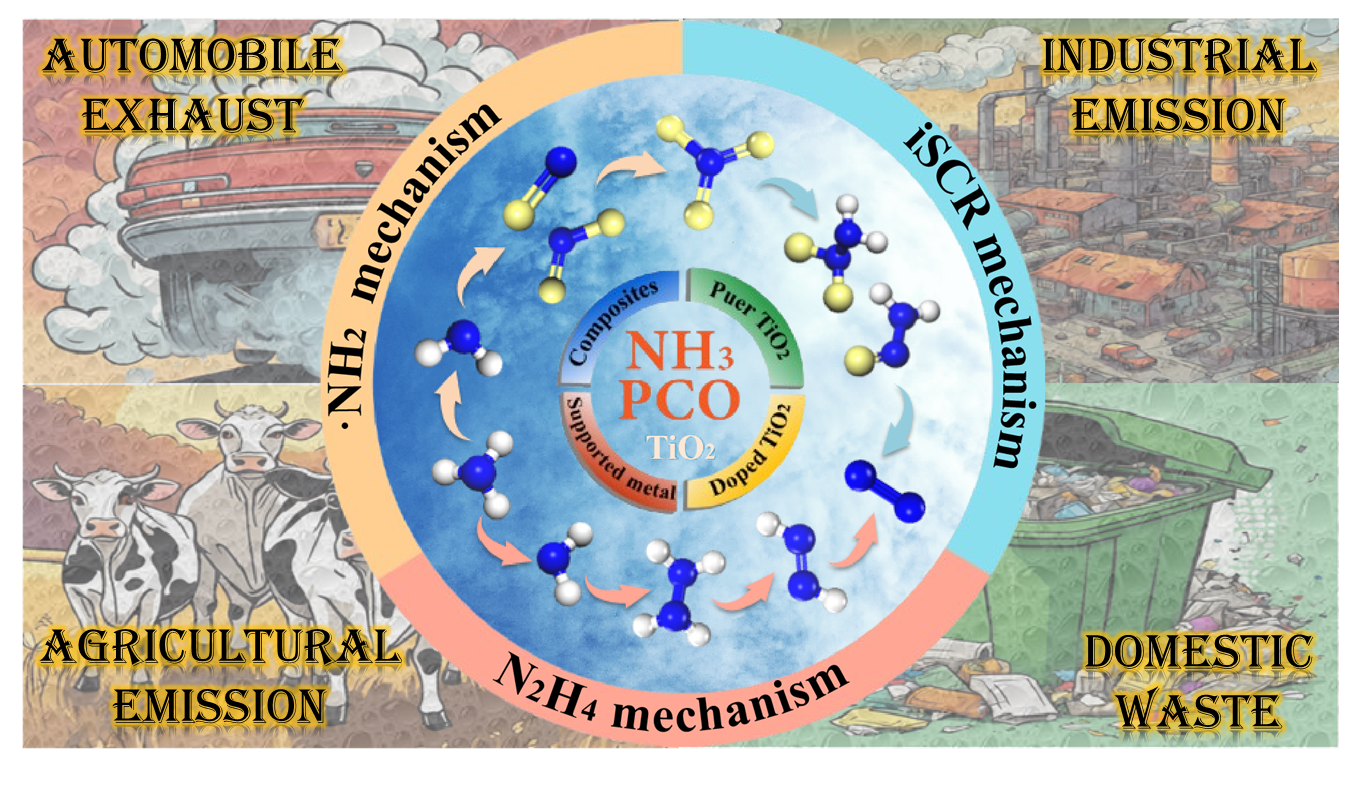
Ammonia
gas (NH3) is a notorious malodorous pollutant released mainly in
agriculture and industry. With the increasing demand for ammonia, environmental
pollution caused by ammonia discharge has seriously threatened human health and
safety. Due to the discrete emission and low concentration of NH3,
photocatalytic oxidation is an economical and efficient treatment strategy. TiO2,
as a common photocatalyst, has been widely used by researchers for the
photocatalytic removal of NH3. In addition, surface modification,
element doping, semiconductor recombination and metal loading are used to
improve the utilization rate of solar energy and carrier of TiO2 so
as to find a catalyst with high efficiency and high N2 selectivity.
Further, at present, there are three main removal mechanisms of NH3 photocatalytic oxidation: ·NH2 mechanism, iSCR mechanism and N2H4 mechanism. Among them, N2H4 mechanism is expected to be
the main removal path of NH3 photocatalytic oxidation in the future
because the removal process does not involve NOx and nitrate. This
review summarizes recent studies on the photocatalytic oxidation of NH₃,
focusing primarily on NH₃ removal efficiency, N₂ selectivity, and the underlying
removal mechanisms. Additionally, the potential future applications of NH₃
photocatalytic oxidation are discussed.