Found 12 results
Perspective
31 December 2024
Offshore Renewable Energy Advance
Offshore renewable energy generation has become an important means to address the energy crisis and climate change, which has gained widespread attention in recent years. This article presents classic domestic and international cases that introduce the development and industrial transformation of generation technologies for offshore wind, offshore photovoltaics, ocean wave energy, tidal energy and temperature difference energy. Offshore power generation projects face challenges in design, safety, long-term operation and economic feasibility. Offshore renewable energy generation is gradually moving towards industrialization, and is expected to become a key component of global energy supply in the future with technological advancements and policy support, providing strong support for tackling climate change and achieving sustainable development goals.

Review
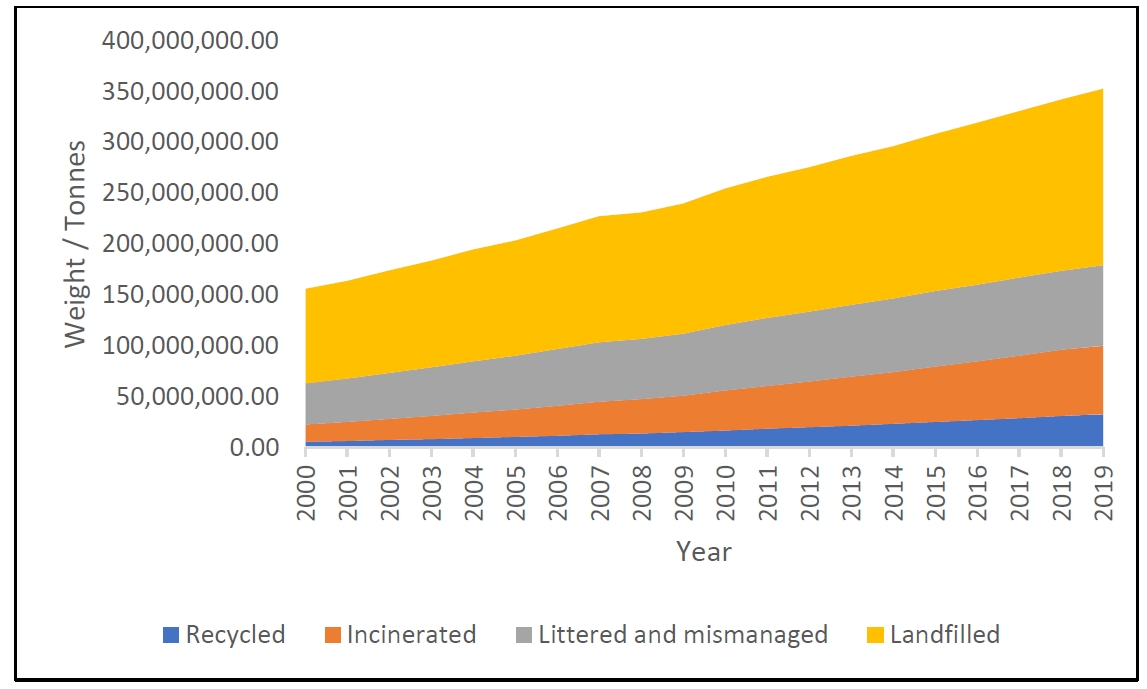
09 December 2024Synthesize and Applications of Biodegradable Plastics as a Solution for Environmental Pollution Due to Non-Biodegradable Plastics, a Review
Biodegradable plastics are a potential sustainable alternative to conventional petrochemical-based non-degradable plastics. Due to their lightweight, flexibility, durability, versatile applications, chemical inertness, electrical and heat insulation, and conductivity, plastics have become an essential material for many industries, with annual production currently exceeding 450 million tons. However, these materials are non-biodegradable, leading to detrimental consequences such as the formation of microplastics from improper disposal and the generation of toxic gases, including furans, dioxins, mercury, and polychlorinated biphenyls, from burning plastic waste. This results in environmental pollution, affecting land, water bodies, and the atmosphere. In response, studies where the focus has been on creating bio-degradable polymers such as polylactic acid, polyhydroxy alkanoates, Polycaprolactone, Poly(butylene adipate-co-terephthalate), and Polybutylene succinate, which were extracted from renewable resources or chemically modified as biodegradable polymers. Biodegradable polymers exhibit a wide range of properties and can now be modified to be used in various applications suitable for substituting some conventional plastic products. Thus, the article highlights the critical issue of environmental pollution caused by non-biodegradable plastics and provides a comprehensive overview of the synthesis processes, properties, novel applications, and challenges associated with the use of biodegradable plastics.
Article
28 November 2024A Review of the Energy Policy in Greece in the Last 50 Years and Its Implications for Prosperity
This paper elucidates the development of electricity production and distribution in Greece from the 1950s to date, in correlation with national and European energy policy. During this period, Greece experienced a multifaceted energy transition, including both the transition of ownership of energy generation companies from public to private and a transition from an energy mix in which coal (lignite) served as a major and inexpensive resource to a mix in which wind power, solar power and natural gas gained a primary role, but with high costs for energy generation. The correlation between electrical energy consumption and economic growth is explored in this context, revealing an increase in consumption before the 2009 recession and a decline thereafter. The study investigates the correlation between escalating electricity prices and legislative dependencies that mandated the purchase of wind- and solar-generated electricity at exorbitant rates, the closure of cost-effective lignite units, and the reliance on natural gas—a commodity susceptible to geopolitical shifts. It also shows that, given the structure of the Greek energy mix, the increase in the share of wind and solar energy in the mix is directly related to the increase in the price of electricity. Highlighting the importance of energy costs for prosperity, this paper underscores, through the detailed review of the Greek energy “landscape”, that the major determinants of electricity prices are both the accessibility to natural resources but also their proper and judicious management.

Article
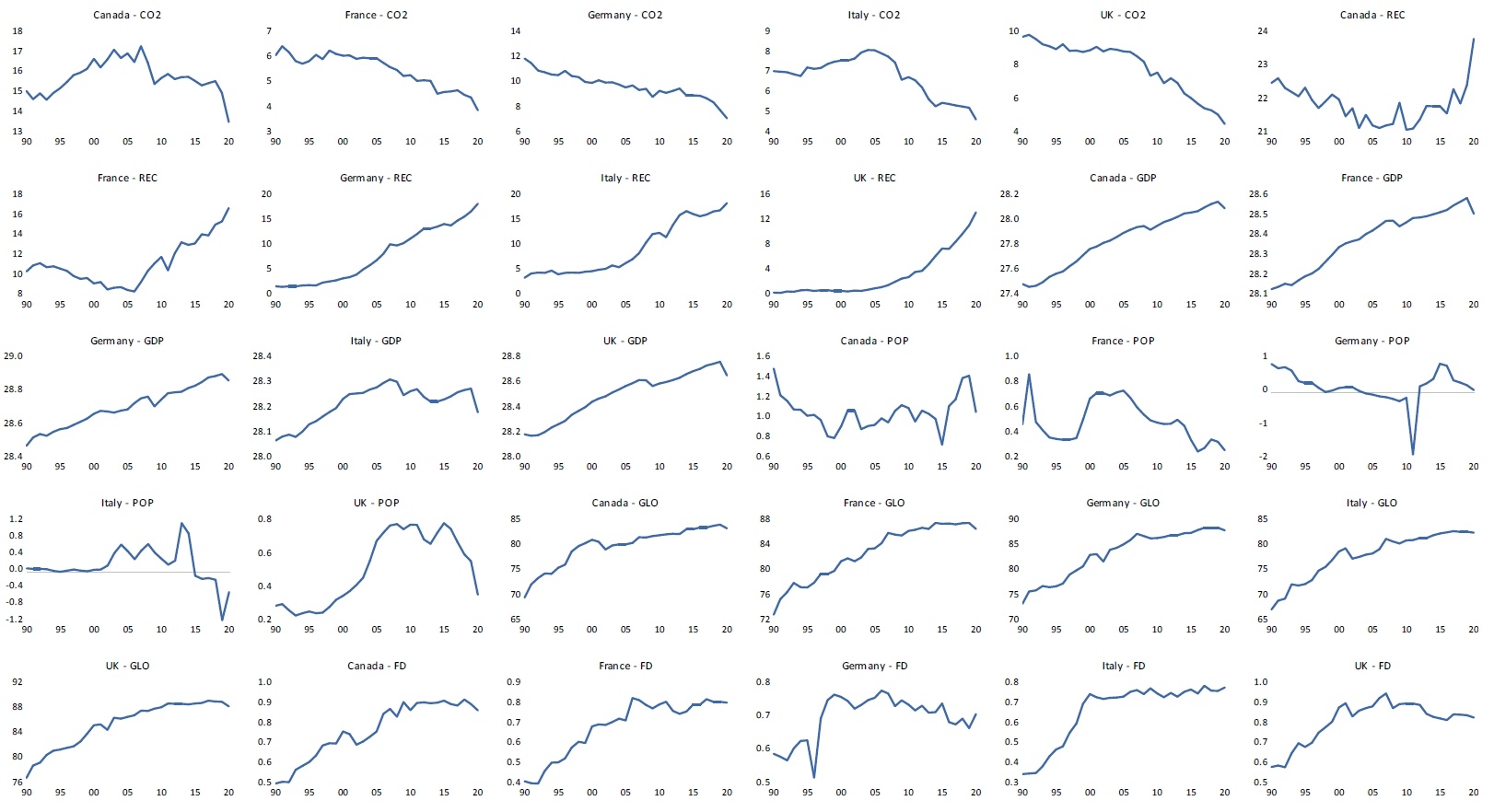
21 November 2024The Impact of Renewable Energy Consumption, Economic Growth, Globalization, and Financial Development on Carbon Dioxide Emissions: Evidence from Selected G7 Economies
The aggregate upsurge in carbon dioxide emissions (CO2) witnessed through environmental degradation and global climate change is a call for great concern. This, therefore, calls for the enactment, utilization and implementation of provisions and policies geared towards curbing this global economic bad without impeding global economic growth rates. This study ascertains the extent to which renewable energy consumption (REC), economic growth (GDP), population growth (POP), globalization (GLO), and financial development (FD) affect carbon dioxide emissions (CO2) in selected G7 economies (France, Germany, Canada, Italy, and the United Kingdom) from 1990–2020. The Dynamic Fixed Effect Autoregressive Distributive Lag (DFE-ARDL) and the Pooled Mean Group ARDL (PMG-ARDL) methods were employed for analysis. The empirical findings for DFE-ARDL showed that REC, GDP, and POP have an adverse association with CO2 in the long-term. However, in the short-term, REC and FD improve the environment, while GDP and POP drive CO2. It is observed that the result for REC in the short and long-run is consistent. The PMG-ARDL results revealed that REC and GLO negatively affect CO2 in the long-run, and in the short-run, GDP spurs CO2, while FD reduces it. The result summary of both methods employed demonstrates that REC, GLO, and FD benefit the environment. At the same time, GDP and POP harm the environment in the short-run but reduce CO2 in the long-run. Conclusively, the research recommends increasing the utilization of renewable energy and policies that enable economic growth and CO2 to move in the opposite direction.
Perspective
09 September 2024Social, Ecological and Economic Synergies of Forests for Sustainability Contradict Projects Involving Large-Scale Deforestation for Energy Production
Good projects and solutions aiming at sustainable development must repair the damage done in past decades by being explicitly designed and monitored to achieve synergetic benefits for the environment and society. We identify environmental, social and economic aspects of sustainability in which enlightened forest management can increase the fulfillment of human and ecological needs and hence the quality of life of present and future generations. Projects aiming at energy production and profits at the cost of biodiversity, nature protection, and human health and well-being are therefore questionable and increasingly socially and politically unacceptable—especially where the viability of alternative options with better social and ecological footprints can be easily demonstrated. This is also true for renewable energy projects. The perspective presented here demonstrates how ostensibly renewable energy projects in natural areas, such as large-scale wind and solar power plants in traditional forests, which are planned, for example, in Germany, may be detrimental to ecological and social sustainability. Forests cut down for such projects are “non-renewable” within reasonable time-scales left to stabilize our climate and ecosystems. Such projects also impair the credibility of the proclaimed role model character and sustainability leadership of Global North countries, which can lead to negative implications for the protection of forests in tropical countries.
Review
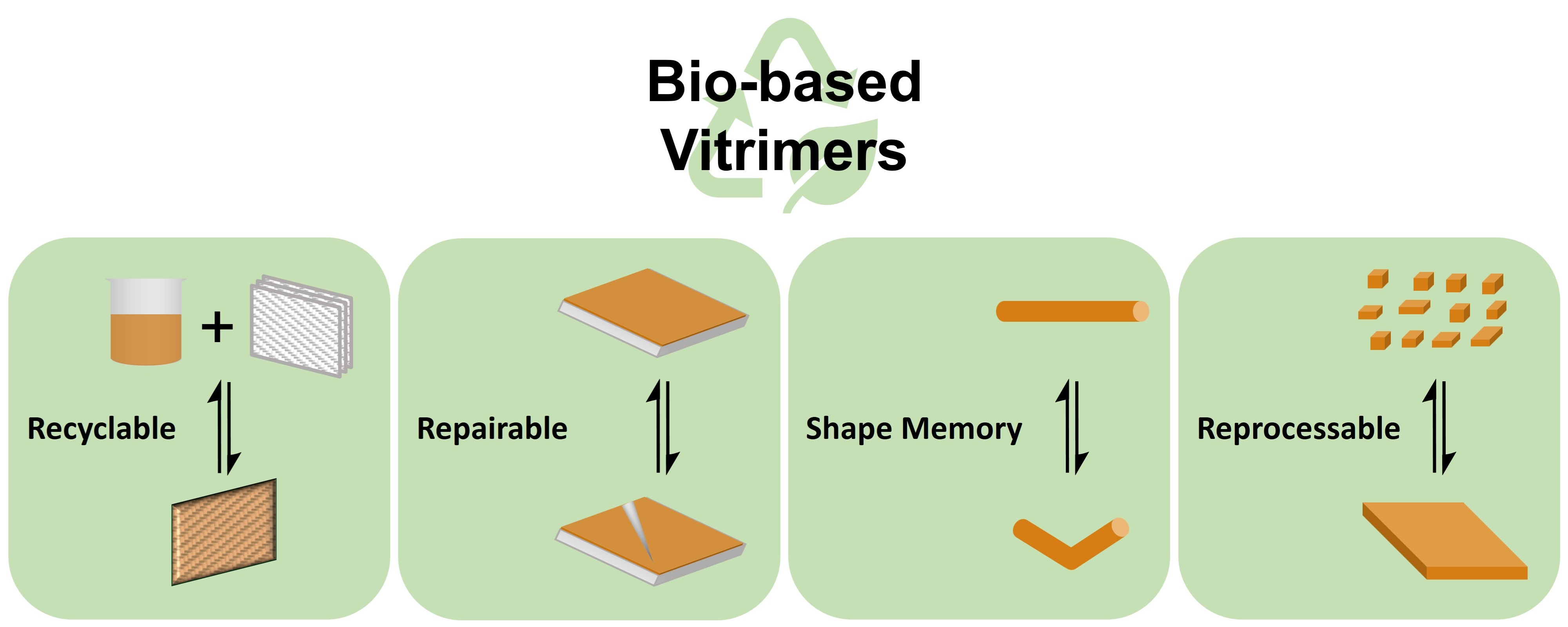
14 June 2024Biobased Vitrimers: A Sustainable Future
Vitrimers are crosslinked polymers containing dynamic covalent linkages. Because of their crosslinked structure, they are stable as thermosets at their service temperatures. At high enough temperatures, dynamic exchange reactions occur and rearrange the polymer network, thus vitrimers become malleable and reprocessable like thermoplastics. The dynamic covalent bonds can also undergo dissociative cleavage reactions under specific conditions, so vitrimers are inherently degradable. To achieve a sustainable future, various biomass resources have been used as raw materials in vitrimer preparation. This review summarizes recent developments in biobased vitrimers and highlights their preparation methods. The limitations of current biobased vitrimers are also discussed.
Article
13 June 2024Optimizing Performance and Design Simulation of a 100 KW Single Rotor Horizontal Axis Wind Turbine
As wind energy becomes increasingly vital in global energy strategies, optimizing wind turbine design is essential. This research focuses on the development of a 100 kW single rotor horizontal axis wind turbine (HAWT) tailored to meet the energy needs of Jamshoro, Pakistan. The turbine design leverages SolidWorks for structural modeling and is validated through comprehensive simulations using ANSYS and Q-Blade. Operating at an optimal wind speed of 6.9 m/s, the turbine achieves maximum efficiency, as indicated by the highest power factor. This efficiency translates to an estimated power output of approximately 100 kW, suitable for common household consumption. The study integrates regional climatic data and wind conditions to enhance turbine performance and durability. The findings offer a sustainable energy solution for Jamshoro, contributing to Pakistan’s renewable energy infrastructure and addressing local energy demands effectively. The focus of this study will be Jamshoro, a region in Pakistan as a case study. The software simulations will consider a variety of elements, including as wind speeds, variable loads, and environmental factors unique to the chosen region (Jamshoro). This research proposes a sustainable solution for addressing the energy demands in Jamshoro by integrating accurate data based on software analysis with real-world concerns, adding to the larger goal of developing sustainable sources of energy in Pakistan.
Article
06 May 2024Assessing Energy Emissions and Environmental Impact of Wool Processing: A Case Study of an Indian Textile Mill
The objective of this study is to investigate and analyze the effect of varying sources of energy inputs and their impact on carbon emissions during wool fiber processing. The method involved industrial visits to the textile wool processing mill and interaction with the manufacturing as well as commercial sourcing teams to gather relevant data. The results and outcome of this analysis indicate that wool wet processing is responsible for a significant carbon emission of about 0.031 tCO2e/unit of production. Coal as a source of energy has the highest carbon emission 0.066 tCO2e/product, while the use of biomass and Pressurized Natural Gas (PNG) had significantly lower CO2 emissions. Further, this study evaluated the scope 1 and scope 2 category emissions produced at the wool processing stage which accounted for 56303.2 tCO2e and 1817.10 tCO2e respectively.

Article
13 March 2024The Potential of Salinity Gradient Energy Using Reverse Electrodialysis to Generate Electricity for Seawater Desalination Plants, an Example from Western Australia
Seawater desalination plays a vital role in addressing the increasing global demand for freshwater. However, the energy-intensive nature of desalination processes and the generation of brine by-products pose environmental challenges. In Western Australia (WA), approximately 48% of freshwater is supplied by two seawater desalination plants employing the energy-intensive seawater reverse osmosis (SWRO) method. These plants are powered by a combination of renewable and conventional energy sources. Typically, the most efficient approach for desalination plants involves a blend of renewable energy sources. Salinity gradient energy (SGE) harnessed through the reverse electrodialysis (RED) system, which derives energy from mixing waters with varying salinities, has emerged as a potential solution. RED utilizes ion-exchange membranes to convert the chemical potential difference between two solutions into electric power. The net specific energy of SGE, calculated based on the Gibbs free energy associated with mixing seawater and wastewater, is estimated at approximately 0.14 kWh per cubic metre of brine for SWRO desalination plants. The combined SGE potential of WA’s two desalination facilities theoretically amounts to approximately 87.4 MWh of energy. However, due to the inherent limitations of the RED system’s current energy efficiency, only about 2.5% of the desalination plant’s energy requirements can be met through this technique. This paper addresses a significant gap in the literature by analyzing the technical and economic constraints of utilizing salinity gradient energy (SGE) through the reverse electrodialysis (RED) system for seawater desalination plants. This marks the first examination of its kind, shedding light on both the technical feasibility and economic challenges of SGE-RED application in this context. The scientific contribution lies in its innovative approach, integrating technical and economic perspectives to provide an understanding of SGE-RED technology’s potential drawbacks and opportunities. By identifying and tackling these challenges, this paper aims to pave the way for optimizing SGE-RED systems for practical implementation in seawater desalination plants.

Article
20 February 2024Wind Influence on the Electrical Energy Production of Solar Plants
Solar energy, as a clean source of energy, plays a relevant role in this much desired (r)evolution. When talking about photovoltaics, despite the multiple studies on parameters that affect the panels operation, concrete knowledge on this matter is still in an incipient stage and precise data remains dispersed, given the mutability of outer factors beyond technology-related properties, hence the difficulties associated with exploration. Wind is one of them. Wind loads can affect the temperature of photovoltaics, whose efficiency is reduced when higher temperatures are reached. The viability of wind as natural cooling mechanism for solar plants and its influence on their electrical energy production is studied in this research work. Some appropriate results were achieved: depending on the module temperature prediction model used and on the photovoltaic technology in question, solar panels are foreseen to be up to approximately 3% more productive for average wind speeds and up to almost 7% more productive for higher speeds. Taking into consideration that wind speed values were collected in the close vicinity of the modules, these results can be proven to be even higher. That being said, this article contributes with accurate insights about wind influence on electrical energy production of solar plants.
