Found 6 results
Review
13 January 2025Comparative Analysis of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis and Progressive Pulmonary Fibrosis: Epidemiology, Pathophysiology, Clinical Features, Diagnosis and Treatment
Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) is a chronic fibrosing interstitial disease of unknown origin, characterized by radiological and histological features consistent with usual interstitial pneumonia (UIP). It is marked by a progressive worsening of dyspnea and a decline in lung function. Both IPF and PPF are comparable because they have poor prognoses with a median survival time from diagnosis of around 2–4 years without antifibrotic therapy. This review shows the main specific characteristics and differences of epidemiology, pathophysiology, clinical and radiological features, treatment, and prognosis of IPF and PPF.
Meeting Report
04 December 2024Progress and Gaps in Respiratory Disease Research and Treatment: Highlights of the IRM 2024 in Shanghai
Respiratory diseases pose a major public health challenge globally, necessitating collaborative efforts between basic researchers and clinicians for effective solutions. China, which is heavily impacted by a broad spectrum of respiratory disorders, has made notable strides in both research and clinical management of these diseases. The International Respiratory Medicine (IRM) meeting was organized with the primary goal of facilitating the exchange of recent research developments and promoting collaboration between Chinese and American scientists in both basic and clinical research fields. This article summarizes key insights from IRM2024, held in Shanghai, where a wide range of topics were discussed, including lung tissue development, disease mechanisms, and innovative therapeutic strategies. By integrating perspectives from basic, translational, and clinical research, IRM2024 highlighted recent advancements, addressed persistent challenges, and explored future directions in respiratory science and clinical practice. The insights gained from IRM2024 are poised to be pivotal in shaping future research and therapeutic approaches, further reinforcing the global commitment to enhancing respiratory health and improving patient outcomes.
Article
26 November 2024Utilization of High Intensity Statins in Patients Hospitalized for Myocardial Infarction
High intensity statin (HIS) therapy decreases LDL cholesterol and risk of recurrent cardiovascular events after acute myocardial infarction (MI). Recognizing the therapeutic significance of HIS, the ACC/AHA cholesterol treatment guidelines have recommended HIS for all patients following acute MI since 2013.The authors sought to define factors that result in continued underutilization and limited adherence to HIS among individuals post MI. This is a retrospective observational analysis of patients who had a diagnosis of MI between 2013 and 2018 at a single, large academic medical center. There was a significant increase in HIS prescriptions upon discharge after MI following, versus prior to 2013. Within the first year of guideline change (2013–2014), only 35.3% of patients with MI were discharged on a HIS compared to 80.1% in 2018. There was no significant difference between race or gender regarding HIS utilization. However, older age predicted a lower likelihood of being appropriately discharged on HIS. The use of statin therapy prior to hospitalization decreased the probability of being appropriately up titrated to HIS on discharge. Strikingly, HIS use was associated with a reduction in the 30-day readmission rate (4.7% versus 6.8%). Increased age was associated with lower rates of HIS use, which could stem from prior statin exposure uncovering titrational statin intolerance prior to the index event, a process that would be much less likely in younger patients, who tend to be statin naive. Although HIS have historically been underutilized in Blacks, this was not observed in the current study. Individuals discharged on HIS had lower readmission rates; while confounding factors separate from a pure treatment effect of HIS attenuating readmission rate may be represented, this remains a key finding underscoring the benefits of statin therapy in lowering societal burden of cardiovascular disease and associated costs.

Review
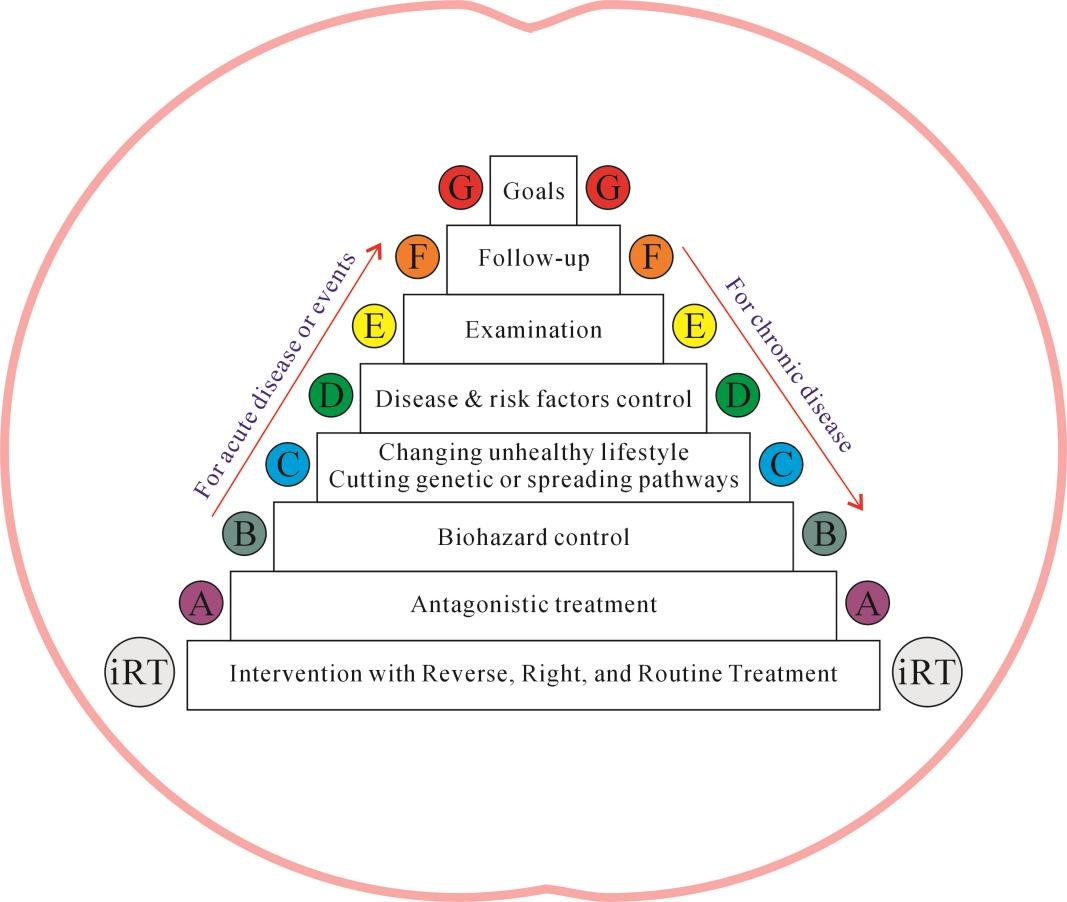
27 August 2024A Novel Comprehensive Program Combining Optimal Medical Treatment with Lifestyle Modification for Type 2 Diabetes
There are more and more individuals with type 2 diabetes (T2D) in the globe. It’s a huge burden of public health and a great challenge in clinical due to a high linkage with atherosclerosis, cardiovascular disease (CVD), stroke, and cancer. However, little is known about a comprehensive program of management and self-management of T2D. This article introduces briefly the current status in T2D and an updated classical standardized comprehensive program which combines optimal medical treatment (OMT) (the glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists, the sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors, and the ultralong-acting, once-daily basal insulin) with lifestyle modification, that is, intervention of RT-ABCDEFG (iRT-ABCDEFG) for control and prevention of T2D, and discusses its advantages and prospects. As an effective comprehensive program and strategy for interventions of diabetes, this program can be used as a reversible, right, and routine treatment. Several pivotal goals including less major adverse cardiocerebrovascular events (MACCE) and diabetic complications, less medical costs, longer life expectancy, lower morbidity and mortality, and higher quality of life, will be realized by consistently practicing this program due to early diagnosis, OMT, and lifestyle modification for overall prevention. All in all, since T2D highly links to CVD and cancer, as well as other MACCE, this novel iRT-ABCDEFG program is very helpful in comprehensive management and self-management of T2D and worth recommending for further application and health care of T2D due to better clinical efficacy and cost-effective relationship.
Article
07 October 2023Comprehensive Evaluation of Sustainable Treatment Technology of Oily Sludge Based on AHP-FCE
Oil is an unsustainable energy since it is non-renewable. However, oil may not be completely replaced in a short time, so the environmental problems caused by the oil development still require our attention. The oily sludge is a kind of hazardous waste produced during the oil development. To reduce the environmental impact caused by oily sludge, low-carbon and sustainable treatment technologies need to be selected. The incineration, chemical extraction and thermal desorption are common technologies for treatment of oily sludge. We calculated the carbon emissions of these technologies. Then the index evaluation system of oily sludge treatment technology was established with the environmental, economic, social, and technical factors. And the weight of evaluation index was determined by the analytic hierarchy process (AHP). Through the investigation of industry experts, we evaluated the treatment technologies by the fuzzy comprehensive evaluation method (FCE). The results showed that the carbon emissions of incineration are 42.70 t CO2-eq/t which is the highest. Meanwhile, it is 4.80 t CO2-eq/t and 0.10 t CO2-eq/t for chemical extraction and thermal desorption, respectively. The comprehensive scores of incineration, chemical extraction and thermal desorption were 4.59, 5.16 and 4.95, respectively. Therefore, the chemical extraction technology is an optimal treatment technology for oily sludge with the relatively low carbon emission and the highest comprehensive technical score. At the same time, the thermal desorption technology has strong application potential with the lowest carbon emissions. This result provides a reference for achieving clean and sustainable energy development processes.

Perspective
07 March 2023Pulsed Ultraviolet C as a Potential Treatment for COVID-19
Currently, low dose radiotherapy (LDRT) is being tested for treating life-threatening pneumonia in COVID-19 patients. Despite the debates over the clinical use of LDRT, some clinical trials have been completed, and most are still ongoing. Ultraviolet C (UVC) irradiation has been proven to be highly efficient in inactivating the coronaviruses, yet is considerably safer than LDRT. This makes UVC an excellent candidate for treating COVID-19 infection, especially in case of severe pneumonia as well as the post COVID-19 pulmonary fibrosis. However, the major challenge in using UVC is its delivery to the lungs, the target organ of COVID-19, due to its low penetrability through biological tissues. We propose to overcome this challenge (i) by using pulsed UVC technologies which dramatically increase the penetrability of UVC through matter, and (ii) by integrating the pulsed UVC technologies into a laser bronchoscope, thus allowing UVC irradiation to reach deeper into the lungs. Although the exact characteristics of such a treatment should yet to be experimentally defined, this approach might be much safer and not less efficient than LDRT.
