Found 297 results
Article
08 February 2025Degradation of Metformin Hydrochloride and Glibenclamide by Several Advanced Oxidation Processes
The degradation of metformin hydrochloride (MET) and glibenclamide (GLI), widely used anti-diabetics, was performed using an electrochemical advanced oxidation process, namely electro-Fenton, and several other Advanced Oxidation Processes (AOPs) of photocatalytic nature, like UV/H2O2, UV/persulfate, and UV/TiO2. The electrochemical behavior of the drugs was first characterized by cyclic and differential pulse voltammetry. The data implied that both drugs present quasi-reversible oxidation. The effect of the applied current and the airflow in the electrogeneration of hydrogen peroxide was studied. Degradations of 60% of the initial drug were obtained for aqueous solutions of 30 mg·L−1 of MET and 15 mg·L−1 of GLI by using photoelectron-Fenton conditions with 1.0 A of current and a Fe2+ concentration of 3.5 mg·L−1, although the removal of MET required 60 min of reaction while for GLI only 45 min were needed. The mineralization (organic carbon removal) percentages after 60 min of treatment were 20%and 30% for electro-Fenton and photo electro-Fenton processes, respectively. For UV/H2O2, UV/persulfate, and UV/TiO2 treatments of MET solutions, the order of observed degradations was UV/PS > UV/H2O2 > UV/TiO2 with maximum values of drug removal of 30% after 60 min of irradiation. This efficiency is lower than the removal observed with the electro-Fenton reaction. For GLI the order of degradation efficiency was UV/PS > UV/TiO2 > UV/H2O2, with maximum values of drug removals of 99.5% after only 10 min of irradiation. This performance is clearly better that in the case of electro-Fenton or photo-electro-Fenton. The removals of the two drugs when dissolved in chemical matrices that mimic real hospital wastewaters and seawater were also studied. They showed a clear dependency on the pharmaceutical of choice. While the degradation of MET was hampered by the presence of other chemicals in the two water matrices, GLI removal was remarkable, pointing towards a possible application in real wastewaters.
Review
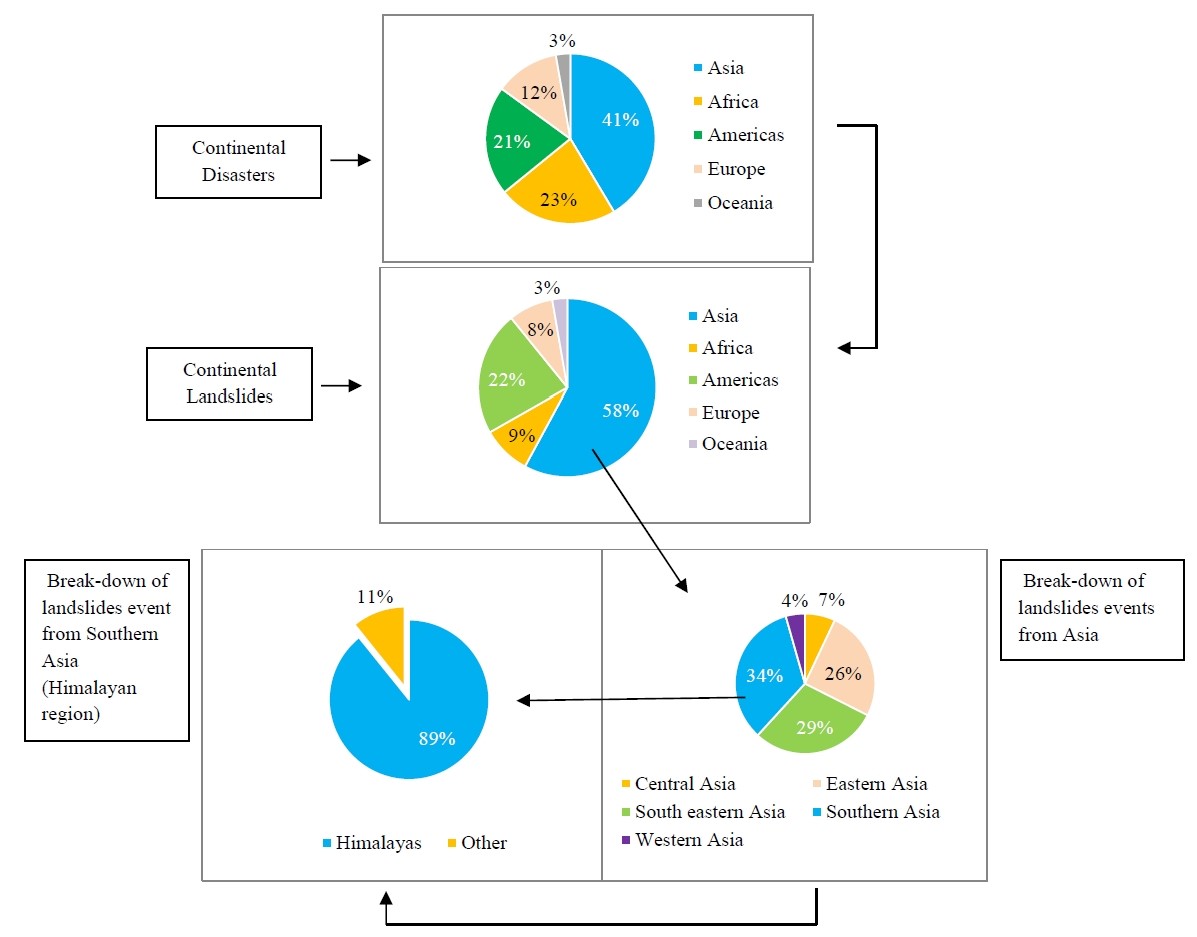
05 February 2025Landslides in the Himalayas: A Comprehensive Review of Hazards, Impacts, and Adaptive Strategies
The Himalayas, known as the ‘Third Pole’, are facing an escalating crisis due to landslides driven by climate change and human activity. The settlements in the Himalayas are increasingly vulnerable due to a surging prevalence of landslides. This systematic review investigates the repercussions of landslide hazards on the inhabitants of the Himalayan Arc and explores the causes and adaptive strategies focusing on the period from 2002 to 2022. Data dealing with the impact of landslides were systematically extracted from Scopus, Web of Science, Pascal & Francis, Science Direct, and Google Scholar databases. The review adhered to the prescribed guidelines of reporting standards for systematic evidence systems (ROSES). The frequency and severity of landslides in the Himalayas are notably high, potentially exceeding those observed in other global regions, due to a combination of specific geological, climatic, and human-induced factors. Thematic categorization identifies that the Himalayan communities confront a multifaceted challenge involving social, natural, economic, human, and physical losses induced by landslides. However, they lack adaptive capacity. The origins of these landslides are diverse, emanating from natural forces, geological phenomena, and human activities within the Himalayas. The review contributes to the understanding of the profound impact that landslides inflict upon the Himalayan region. By consolidating data from diverse databases, the study illuminates the urgent need for comprehensive strategies to bolster resilience and mitigate the escalating threats posed by landslides in this vulnerable geographic expanse.
Review
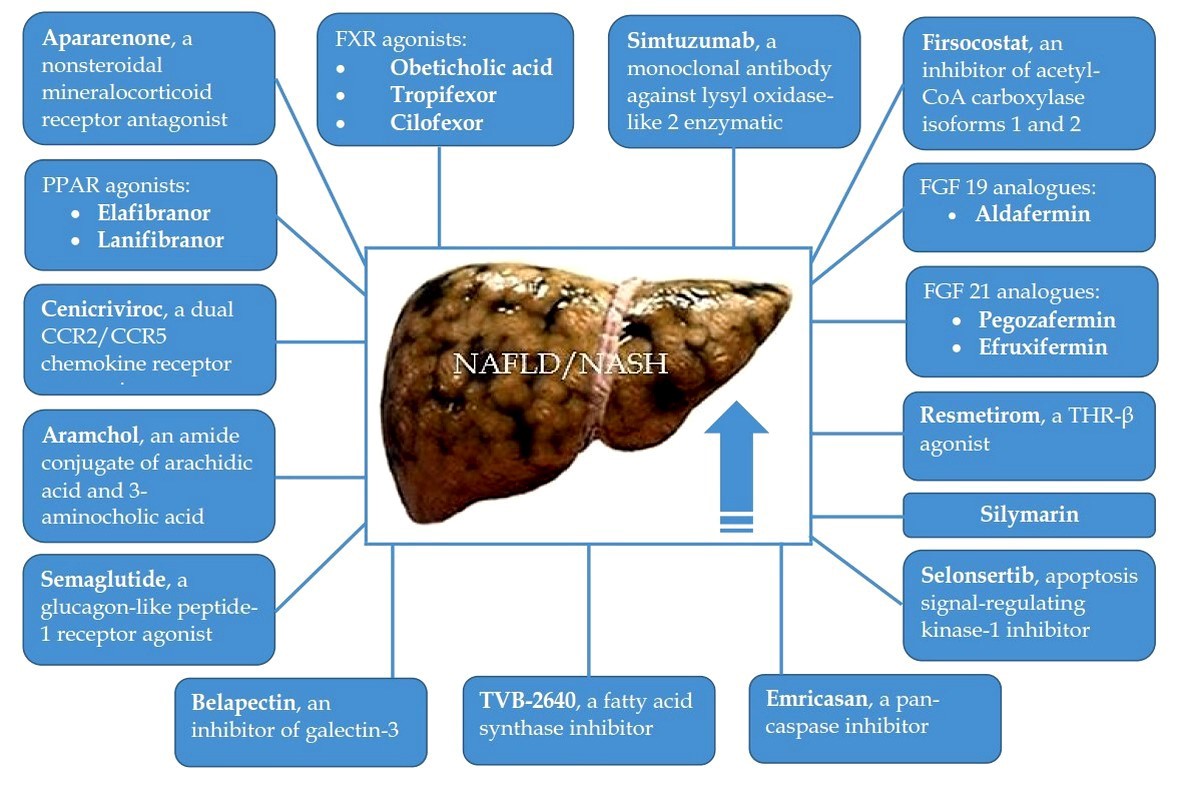
05 February 2025Perspectives of Drug Therapy for Non-Alcoholic Steatohepatitis-Related Liver Fibrosis
Liver fibrosis (LF) is an adverse event of the natural course of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) since its progression leads to the development of liver cirrhosis, which is associated with poor prognosis. In addition, there is evidence that the presence of advanced LF may be a strong independent predictor and risk factor for cardiovascular disease in NASH patients, which is the main cause of their death. Based on the severity of the problem, the study and implementation of drugs for the treatment of NASH-related LF is extremely necessary. The purpose of this review was to describe phase II and III randomized controlled trials (RCTs) evaluating the efficacy and safety of drug therapy for NASH-related LF. To date, the possibilities for pharmacological treatment of NASH-related LF are very limited. However, in recent years, several drugs have been evaluated in NASH patients with LF (F2–3), and in some cases with compensated liver cirrhosis, in large phase II and III RCTs, and they have shown promise. It can be assumed that drugs that have shown efficacy and safety in phase II and III RCTs will be recommended for testing and confirming practical benefits in phase IV RCTs. Besides, an in-depth study of the cellular and molecular mechanisms of NASH-related LF will contribute to the development of new medications, the introduction of which will expand the possibilities of its drug therapy.
Article
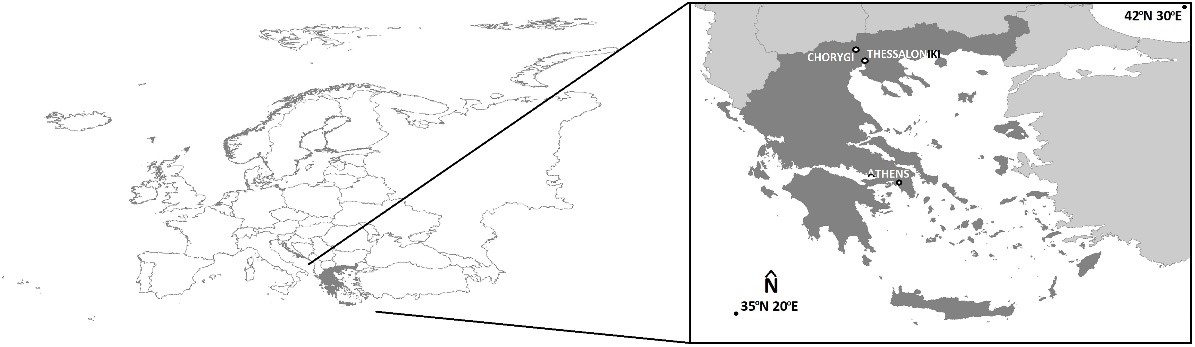
20 January 2025Visible Monuments above and below Ground Level, a Time-Honored Site from the Late Bronze Age to Modern Times
Due to the complex geometry of the monuments, it is often necessary to adapt the image collection process for their mapping. For the optimal mapping of the stronghold of Lazaritsa Chorygi (Greece) and its slopes, vertical, inclined, and horizontal images from different heights were collected using an Unmanned Aircraft System. Thus, for a monument of special archaeological/historical interest and natural beauty, a large set of high-spatial resolution data and final products (digital surface model and orthophotomosaic with spatial resolution 5.6 cm and 2.8 cm, respectively) is available. In addition, in the wider area of the fortified site, military structures (fire trenches, communication trenches, shelters, front and support trenches, and strong points) of the Great War length of 9 km were identified and mapped, which were identified in the 2003 or 2004 Google Earth Pro images, but worryingly are almost absent from the contemporary Google Earth Pro images.
Review
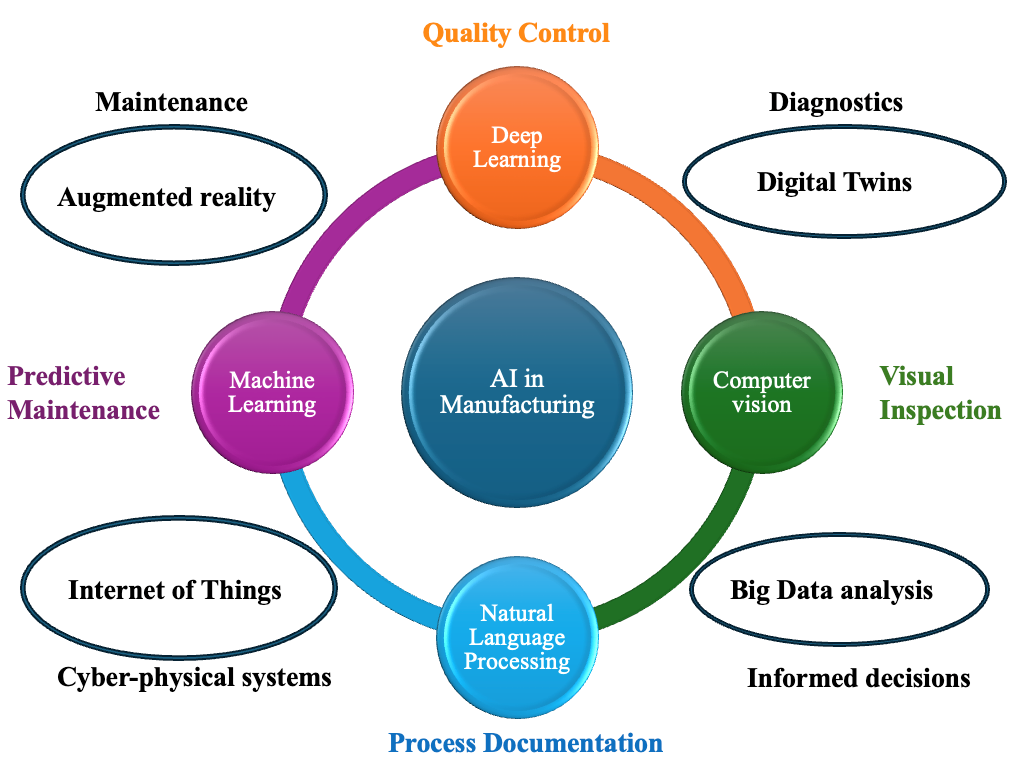
14 January 2025Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning for Sustainable Manufacturing: Current Trends and Future Prospects
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) are transforming manufacturing processes, offering unprecedented opportunities to enhance sustainability and environmental stewardship. This comprehensive review analyzes the transformative impact of AI technologies on sustainable manufacturing, focusing on critical applications, including energy optimization, predictive maintenance, waste reduction, and circular economy implementation. Through systematic analysis of current research and industry practices, the study examines both the opportunities and challenges in deploying AI-driven solutions for sustainable manufacturing. The findings provide strategic insights for researchers, industry practitioners, and policymakers working towards intelligent and sustainable manufacturing systems while elucidating emerging trends and future directions in this rapidly evolving field.
Review
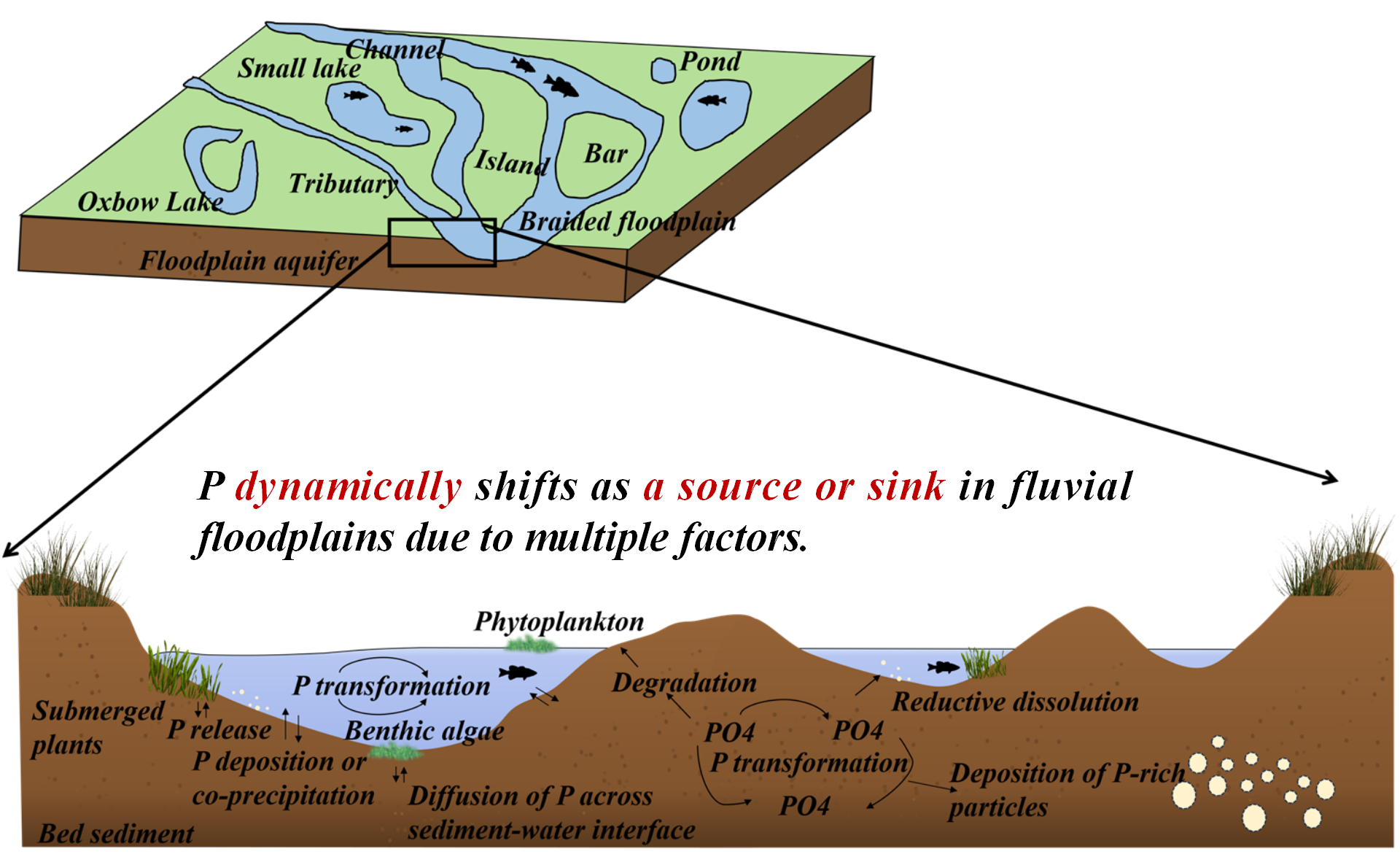
14 January 2025A Review of Phosphorous in Fluvial Floodplains: Source or Sink?
Fluvial floodplains are water-land transitional zones, playing an important role in hydrological and ecological systems. To date, the phosphorus migration and transformation in floodplain sediments remain elusive, which poses a large effect on river nutrient levels and primary productivity. This review summarized the sedimentary characteristics of floodplains and analyzed the spatial differences and temporal variations in phosphorus distribution. We further analyzed their potential change in floodplains under various conditions, determining the sedimentation and mineralization process of phosphorus. Meanwhile, phosphorus in the sediment will experience dynamic fluctuation as a source or sink of fluvial floodplains based on varying factors, including hydrological conditions, climate variations, biological activity, and pedological characteristics. In particular, the productivity and community population in floodplains, like vegetation and fishes, will be primarily associated with the periodic changes in phosphorus through food chain. Lastly, this review provided corresponding perspectives on improving the phosphorus administration in river floodplains based on existing problems. In total, it is anticipated that it will enhance the understanding of phosphorus resources or sink in the fluvial floodplains, contributing to the stability of aquatic ecosystems.
Review
13 January 2025Comparative Analysis of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis and Progressive Pulmonary Fibrosis: Epidemiology, Pathophysiology, Clinical Features, Diagnosis and Treatment
Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) is a chronic fibrosing interstitial disease of unknown origin, characterized by radiological and histological features consistent with usual interstitial pneumonia (UIP). It is marked by a progressive worsening of dyspnea and a decline in lung function. Both IPF and PPF are comparable because they have poor prognoses with a median survival time from diagnosis of around 2–4 years without antifibrotic therapy. This review shows the main specific characteristics and differences of epidemiology, pathophysiology, clinical and radiological features, treatment, and prognosis of IPF and PPF.
Article
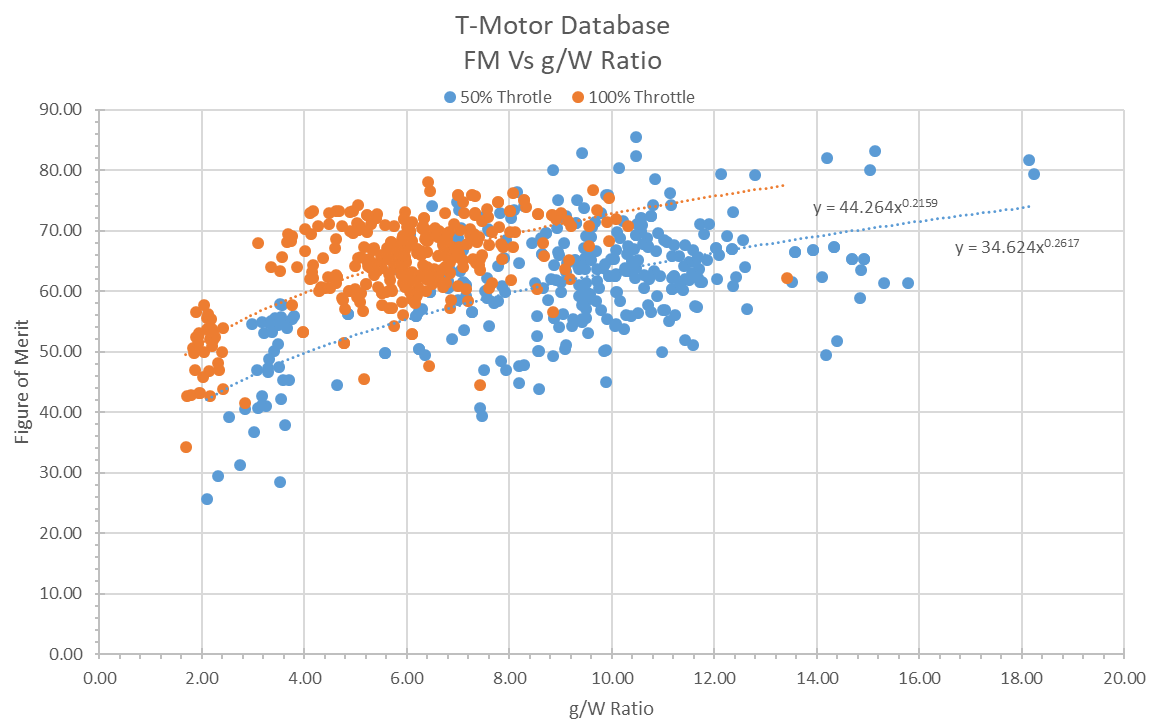
10 January 2025Investigation of the Performance Characteristics of Unequal Co-Axial Rotors
The behaviour of co-axial rotors is well understood, and they are especially practical for large UAVs due to their increased thrust without changing the vehicle footprint. However, for co-axial systems with varying propeller diameters between the two disks, research is more limited. The goal of this paper was to determine an optimal configuration for several different unequal co-axial setups using numerous different propeller combinations and separation ratios. Propellers with diameters of 26 and 29 inches are tested at separation ratios of 0.05 to 0.35. Thrust and power were collected using an off-the-shelf FS15-TYTO thrust stand, with the upstream and downstream propellers running at equal throttles. From this, performance was assessed through efficiency, thrust, and power consumption, and comparisons were made to an ideal combination without losses. The results show that for unequal combinations, the user should place the smaller propeller upstream for greater efficiency, but for maximum thrust capacity, two equal propellers are preferred. When compared to two independent rotors of the same size, a 26″ upstream rotor and a 29″ downstream rotor minimised thrust loss to 16%, compared to 23% for the opposite arrangement. It was also found that the optimal separation ratio is always approximately 0.2.
Article
09 January 2025Advanced Materials: Nature of Strongly Correlated Quantum Spin Liquid in Sr3CuNb2O9
Quantum spin liquids of frustrated magnets are among the most attractive and basic systems in physics. Frustrated magnets exhibit exceptional properties as insulators and metals, making them advanced materials that represent materials for future technologies. Therefore, a reliable theory describing these materials is of great importance. The fermion condensation theory provides an analytical description of various frustrated quantum spin liquids capable of describing the thermodynamic and transport properties of magnets based on the idea of spinons, represented by chargeless fermions filling the Fermi sphere up to the Fermi momentum pF . We show that the low temperature thermodynamic of Sr3CuNb2O9 in magnetic fields is defined by strongly correlated quantum spin liquid. Our calculations of its thermodynamic properties agree well with recent experimental facts and allow us to reveal their scaling behavior, which is very similar to that observed both in heavy-fermion metals and in frustrated magnets or insulators. We demonstrate for the first time that Sr3CuNb2O9 belongs to the family of strongly correlated Fermi systems that form a new state of matter.

Review
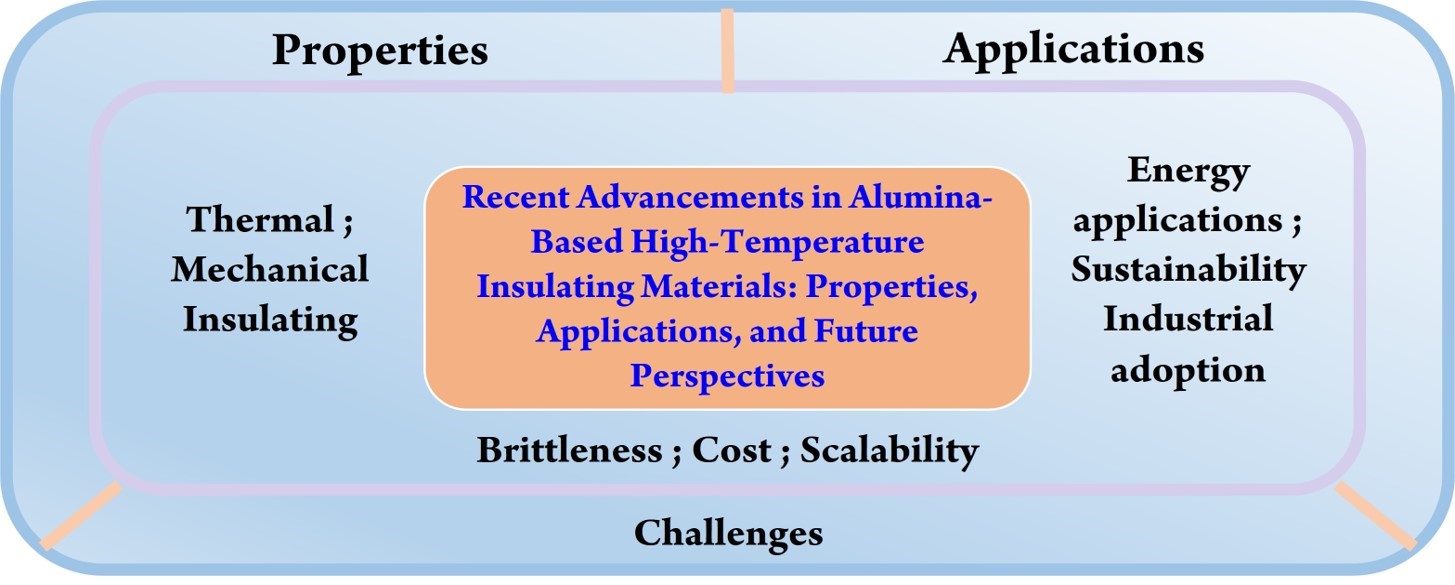
09 January 2025Recent Advancements in Alumina-Based High-Temperature Insulating Materials: Properties, Applications, and Future Perspectives
As a high-temperature thermal insulation material with excellent mechanical properties, alumina (Al2O3)-based materials hold significant potential for applications in aerospace, advanced manufacturing, automobiles, industrial furnaces, and other fields. However, the inherent brittleness of alumina poses a limitation to its wider application. Therefore, there is a pressing need to develop alumina-based materials that offer high toughness while retaining superior mechanical properties. This paper begins by exploring the structure of alumina, highlighting its thermal conductivity, insulation, and mechanical properties in high-temperature environments. It then reviews the classification and synthesis methods of alumina-based materials, along with the latest advances in design strategies. Notably, the rational design of alumina composition, structure, and morphology is emphasized as crucial for optimizing material performance, thereby supporting the industrial development and application of these materials in high-tech sectors. Finally, the paper discusses the challenges and evolution of alumina-based materials in real-world industrial applications and suggests potential directions for future development.