Found 5 results
Review
15 November 2024Ion Channels in the Immune Response of Asthma
Asthma is a common respiratory disorder characterized by chronic inflammation of the lower airways, contributing to significant morbidity, mortality, and a substantial global economic burden. It is now understood as a heterogeneous condition, with ongoing research shedding light on its complex immunological underpinnings. Ion channels, which are specialized transmembrane proteins that facilitate ion movement based on electrochemical gradients, play a crucial role in the pathophysiology of asthma. Ion channels regulate essential processes like maintaining epithelial hydroelectrolyte balance and also play a role in modulating immune responses involved in asthma. We discuss the connection between ion channel activity and immune regulation in asthma, focusing on ion channel regulation of immune cell behavior, airway hyperresponsiveness, and inflammation in asthma. Understanding ion channels in asthma could lead to the development of targeted therapies modulating their activity, thereby enhancing disease management and patient outcomes.
Article
04 November 2024Diversity and Meta-Analysis of Microbial Differential Abundance in Nasal Metatranscriptomic Profiles of Asthma
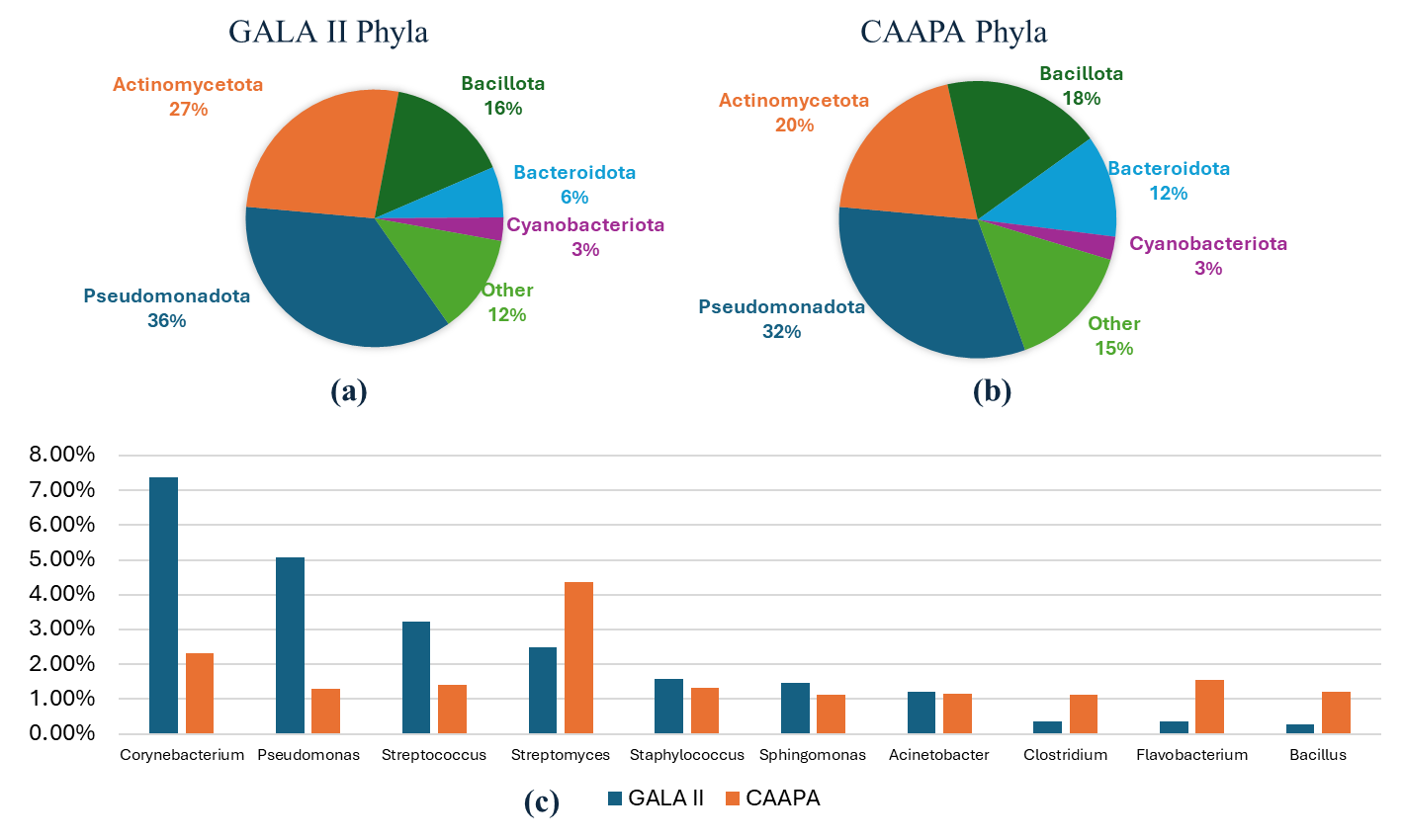
Asthma affects millions worldwide and involves complex genetic, immunological, and environmental factors. The nasal microbiome is increasingly recognized for its role in asthma development, but inconsistent results and small sample sizes have limited a clear understanding. We aimed to clarify the nasal microbiome’s role in asthma using large datasets and meta-transcriptomic analysis. RNA-seq data was analyzed from two large public studies: GALA II (694 children of Puerto Rican heritage; 441 asthmatics, 253 controls) and CAAPA (562 individuals of African ancestry; 265 asthmatics, 297 controls). After quality control and host read removal, microbial reads were annotated using Kraken2. α and β diversity analyses compared microbial diversity between asthmatic and control groups. Differential abundance analysis was conducted separately, controlling for age and sex, with results combined via meta-analysis. We found that asthmatic patients exhibited significantly higher α diversity indices (Shannon, Berger-Parker, Inverse Simpson, Fisher’s) in nasal microbiota compared to controls in GALA II, with similar trends in CAAPA. β diversity analysis showed significant differences in microbial composition in GALA II data. Differential abundance analysis identified 20 species in GALA II and 9 species in CAAPA significantly associated with asthma. Meta-analysis revealed 11 species significantly associated with asthma, including Mycobacterium_tuberculosis. Our study demonstrates increased nasal microbiome α diversity in asthmatic patients and identifies specific microbial species associated with asthma risk. These findings enhance understanding of asthma pathogenesis from the nasal microbiome perspective and may inform future research and therapeutic strategies.
Commentary
18 September 2024Primed Lung−Vagus−Brainstem Circuit by Allergen Triggers Airway Hyperactivity
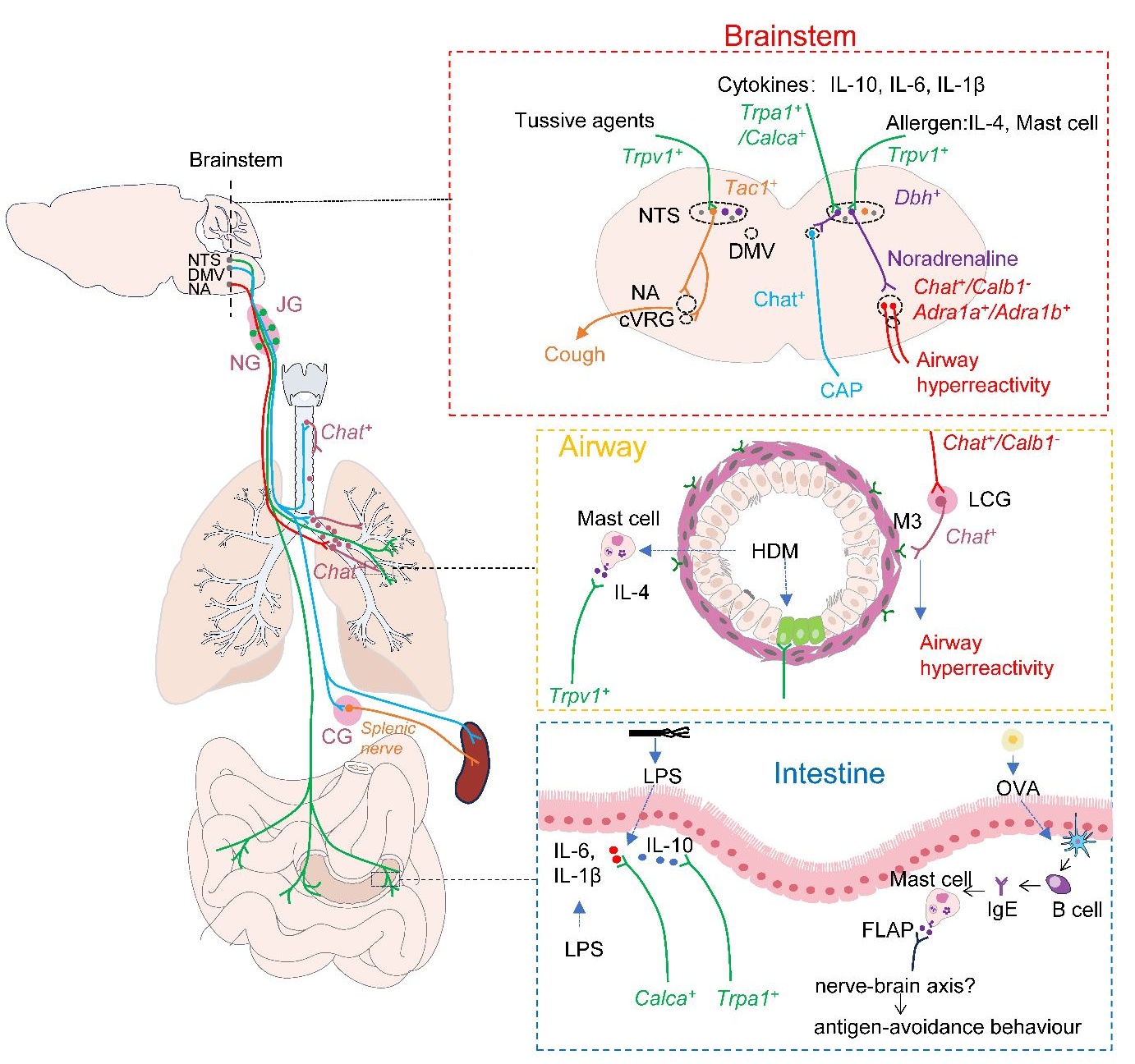
The nucleus of the solitary tract (NTS) is the primary hub for sensing and integrating respiratory information. It integrates input from the vagus and glossopharyngeal nerve. It interacts with other brainstem nuclei, such as the nucleus ambiguus (NA) and the dorsal motor nucleus of the vagus (DMV), to transmit information and initiate a neuroreflex response to respiratory stimuli. In a recent issue of the journal Nature, Su et al. demonstrated that Dbh+ neurons in the NTS can receive signals from vagal Trpv1+ sensory neurons that sense allergen−induced IL−4 production in mast cells and pass the signal to Chat+ neurons in the NA by releasing norepinephrine. Subsequently, NA Chat+ neurons drive allergen−induced airway hyperresponsiveness by projecting onto cholinergic pulmonary ganglia in the lungs. This study not only provides new insights into the regulation of allergen−induced airway hyperresponsiveness by lung−vagus–brainstem interoceptive circuit but also provides us with new strategies to combat asthma.
Review
25 June 2024Solute Carrier Family 26 Member 4 (SLC26A4), A Potential Therapeutic Target for Asthma
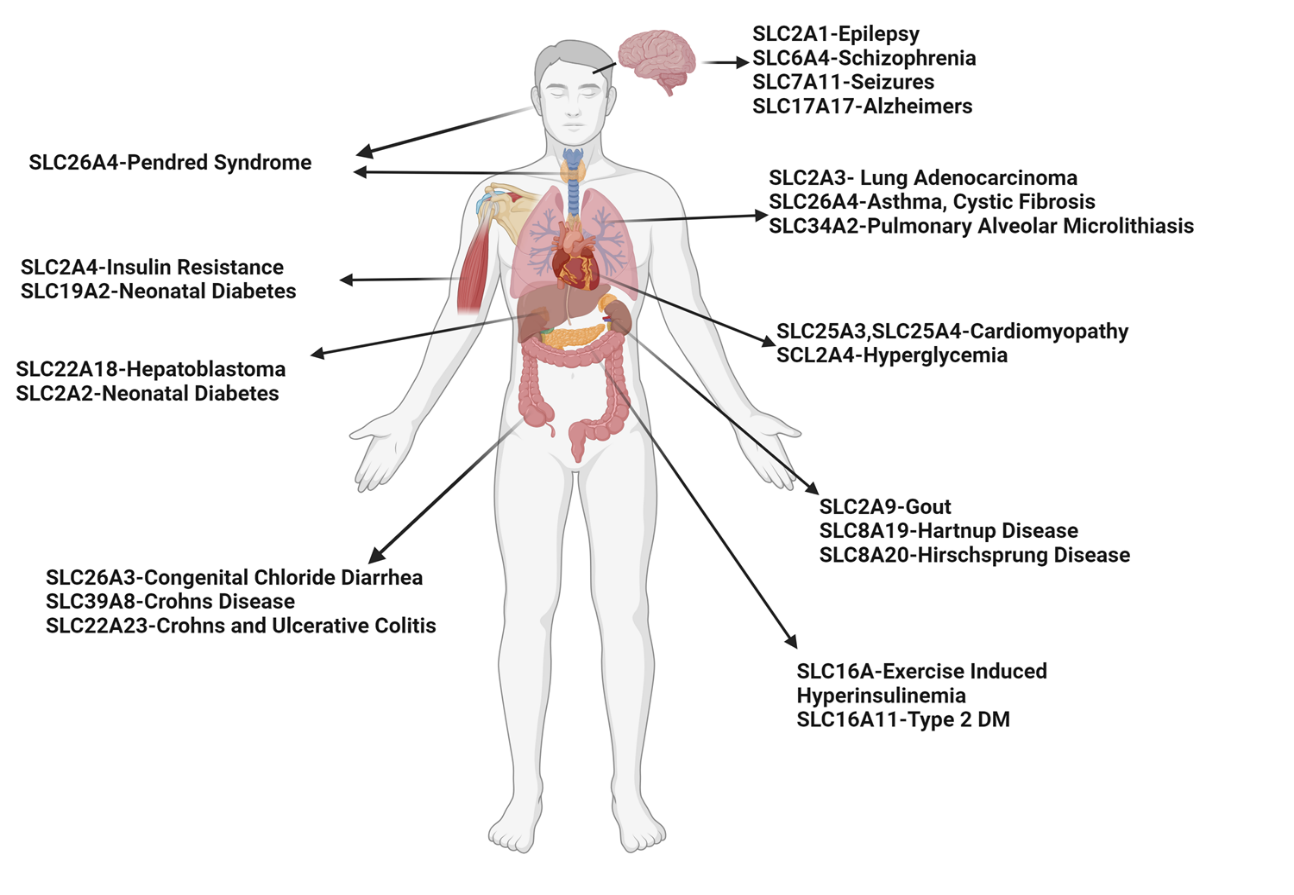
Asthma is a prevalent respiratory condition with multifaceted pathomechanisms, presenting challenges for therapeutic development. The SLC (Solute Carrier) gene family, encompassing diverse membrane transport proteins, plays pivotal roles in various human diseases by facilitating solute movement across biological membranes. These solutes include ions, sugars, amino acids, neurotransmitters, and drugs. Mutations in these ion channels have been associated with numerous disorders, underscoring the significance of SLC gene families in physiological processes. Among these, the SLC26A4 gene encodes pendrin, an anion exchange protein involved in transmembrane transport of chloride, iodide, and bicarbonate. Mutations in SLC26A4 are associated with Pendred syndrome. Elevated SLC26A4 expression has been linked to airway inflammation, hyperreactivity, and mucus production in asthma. Here, we review novel insights from SLC gene family members into the mechanisms of substrate transport and disease associations, with specific emphasis on SLC26A4. We explore triggers inducing SLC26A4 expression and its contributions to the pathogenesis of pulmonary diseases, particularly asthma. We summarize the inhibitors of SLC26A4 that have shown promise in the treatment of different phenotypes of diseases. While SLC26A4 inhibitors present potential treatments for asthma, further research is imperative to delineate their precise role in asthma pathogenesis and develop efficacious therapeutic strategies targeting this protein.
Article
31 March 2024
The Asthma Risk Gene, GSDMB, Promotes Mitochondrial DNA-induced ISGs Expression
Released mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) in cells activates cGAS-STING pathway, which induces expression of interferon-stimulated genes (ISGs) and thereby promotes inflammation, as frequently seen in asthmatic airways. However, whether the genetic determinant, Gasdermin B (GSDMB), the most replicated asthma risk gene, regulates this pathway remains unknown. We set out to determine whether and how GSDMB regulates mtDNA-activated cGAS-STING pathway and subsequent ISGs induction in human airway epithelial cells. Using qPCR, ELISA, native polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis, co-immunoprecipitation and immunofluorescence assays, we evaluated the regulation of GSDMB on cGAS-STING pathway in both BEAS-2B cells and primary normal human bronchial epithelial cells (nHBEs). mtDNA was extracted in plasma samples from human asthmatics and the correlation between mtDNA levels and eosinophil counts was analyzed. GSDMB is significantly associated with RANTES expression in asthmatic nasal epithelial brushing samples from the Genes-environments and Admixture in Latino Americans (GALA) II study. Over-expression of GSDMB promotes DNA-induced IFN and ISGs expression in bronchial epithelial BEAS-2B cells and nHBEs. Conversely, knockout of GSDMB led to weakened induction of interferon (IFNs) and ISGs in BEAS-2B cells. Mechanistically, GSDMB interacts with the C-terminus of STING, promoting the translocalization of STING to Golgi, leading to the phosphorylation of IRF3 and induction of IFNs and ISGs. mtDNA copy number in serum from asthmatics was significantly correlated with blood eosinophil counts especially in male subjects. GSDMB promotes the activation of mtDNA and poly (dA:dT)-induced activation of cGAS-STING pathway in airway epithelial cells, leading to enhanced induction of ISGs.
