Found 14 results
Review
14 March 2025Mechanistic Insights into Photocatalytic WO3 for Hydrogen Generation
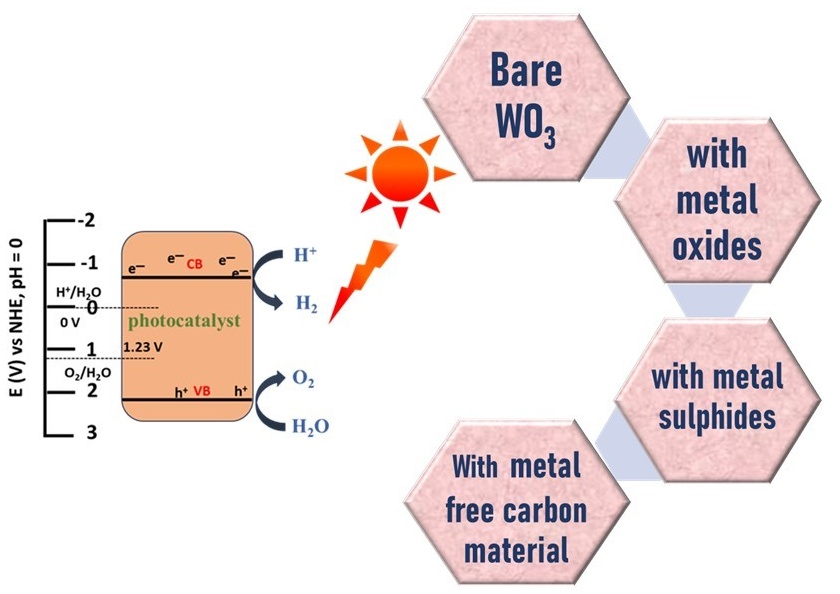
Growing environmental concerns and the limitations of fossil fuel resources have recently led to increased focus on clean and renewable energy sources. Hydrogen (H2) has gained importance as an alternative clean fuel with its potential to become the primary chemical energy carrier. Photocatalytic hydrogen generation offers a capable solution to the energy crisis and has gained significant attention as a renewable energy solution, offering independence from fossil fuels and zero carbon dioxide emissions. Tungsten oxide (WO3) offers to be a promising photocatalyst for Hydrogen Evolution Reaction (HER) with its ability to tune the band gap, robust absorption in the visible spectrum range, steadiness in harsh reaction conditions, low cost, and reduced toxicity. Various synthetic methods can be employed to fabricate photocatalysts with diverse morphologies, sizes, and structures, all of which significantly influence their catalytic performance to varying extents. This review goals to explicitly highlight and discourse the main properties of WO3 and its modifications for photocatalytic HER via different synthesis methods. Modification in WO3 to its corresponding composites, heterojunctions are explicitly explained in this review.
Article
21 February 2025Porous Cu(Mn)-Doped ZnO-MgO Nanocomposites for Photocatalytic and Antibacterial Applications
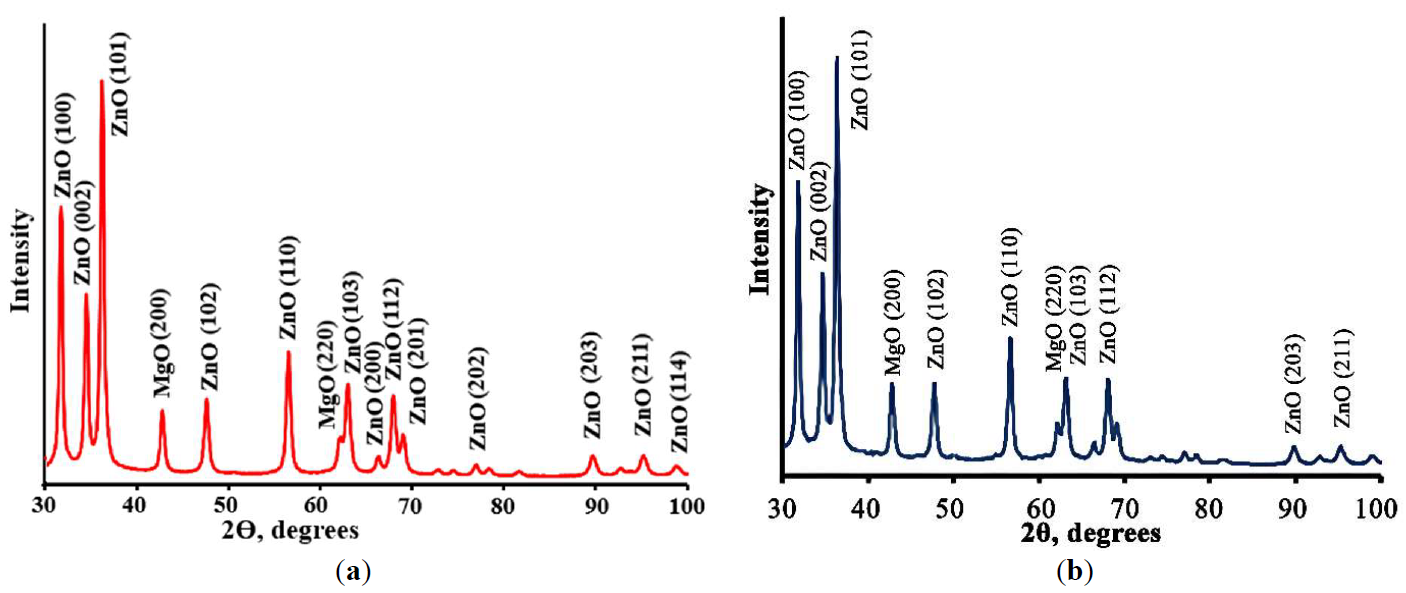
Porous Cu(Mn):ZnO-MgO composites synthesized by polymeric sol-gel method were characterized. The crystal structure, morphology, spectral properties, the ability of the photogeneration of chemically active singlet oxygen under external visible irradiation, photocatalytic and antibacterial properties of porous composites were studied. Obtained composites consist of small ZnO and MgO crystals having size less than 20 nm. It was found that Cu2+ and Mn2+ ions are embedded into the lattices of ZnO and MgO crystals, altering their crystal cell parameters. The band gap values of obtained composites are 3.41 ÷ 3.42 eV which are slightly higher than the band gap of pure ZnO. Prepared materials demonstrate a high ability of photogeneration of chemically active singlet oxygen under blue light (λ = 405 nm) irradiation. It was found that dependencies of the intensity of singlet oxygen photogeneration from the power density of visible irradiation are linear. Photocatalytic decomposition of the diazo dye Chicago Sky Blue in solutions under UV and blue light irradiation proceeds rapidly in the presence of the prepared composites (constants rate of photocatalytic dye decomposition under UV irradiation are 0.024 min−1 and 0.025 min−1 for ZnO-MgO composites doped with Cu and Mn, correspondingly). Porous composites demonstrate superior antibacterial activity against gram-positive bacteria. These materials are promising for practical application in medicine and photocatalytic technologies of air and water cleaning.
Article
17 February 2025Comparative Study of Elastomer Nanocomposites Respectively Containing SWCNTs and MWCNTs
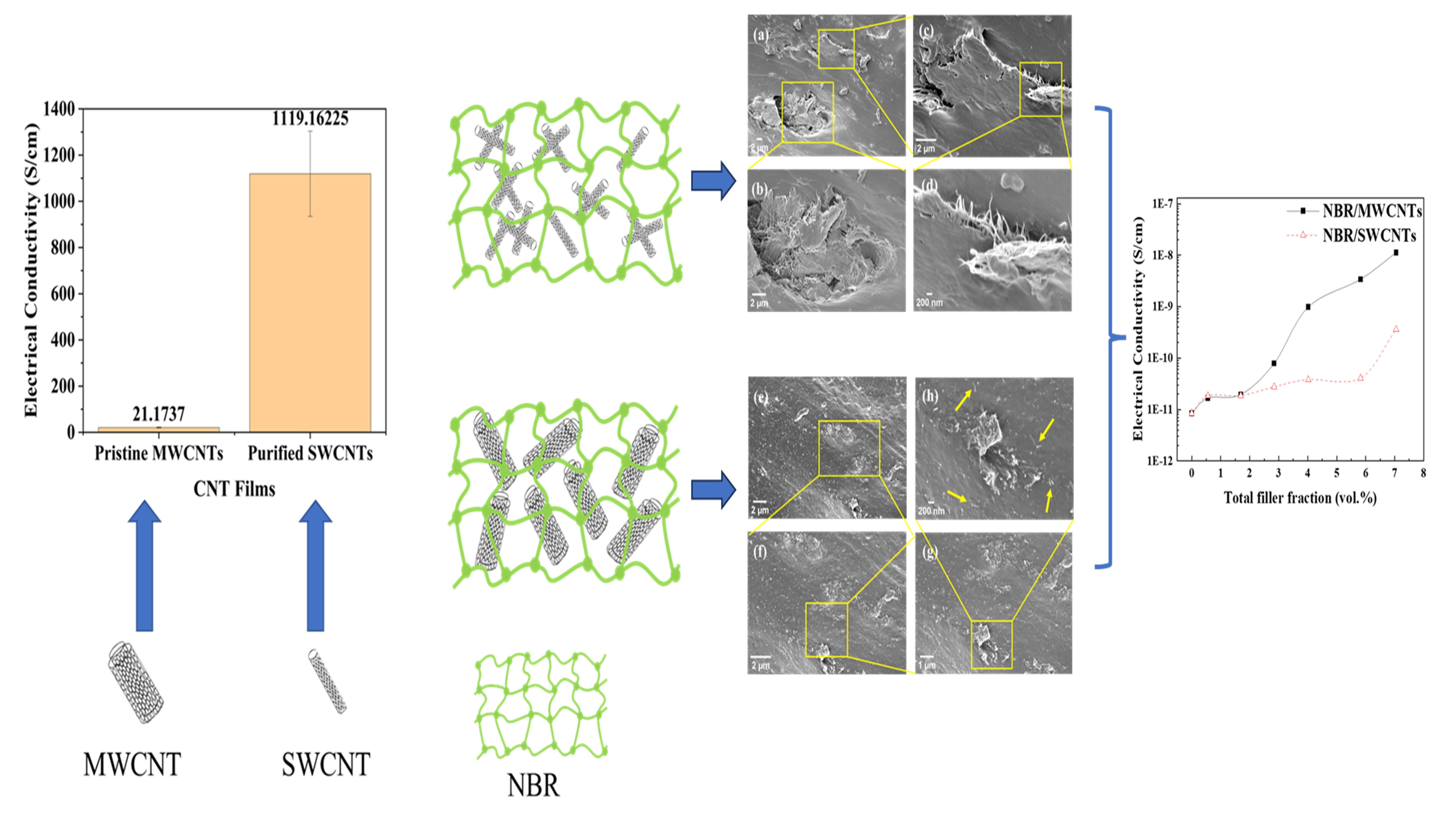
Carbon nanotubes (CNTs) are essential for providing polymers with mechanical reinforcement and multifunctional properties. This study investigated two groups of nitrile butadiene rubber (NBR) nanocomposites containing single-walled carbon nanotubes (SWCNTs) and multi-walled carbon nanotubes (MWCNTs), respectively. SWCNTs were purified to remove appro-ximately 20 wt.% of impurities, and both CNTs were modified with polyethylene glycol tert-octylphenyl ether (Triton X-100) before emulsion compounding and 2-roll milling with NBR. MWCNTs were found to disperse in the elastomer matrix relatively uniformly, while SWCNTs formed aggregates. Consequently, NBR/MWCNT nanocomposites exhibited superior mechanical properties, e.g. a tensile strength of 10.8 MPa at 4.02 vol.% MWCNTs, compared to 5.6 MPa for NBR/SWCNT nanocomposites. Additionally, NBR/MWCNT nanocomposites exhibited more remarkable electrical conductivity and swelling resistance to toluene. The diameter of elastomer macromolecules (0.2–0.5 nm) is close to that of SWCNTs (1–2 nm), and their single graphene wall with a hollow structure makes SWCNTs almost as flexible as elastomer macromolecules. This similarity suggests that SWCNTs should be treated as a special type of polymer. SWCNTs cannot disperse as uniformly as MWCNTs in the elastomer matrix, likely due to their smaller size and lower sensitivity to mechanical shearing during the emulsion compounding and 2-roll milling process.
Communication
08 January 2025Development of Eco-Friendly Composites Using Poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyvalerate) and Diss Fibers (Ampelodesmos Mauritanicus)
In response to the growing environmental threats and pollution linked to synthetic plastics, current scientific inquiry is prioritizing the advancement of biodegradable materials. In this context, this study investigates the possibility of developing fully biodegradable materials using plant fibers extracted from the Diss plant (Ampelodesmos mauritanicus) as reinforcement in poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyvalerate) (PHBV)-based biocomposites. The biocomposites were prepared by melt blending in the following weight ratio: PHBV/Diss fibers 80/20. The chemical structure of Diss fibers was characterized by Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) and X-ray fluorescence spectrometry (XRF). The impact of Diss fibers on the mechanical properties of biocomposites has also been investigated in comparison to neat PHBV. FTIR and XRF analyses identified cellulose, hemicellulose, and lignin as the main components of Diss fibers. On the other hand, the results showed a significant enhancement of Young’s modulus (⁓21%) of PHBV/DF biocomposites in comparison to neat PHBV due to a better dispersion of the fibers in the matrix, as confirmed by atomic force microscopy (AFM) images.
Review
30 December 2024
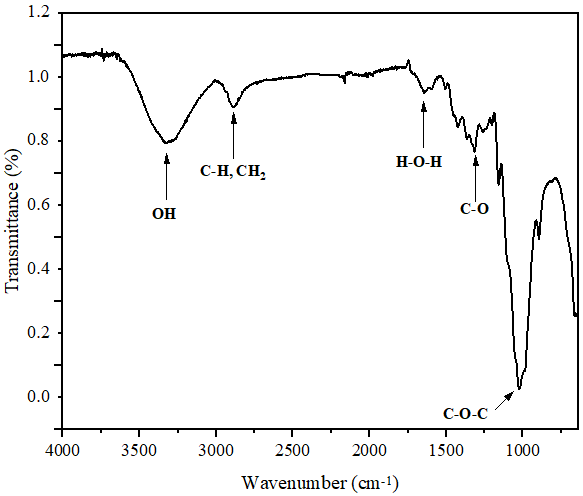
Fire-Retardant
Wastepaper Reinforced Waste Polyethylene Composite: A Review
The increase in fire
outbreaks recently and the need for eco-friendly and fire-resistant materials
have inspired a wave of studies, focusing on producing innovative composite
materials with effective fire-resistant properties. This review delves into the
world of fire-resistant wastepaper-reinforced waste polyethylene composites.
Using wastepaper as a strengthening factor in polyethylene matrices, combined
with fire-retardant additives like nanoparticles, introduces a hopeful path for
waste management and improved material properties. This work carefully
considers the combining approaches, physical and mechanical properties,
fire-resistant mechanisms, and environmental impacts of these composites. The
review underscores the possible and potential applications, difficulties, and
prospects of such environmentally friendly materials in various industries.
Understanding these composites’ blending, attributes, and conceivable
utilization is essential for advancing maintainable and fire-safe material innovation
in pursuing a greener future.
Article
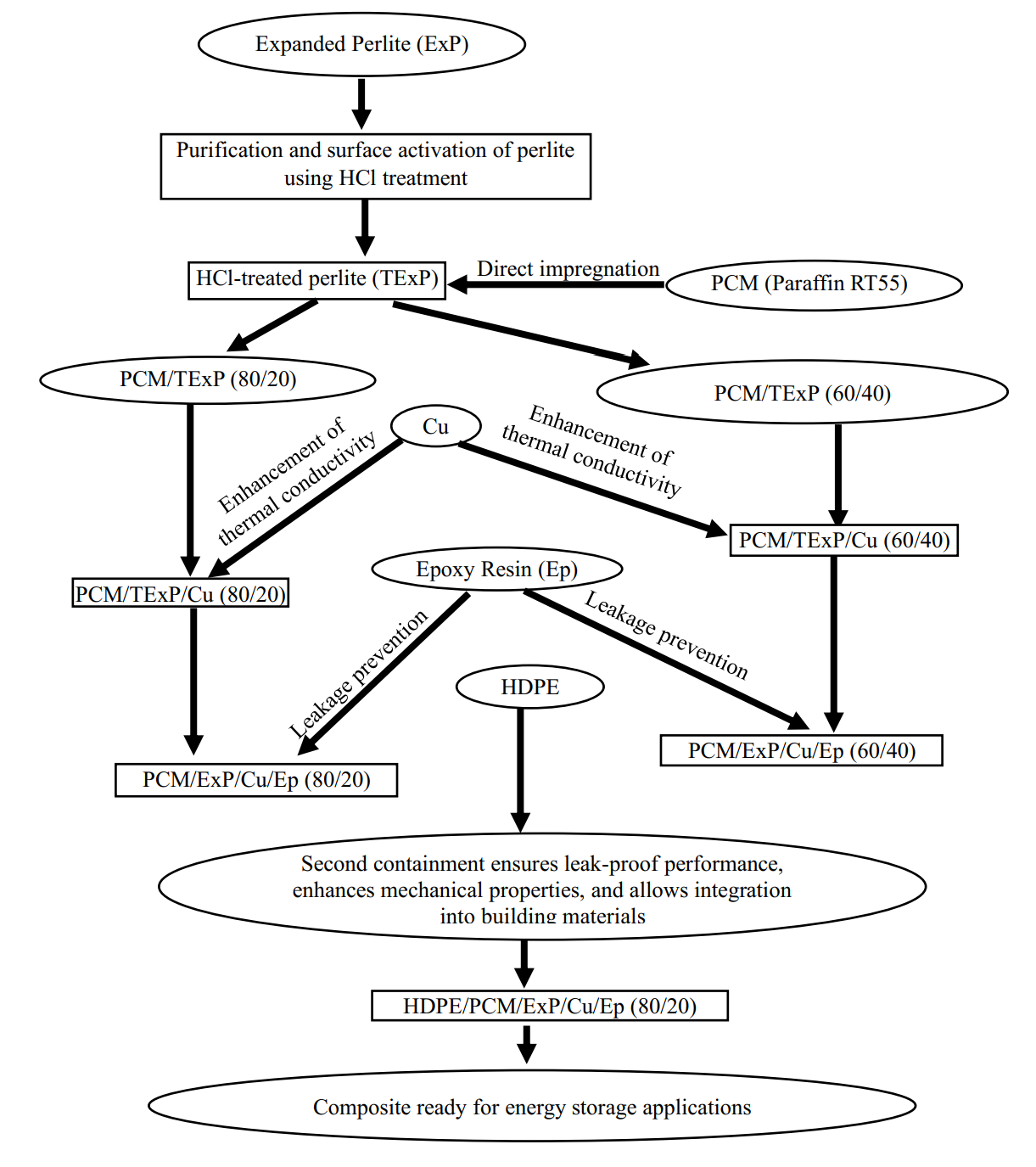
20 December 2024Preparation of a New Shape-Stable Phase-Change Material Based on Expanded Perlite, Paraffin, Epoxy, Copper and High-Density Polyethylene
Phase change materials (PCMs) face challenges such as low thermal conductivity and leakage, often addressed through attempts at encapsulation or integration into polymer matrices or porous materials. This study uses expanded perlite to prepare a PCM composite. The perlite is treated with hydrochloric acid to remove impurities and improve its absorption, then impregnated with paraffin at 65 °C, with the addition of copper to enhance thermal conductivity. After drying, the material was coated with epoxy resin to prevent leakage and mixed with high-density polyethylene (HDPE) to improve its mechanical strength and facilitate integration with other materials. Characterization techniques, including differential scanning calorimetry (DSC), thermogravimetric analysis (TGA), and scanning electron microscopy (SEM), evaluate the structure and properties of the composite. TGA results show that acid treatment increases paraffin absorption to 80% by weight, while weight loss tests confirm the effectiveness of the epoxy coating against leaks. A decrease in melting temperatures was observed in all HDPE blends, ranging from 4.72 °C to 9.58 °C, likely due to the integrated elements interfering with the reorganization of the molecular chains of HDPE. Although the preparation improved thermal conductivity, thermal tests revealed that increasing the (perlite/PCM) phase in HDPE is essential for further optimization, highlighting the potential of the composite as an effective energy storage solution for sustainable systems.
Article
12 December 2024Adsorption of Bisphenol A and 2,6-Dichlorophenol in Water Using Magnetic Phosphogypsum Composite Materials
Phenolic pollutants in water bodies pose a huge threat to human health and environmental safety. In this paper, a hydrophobicity-enhanced magnetic C-SiO2/MPG composite was prepared by a two-step method to remove bisphenol A (BPA)and 2,6-dichlorophenol (2,6-DCP), typical phenolic trace pollutants in livestock wastewater and natural water bodies. The results of pH gradient experiments showed that C-SiO2/MPG showed a stable removal effect on BPA in the pH range of 2–11. The adsorption of 2,6-DCP by C-SiO2/MPG peaked at pH = 2, while the adsorption of 2,6-DCP by C-SiO2/MPG was severely inhibited under alkaline conditions. The PSO kinetic model and the Langmuir isotherm model can better describe the adsorption process of BPA and 2,6-DCP on C-SiO2/MPG, indicating that the monolayer chemical adsorption has a rate-controlling step. With the Langmuir equation fitting, the maximum adsorption capacity of C-SiO2/MPG for BPA and 2,6-DCP at 298 K was calculated to be 561.79 mg/g and 531.91 mg/g, respectively. The results of adsorption thermodynamics indicated that the adsorption of BPA and 2,6-DCP on C-SiO2/MPG was spontaneous, accompanied by a process of entropy decrease. C-SiO2/MPG showed good environmental resistance and repeated use stability for BPA and 2,6-DCP in electrolyte ion interference, actual water samples and cycle experiments. Mechanism analysis showed that the adsorption of BPA and 2,6-DCP on C-SiO2/MPG was mainly controlled by hydrogen bonding and hydrophobic interactions. This study designed an efficient adsorbent for phenolic pollutants that can be used in actual wastewater and broadened the resource utilization of industrial waste phosphogypsm.

Article
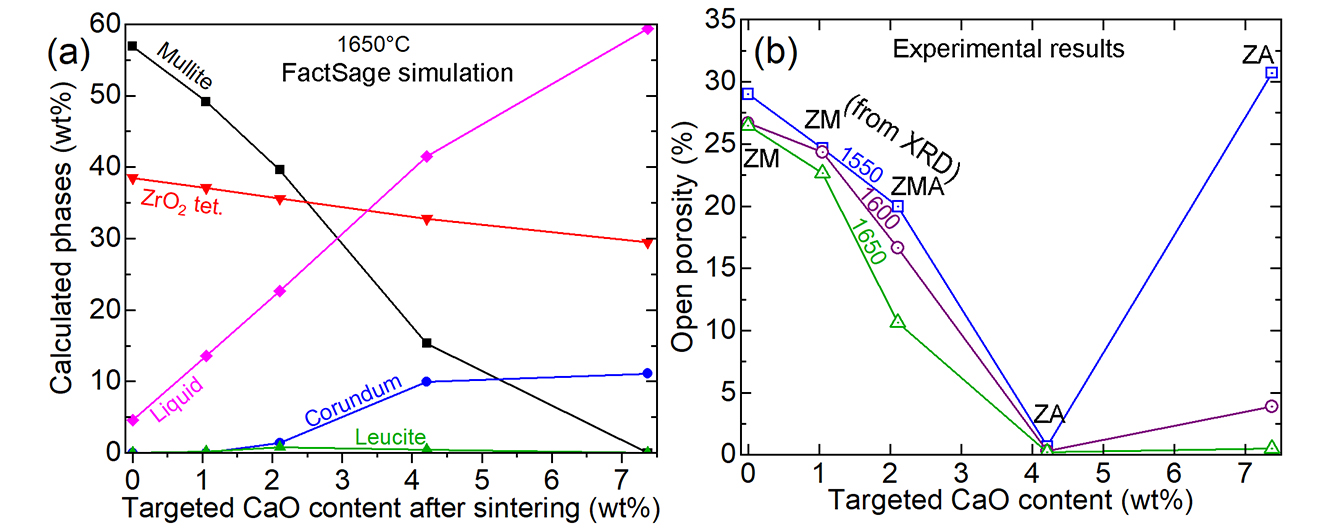
19 November 2024Calcite as a Mineralizer and Stabilizer for Low-Cost Zirconia-Mullite-Alumina Composites Synthesized from Siliceous Clay, Alumina and Zirconia
Fused zirconia-mullite (ZM) and zirconia-alumina (ZA) are expensive aggregates used in refractory formulations to enhance thermal shock tolerance and corrosion resistance, respectively. A cost-effective alternative approach was explored in this work to produce 37.4 wt% ZrO2 containing ZM utilizing conventional reaction sintering of siliceous clay, calcined alumina and monoclinic ZrO2. A series of chemical reactions ensued from 1200 °C, forming low quartz and cristobalite from the clay, in situ ZrSiO4, monoclinic ZrO2, α-Al2O3 and traces of leucite. 1600 °C was required to fully form mullite and monoclinic ZrO2 but it had 26.5% porosity even after firing at 1650 °C for 2 h. It consisted of small equiaxed primary mullite grains secondary mullite rods, and scattered and clustered, round ZrO2 grains. With 1.05% CaO addition, tetragonal ZrO2 formed, but 22.7% porosity remained despite the presence of 13.5% liquid phase having a low viscosity (0.6 Pa.s, from FactSage). With 2.11% CaO, porosity reduced to 10.7% but mullite partly dissolved, forming α-Al2O3 (ZMA aggregate). The added CaO mostly remained in the intergranular glassy phase rather than inside the ZrO2 grains but increased the thickness of the secondary mullite and the ZrO2 grains. Mullite was completely lost with 4.21% CaO doping but favorably formed cubic ZrO2 containing up to 0.26 at% Ca, interlinked α-Al2O3 rods and attained a low porosity of 0.2%. This ZA aggregate is limited to 1550 °C application temperature as excess liquid phase drained out beyond that. 7.37% CaO addition was detrimental as it formed an excessive anorthite-like liquid phase that percolated out at 1550 °C with 5.6% weight loss. Thus, in ZM-based calcium aluminate cement bonded refractory castables, the final CaO content should be restricted to below 2.1% to avoid partial dissolution of mullite.
Article
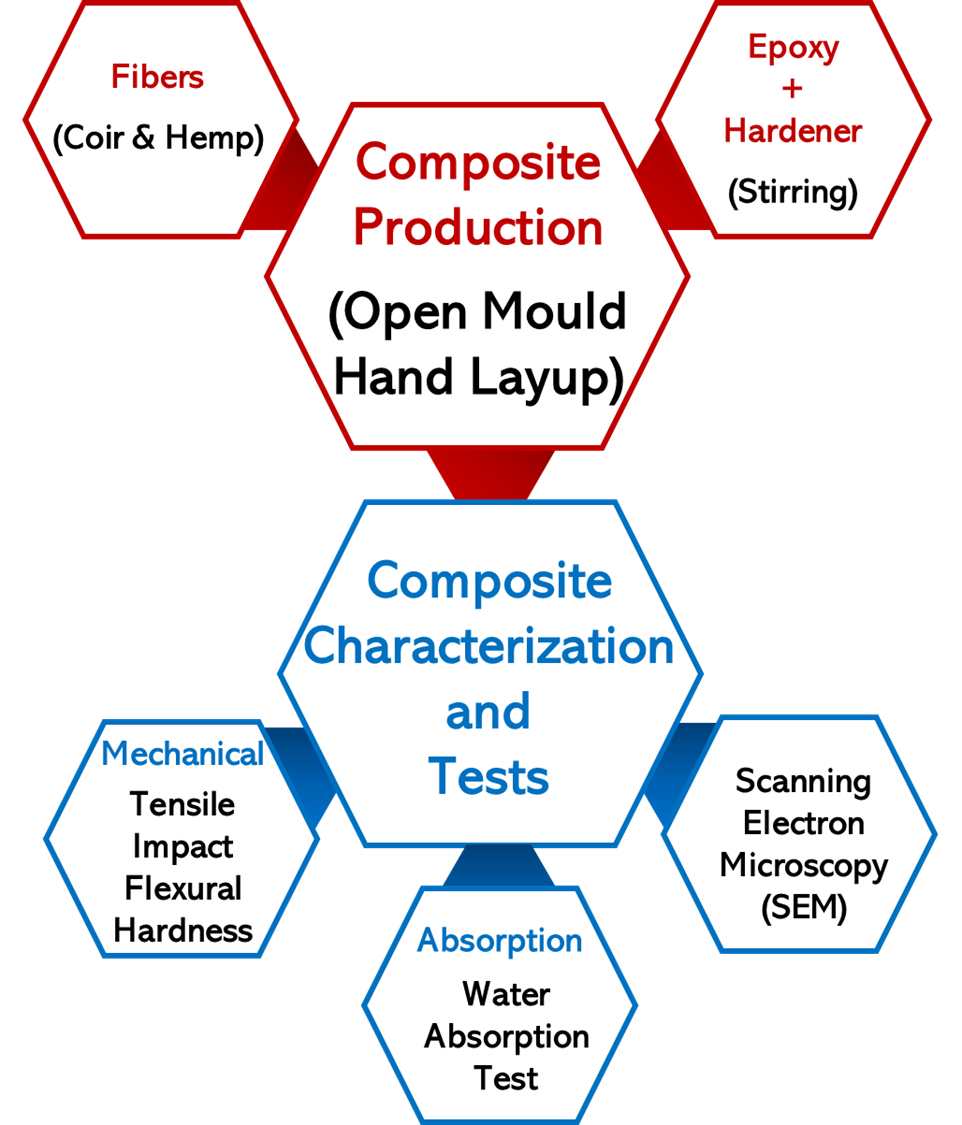
01 November 2024Alkaline Modified Coir and Unmodified Hemp Fiber Reinforced Epoxy Based Composite for Automotive Application
The growing demand for sustainable materials in the automotive industry has prompted research into natural fiber-reinforced composites. To reduce carbon footprints and enhance product sustainability, the sectors increasingly focus on renewable and biodegradable materials. Composites made from natural fibers, such as coir and hemp, offer a promising solution for creating lightweight, high-performance components with a reduced environmental impact.In this study, an experimental investigation was conducted to examine the impact of single and hybrid and treated and untreated fibers, on the properties of epoxy-based composites. Untreated hemp fiber with treated Coir fiber was used for the research. The composites were fabricated through the open mould hand lay-up technique. Samples were prepared by randomly dispersing the fibers in the epoxy matrix before pouring them into the respective moulds prepared according to ASTM standards. Tensile, impact, and hardness tests were conducted on the cured samples to determine their mechanical properties, while a scanning electron microscope was used to evaluate the fractured surface. Water absorption tendencies were also determined. The results showed that the sample denoted as 5CF wt.% had the best property combination with tensile strength (32.4 MPa), tensile modulus (11.9 GPa), flexural strength (167.0 MPa), and impact strength (46.8 kJ/mm2). It was discovered that hemp fiber-based composites were not enhanced properly due to lack of fiber surface modifications. Though optimum results were obtained from treated coir fiber-based single/distinct composite, untreated hemp fiber was discovered to aid some flexural modulus and hardness properties in the hybrid composite based on the best results obtained in its distinct-based composite. Therefore, untreated hemp fiber can be used in hybrid form with treated coir fiber where one of the fibers is scarce or when fiber surface medication is difficult to achieve. Thus, the results showed that 5CH-based composites are the most suitable composition for automotive components development where high-mechanical properties are essential.
Article
28 May 2024Efficacy and Cytocompatibility of a Pressure Garment—Silicone Composite Dressing Material for Scar Healing
Pressure garment therapy (PGT) and silicone gel sheeting (SGS) predominate non-invasive interventions for burn injuries, but the market lacks a composite solution combining pressure garment fabric (PGF) and medical-grade silicone (e.g. Biopor®AB) for multi-therapeutic efficacy. To address this gap, a versatile composite dressing of PGF-Biopor®AB was developed. PGF-Biopor®AB incorporates dual PGF-SGS therapy, mechanotherapy, and active moisture management, to facilitate recovery of hypertrophic subsidiary structures. The PGF structure enables the application of PGT, while the Biopor®AB silicone characteristics enforce silicone gel therapy (SGT). The PGF-SGS efficacy optimization not only reduces tension but also facilitates water vapor and oxygen penetration, along with hydration of the stratum corneum. Mechanotherapy, involving tension-shielding and pressure redistribution, promotes the reorganization of the collagen-fiber network. For active moisture management, the incorporation of a microchannel structure with active nylon absorbency facilitates effective moisture control through water absorption, retention, and cellular pathways of transport. In this study, the microscale features in the structure were further investigated. Under ISO 10993-5 standard, an over 70% cell viability in 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide (MTT) assay containing the L929 cell line verified the enhanced cell growth and inhibited proliferation, endorsing the safe usage of PGF-Biopor®AB. Patient studies of one-month efficacy in both high and low-cell-density samples and an early scarless healed wound suggest that over 70% cell viability is sufficient for optimal scar therapeutics. The multifaceted scar repair roles are fulfilled by addressing persistent inflammation, insufficient oxygenation, low levels of perfusion, and scar-healing tension, hence realising the multi-therapeutic efficacy of the composite dressing.