Found 4 results
Review
02 April 2025Wide-Bandgap Semiconductors: A Critical Analysis of GaN, SiC, AlGaN, Diamond, and Ga2O3 Synthesis Methods, Challenges, and Prospective Technological Innovations
The increasing demand for high-performance Wide-Bandgap (WBG) semiconductors, including GaN, SiC, and emerging Ultrawide-Bandgap (UWBG) materials such as Ga2O3 and diamond, has driven significant advancements in epitaxial growth techniques. However, achieving scalability, defect-free growth, and sustainability remains a major challenge. This review systematically evaluates Molecular Beam Epitaxy (MBE), Metal-Organic Chemical Vapor Deposition (MOCVD), Hydride Vapor Phase Epitaxy (HVPE), and other novel growth and hybrid growth techniques, emphasizing energy efficiency, defect control, and environmental impact. Industry 4.0-driven AI-based process optimization and closed-loop recycling have emerged as transformative strategies, reducing waste and improving manufacturing efficiency. Key findings reveal that HVPE enables rapid defect-free GaN fabrication, Hot-Filament CVD enhances SiC growth with superior thermal properties, and Atomic Layer Epitaxy (ALE) achieves sub-nanometer precision crucial for next-generation quantum and RF applications. Despite these advancements, p-type doping in UWBG materials, substrate compatibility, and thermal management remain unresolved challenges. Future research must focus on scalable eco-friendly epitaxy, novel doping mechanisms, and policy-driven sustainability efforts. This review provides a comprehensive roadmap for sustainable WBG semiconductor manufacturing, bridging materials innovation, energy efficiency, and industrial adoption to support the next generation of power electronics and optoelectronics.
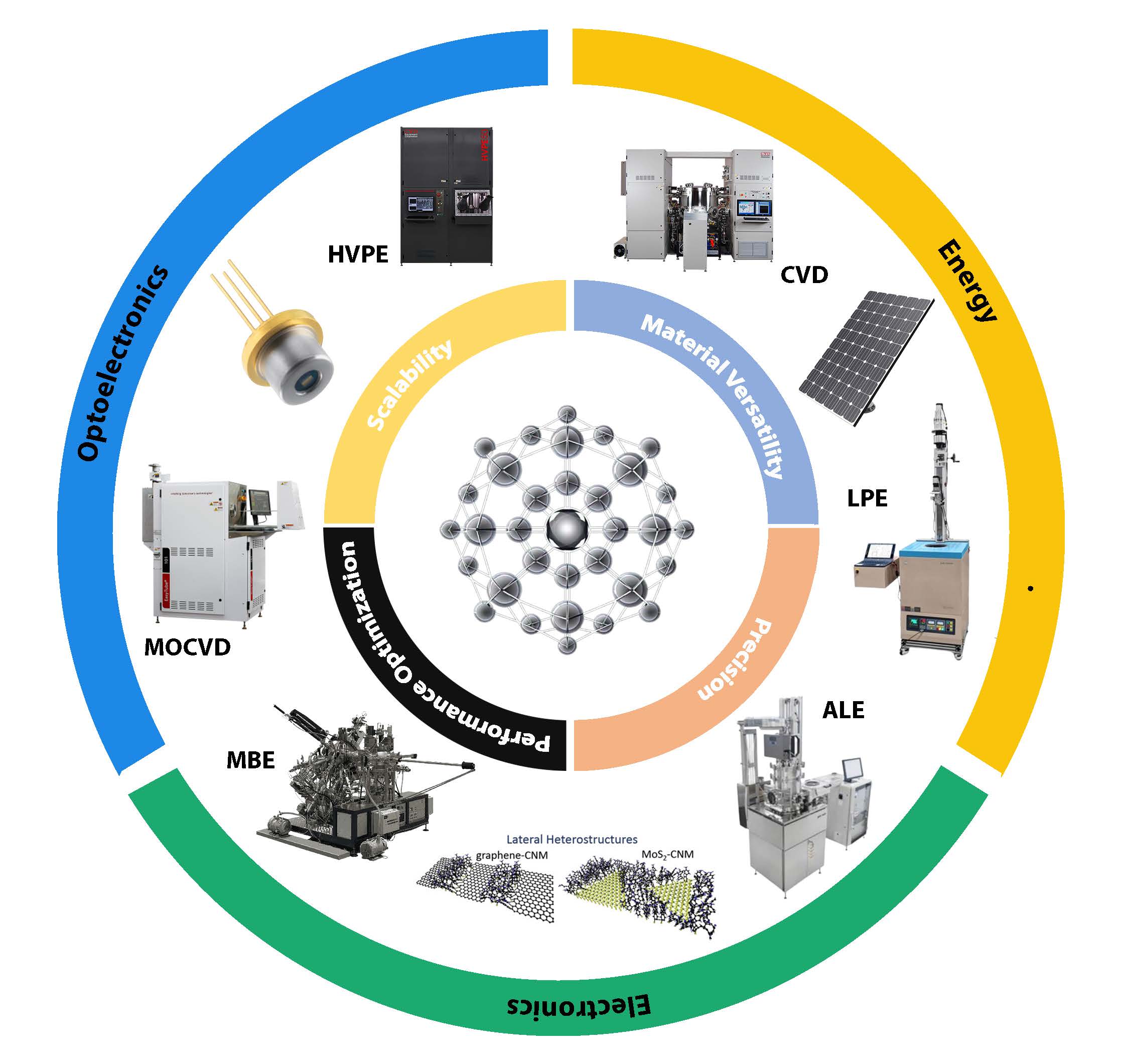
Review
25 February 2025Innovations in IN939: From Cast Alloy to Additive Manufacturing
Nickel-based superalloys are the most reliable material choice for the hot sections of turbines. These superalloys are mainly employed in aircraft engines, particularly in the combustor and turbine sections. In this scenario, the growing need for materials that can endure high temperatures while retaining their strength has driven the development of IN939. Although IN939 holds these significant important properties and applications, it has received less attention in recent literature than other superalloys. This review aims to comprehensively analyze the main research on IN939 over the past 50 years. From 1970 to 1980, research primarily focused on the development of IN939 through casting methods. Between 1980 and 1990, the emphasis shifted to studying its oxidation resistance and microstructural stability during service. The period from 1990 to 2000 focused on repairing components after long service time at high temperatures. In recent decades, advances in additive manufacturing techniques have led to growing interest in developing IN939 using methods like laser powder bed fusion (LPBF). Research in the area has demonstrated that the LPBF technique offers a promising approach to manufacturing high-performance IN939 components.
Article
09 January 2024Climate Change Adaptation Strategies for Grape Cultivation in Yamanashi Prefecture of Japan
Climate change impacts agricultural production, especially fruits. Amongst fruits, the grape is economically valuable and highly affected by climate change. Therefore, climate adaptation strategies are essential in overcoming the detrimental effects of climate change on grape cultivation. The study summarises adaptation strategies for grape cultivation in general and focuses on climate change. The Yamanashi prefecture in Japan is taken for the case study. Our findings indicate a decline in grape production in Japan and Yamanashi prefecture. This is attributed to the effects of climate change. Following this, various support measures (adaptative, mitigation, others) provided by the Yamanashi government towards grape cultivation are summarised and analyzed. The study concludes by offering recommendations by drawing lessons from the literature review on adaptation strategies for grape cultivation, focusing on overcoming climate change impact in the context of Yamanashi prefecture.

Article
15 November 2023Local Production, Consumption, and Innovation: Enhancing Sustainability through SMEs in Japan
The study focuses on the process of business development with the use of food tech and open innovation by Small and Medium-sized Enterprises (SMEs) in Japan to create a sustainable ecosystem in the regional economy. Production of alternative food materials is introduced in the new business of SMEs with the hope to reduce carbon footprint. SMEs need to create an SME ecosystem that integrates consumers as vital partners in the process of introducing new alternative food items to the market as agents of change. Innovative ways of inventing new food products involve the processes of sourcing ingredients, creating new recipes for alternative food products, and incorporating local food culture and methods of food preparation. Therefore, it is crucial for SMEs to involve local producers as well as consumers as stakeholders in innovation. Some case examples of SMEs producing plant-based alternative meats in Japan are reviewed in this study to highlight key factors impacting the outcome of innovation in the products and processes of SMEs seeking sustainable solutions. The significance of the study lies in acknowledging catalytic roles of SMEs in regional settings and interactive roles of consumers as product buyers as well as active players who consciously opt for certain products and modes of consumption driven by their inclination to support sustainability. Based on the findings of the study, some policy suggestions are also made for enhancing sustainability and revitalizing the local economy through SMEs.
