Found 2 results
Review
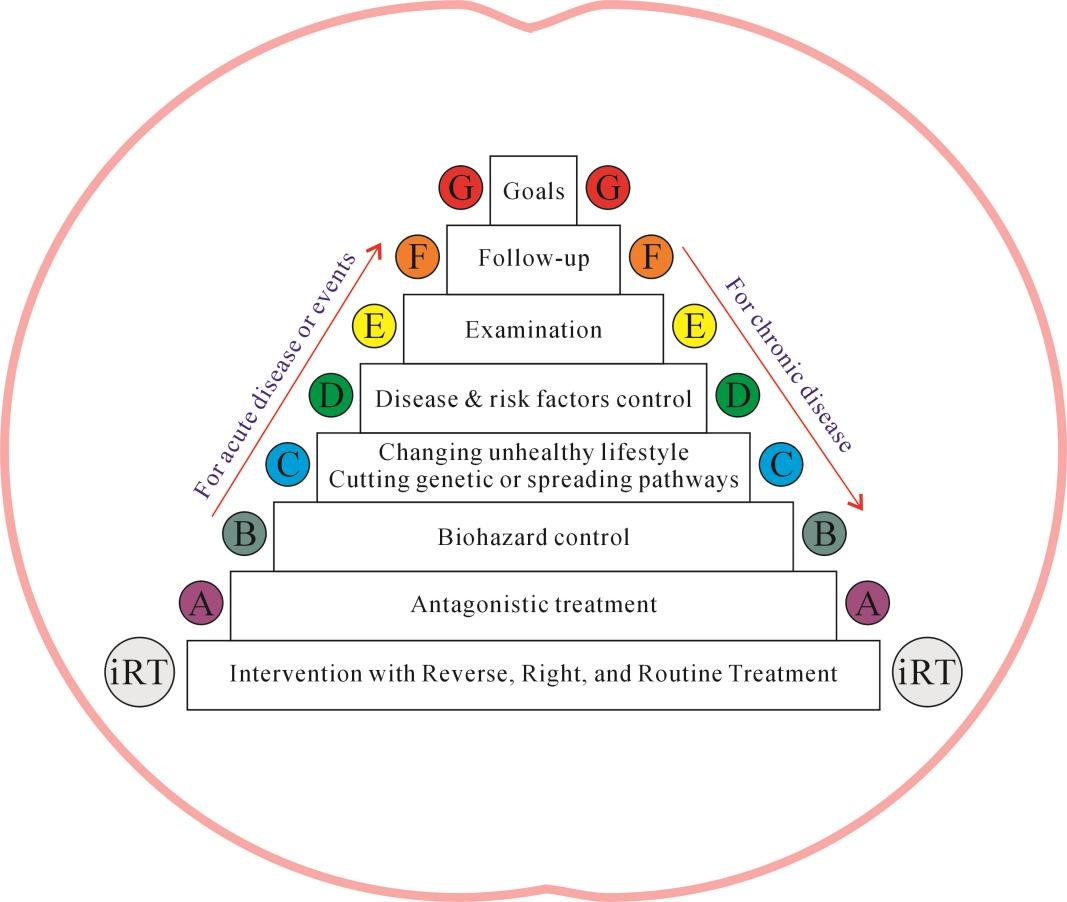
27 August 2024A Novel Comprehensive Program Combining Optimal Medical Treatment with Lifestyle Modification for Type 2 Diabetes
There are more and more individuals with type 2 diabetes (T2D) in the globe. It’s a huge burden of public health and a great challenge in clinical due to a high linkage with atherosclerosis, cardiovascular disease (CVD), stroke, and cancer. However, little is known about a comprehensive program of management and self-management of T2D. This article introduces briefly the current status in T2D and an updated classical standardized comprehensive program which combines optimal medical treatment (OMT) (the glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists, the sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors, and the ultralong-acting, once-daily basal insulin) with lifestyle modification, that is, intervention of RT-ABCDEFG (iRT-ABCDEFG) for control and prevention of T2D, and discusses its advantages and prospects. As an effective comprehensive program and strategy for interventions of diabetes, this program can be used as a reversible, right, and routine treatment. Several pivotal goals including less major adverse cardiocerebrovascular events (MACCE) and diabetic complications, less medical costs, longer life expectancy, lower morbidity and mortality, and higher quality of life, will be realized by consistently practicing this program due to early diagnosis, OMT, and lifestyle modification for overall prevention. All in all, since T2D highly links to CVD and cancer, as well as other MACCE, this novel iRT-ABCDEFG program is very helpful in comprehensive management and self-management of T2D and worth recommending for further application and health care of T2D due to better clinical efficacy and cost-effective relationship.
Article
02 July 2024Early Risk Indicators for DSM-IV Diagnoses in Adolescents and Young Adults with Intellectual Disabilities
To identify risk indicators at ages 6–18 years that are associated with DSM-IV diagnoses in adolescents and young adults with intellectual disabilities five years later. To assess the potential health gain and efficiency of preventive interventions targeting these risk indicators. Parents reported on potential child, parental, and environmental risk indicators. Five years later, parents were interviewed using a standardised psychiatric interview schedule (DISC-IV) to assess DSM-IV diagnoses in children with ID (N = 614) at the age of 11 to 24 years. Logistic regression and linear probability models were used to test the contribution of risk indicators to the prediction of DSM-IV diagnoses. Deviant levels of internalising and externalising problems, inadequate adaptive behaviour, and parental psychopathology predicted psychiatric disorder. Children/adolescents exposed to multiple risk indicators were at greater risk of developing DSM-IV disorders. Strategies aiming for the risk reduction of psychiatric disorders in children/adolescents with ID should focus on intervening at an early age, improving psychopathology and adaptive behaviour skills of the children/adolescents, and supporting their parents.
