Guest Editor (1)

Deadline for manuscript submissions: 30 September 2025.

| Index | Description | Row |
| Si Pi Ii ri Normal |
Sustainability Probability of each Pillar Impact of each Pillar Normalized ratio of each Pillar |
1 2 3 4 |
| Si = ∑ (Pi * Ii * ri Normal) |
||
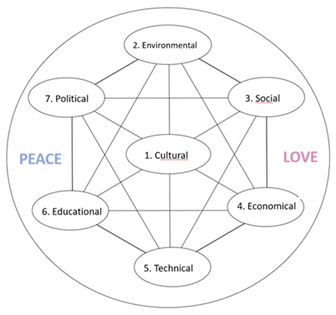
Technological innovations, education, business and society change quickly and often unpredictably. The fusion of artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning, augmented reality (AR), virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (XR) opens a new era in which work, production, communication and thought processes are massively transformed. In this context, the challenge arises: How can small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) adapt to this accelerated change? This study highlights a path forward and introduces the concept of “SME 5.0” or “Hybrid SME” or “SME of Tomorrow” as a comprehensive solution to address the complexities of the digital age. In this integrated exploration of the X.0 Wave Theory and SME 5.0 Concept, the framework for human civilization’s evolution and technological shifts converges with a practical roadmap for small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) navigating the dynamic digital landscape. Acknowledging transformative waves in technology, economics, and societal structures within the X.0 Wave Theory, the study accentuates the ongoing nature of these shifts. It advocates for a long-term perspective, urging policymakers and industry leaders to consider potential future scenarios to devise strategies fostering innovation, competitiveness, and privacy safeguards. Simultaneously, the study introduces SME 5.0 as a holistic solution for SMEs, aligning with the transformative success envisioned by the X.0 Wave Theory. Proposing the Seven Pillars of Sustainability (7PS) framework tailored to SMEs, the concept emphasizes digitalization and sustainable technology. The title, “Harmonizing the X.0 Wave Theory and SME 5.0 Concept”, encapsulates the synergy between theoretical underpinnings and practical solutions. The subtitle, “Fostering Sustainable Collaboration, 7PS Engineering, and Overcoming Legal Challenges in the Digital Age”, provides a glimpse into the study’s focus on practical implications, sustainability, engineering, and legal considerations for SMEs in the rapidly evolving digital era.
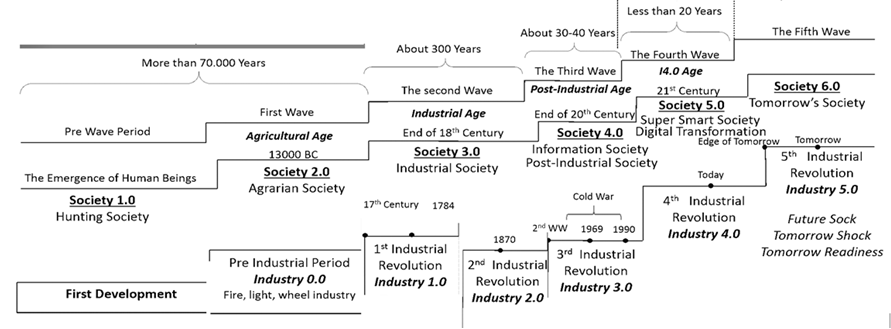
This paper delves into the X.0 Wave/Tomorrow Age Theory, a comprehensive framework conceived, invented, introduced, and developed by Prof. Dr. Hamid Mattiello between 2010 and 2017, to analyze the evolution of human civilization through distinct epochs of knowledge, technology, and business (KTB). The theory segments history into transformative waves, from the first development (X.0 ≤ 1.0) and Agricultural Age (X.0 = 1.0) and the X.0 Wave/Tomorrow Age Theory (2.1 ≤ X.0 ≤ 2.2) spanning the 17th Century to 1870, to the current Age of Artificial Intelligence (X.0 = 4.0). It also projects into the anticipated Human Age (X.0 = 5.0) and Transhuman Age (X.0 = 6.0) and beyond (6.0 ≤ X.0). Each wave represents a revolutionary phase characterized by significant advancements that shape societies, industries, and technologies. The X.0 Wave Theory integrates these historical phases with the Seven Pillars of Sustainability (7PS) to evaluate their societal impacts. The paper explores how these waves influence future developments by examining historical roots, emerging technological paradigms, and socio-economic dynamics. It examines how advancements in AI, biotechnology, and virtual reality are reshaping industries and global business practices, while also addressing the ethical and sustainability considerations essential for navigating these changes. By forecasting future trends, confronting current challenges, and preparing for potential crises, the X.0 Wave Theory offers a robust framework for understanding and adapting to the rapid pace of technological evolution. This paper provides deep insights into how these transformative waves shape our past, present, and future, offering valuable perspectives for navigating the complexities of an increasingly digital and interconnected world.