Artiles
Communication
30 December 2024Magnetic Solid Phase Extraction of Paeonol and Paeonoflorin from Moutan Bark with Magnetic Graphene Oxide
Herbal medicine plays an
important role in modern medicine and separation of the active ingredients from
herbal medicine is vital for convenient and safe usage. Paeonol and
paeonoflorin are the active ingredients in the widely used herbal medicine of
moutan bark. In this study, the composite of graphene oxide-Fe3O4 nanoparticles (GO-Fe3O4) was synthesized and used as a magnetic
absorbent to extract paeonol and paeonoflorin from the herbal medicine of
moutan bark. The adsorption of paeonol and paeoniflorin on GO-Fe3O4 rapidly reached equilibrium (within 10 min) due to the high absorption
capability of GO. Thermodynamics and kinetics for the absorption process were
studied. The optimal condition for the elution of the target compound from GO-Fe3O4 was the use of 2 mL of a mixed solvent (methanol and dichloromethane, 1:1 by
volume) with 0.2% formic acid for 5 min. The GO-Fe3O4 adsorbent possesses the advantages of rapid adsorption and convenient
separation. GO-Fe3O4 can be used over 6 times without
losing absorbing capacity. This method is efficient, convenient and rapid, thus
possesses a high potential for the separation of active ingredients from herbal
medicine.
Article
27 December 2024Effect of Magnesium Aluminum Silicate Addition on the Ablation Resistance of BN Matrix Ceramics
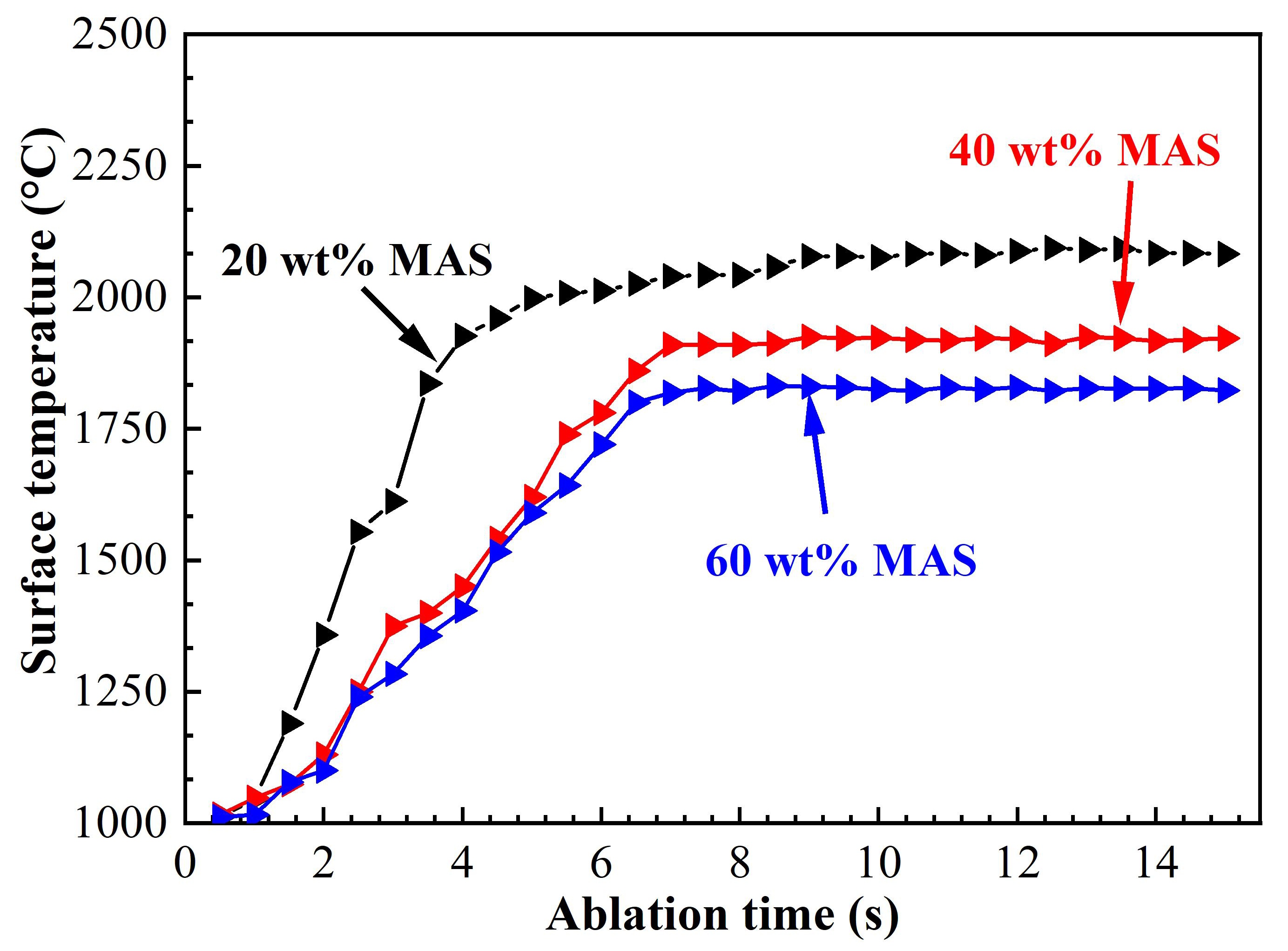
Ablation resistance is a critical factor in evaluating the performance of BN-based ceramic composites under extreme service conditions. This study investigates the ablation behavior and underlying mechanisms of BN-MAS wave-transparent ceramic composites with varying magnesium aluminum silicate (MAS) content through oxyacetylene torch tests. The results reveal that increasing the MAS content reduces the mass ablation rate from 0.0298 g/s to 0.0176 g/s and the linear ablation rate from 0.149 mm/s to 0.112 mm/s. The incorporation of MAS into h-BN ceramics significantly lowers the surface ablation temperature, primarily due to the evaporation of B2O3 (g) and MAS ceramics. Cross-sectional analysis of the ablated composites indicates the presence of micro- and macro-spallation in the ablation center. The primary ablation products are magnesium-aluminum borosilicate glass and mullite. Key ablation mechanisms include the oxidation of h-BN under flame exposure, the erosion of viscous oxidation products, and the physical degradation of the matrix caused by the high-velocity gas flow.
Article
24 December 2024Hydrodynamic Performance of a Hybrid Floating Power Dock Combining Multi-Cantilever Type Buoys
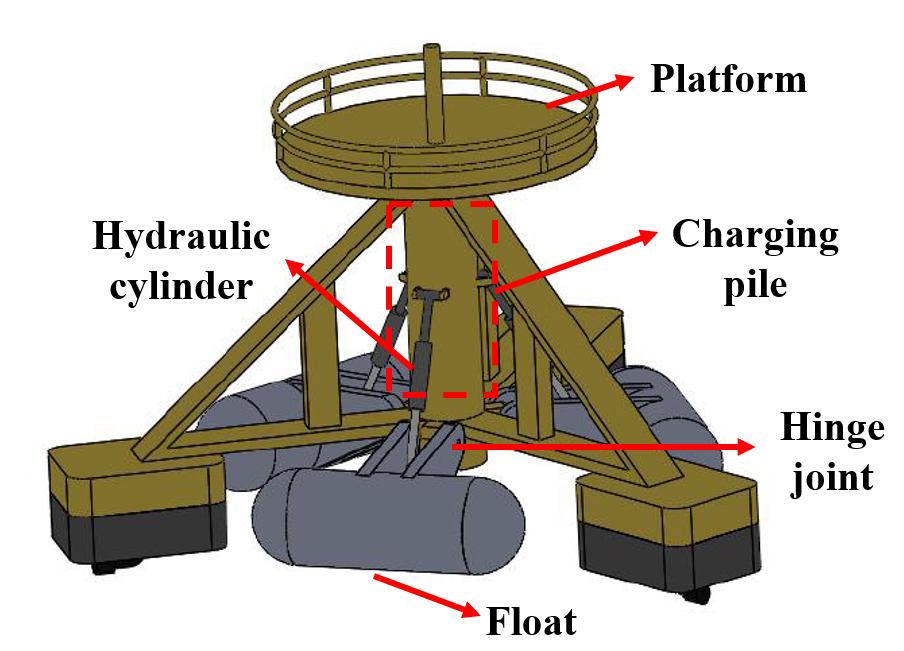
This paper proposes a novel three-dimensional oscillating pendulum wave energy converter (WEC) that integrates an oscillating float dock station. The device captures wave energy by utilizing both the pitch and roll motions of its primary float and the pendular motion of a buoy. A time-domain analysis method is used to numerically evaluate the hydrodynamic behavior and energy conversion efficiency of the WEC. In ANSYS AQWA, a multi-cantilever WEC model is employed to address the fluid-solid coupling, calculating the device’s motion response and capturing the width ratio under various environmental conditions. Additionally, by modifying key geometric parameters including float radius, length, and cantilever angle, the study examines the rotation at the articulation point and the capture width ratio variation for different device configurations. Results indicate that the device achieves a maximum capture width ratio at a float radius of approximately 120 mm under T = 1.4 s, and a 130 mm for wave periods of 1.5 s and 1.6 s. The highest average capture width ratio is reached at a power take-off (PTO) damping coefficient of 400 N·s/m. The study further investigates the effect of cantilever angle and float length, aiding in the optimization of these geometric parameters.
Review
24 December 2024Age Estimation through Analysis of Suture Synostosis in Forensic Practice: A Mini Review
Age estimation is essential in forensic sciences. The examination of neurocranium suture closure, along with other methods, is used to estimate age in skeletal remains. The aim of this review was to identify in the literature methods used through neurocranial sutures for estimating age and analyze the recommendations by its researchers. One electronic research database, Pubmed, was investigated using the following restricted keywords: “age estimation”, “suture” and “forensic”. A search was conducted in March 2024 resulting in 12 articles being included in the final review. The articles were published between 2010 and 2024. Many studies recommend combining suture age estimation with other methods to improve accuracy in both dry skulls and CT scans, as cranial suture results alone are often insufficient. There is still no consensus on the endocranial versus ectocranial evaluation of sutures, with researchers calling for further studies. Population characteristics also affect results, highlighting the need for broader research. Despite its limitations, cranial suture closure remains valuable, with new technologies offering potential improvements.

Article
23 December 2024The Influence Mechanism and Test of Transformation for Cultivated Land Use on the Economic Resilience of Agricultural Crop Production Industry
Under the current multiple impacts, such as tightening resource and environmental constraints, low agricultural economic benefits and rural labor loss, improving the resilience of the planting economy has become the only way to ensure China’s food security and the stable operation of the social economy. As an important way of agricultural production factor, the transformation of cultivated land has a great influence on the development of the agricultural crop production industry. Based on the elaboration of the logical relationship and influence mechanism of the economic resilience of the agricultural crop production industry, the effect and regional differences of the economic resilience of the agricultural crop production industry are empirically tested by a double fixed regression model. It is found that the economic resilience level of the agricultural crop production industry in China is on the rise, but the regional differences are obvious; the transformation for cultivated land use can significantly promote the economic resilience level of agricultural crop production industry and the results are stable; there is regional and dimensional heterogeneity in the impact of cultivated land use transformation on the economic resilience of agricultural crop production industry. Based on this, we can promote the transformation of cultivated land use from three aspects: production, life, and ecology. Especially, attention should be paid to the orderly promotion of the transformation of farmland utilization in the main grain-producing areas and the improvement of the economic resilience of the agricultural crop production industry. Consolidate regional advantages while driving the improvement of economic resilience in the main grain sales areas’ agricultural crop production industry to achieve the goal of sustainable and stable development of China’s agricultural crop production industry.

Article
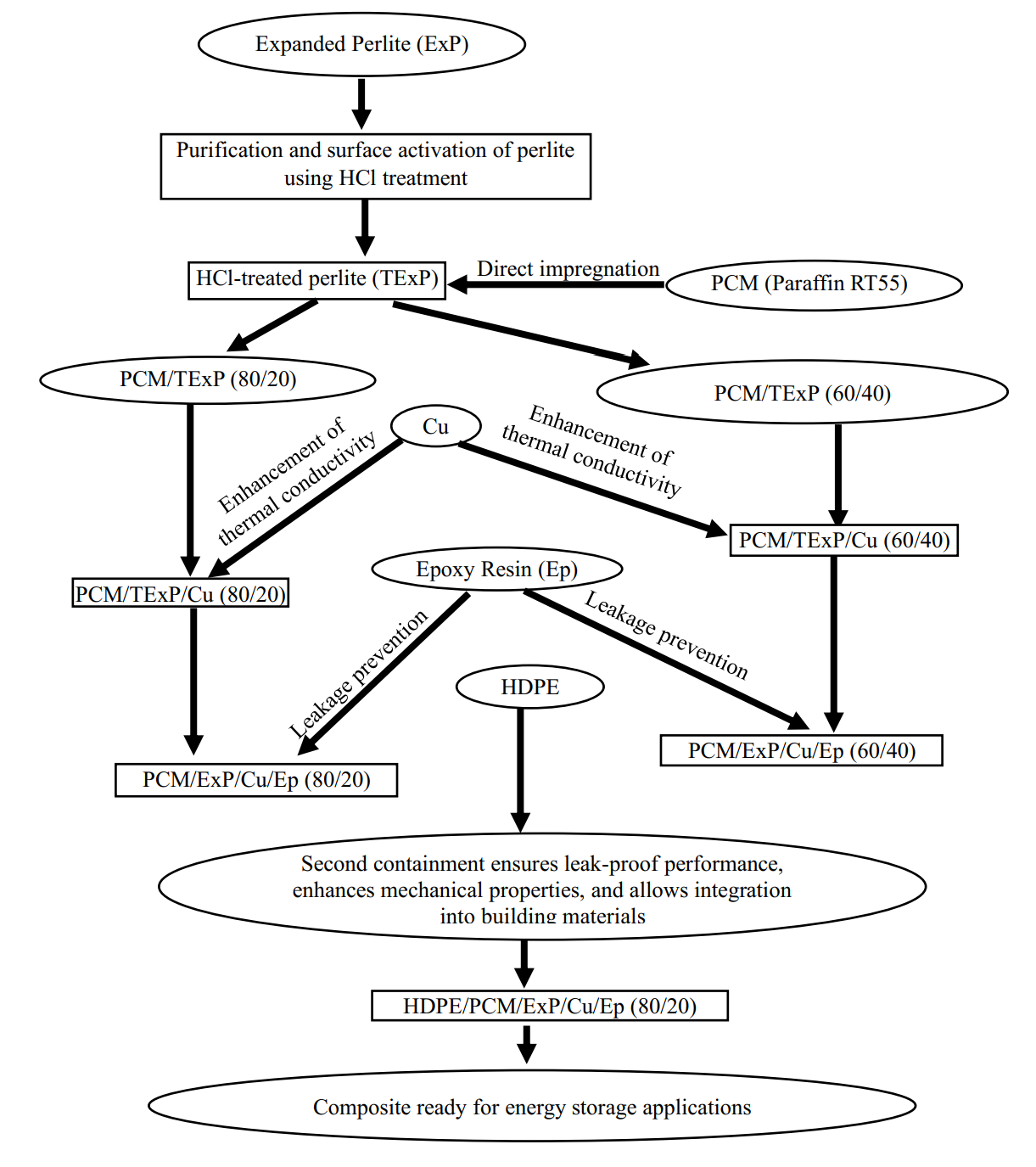
20 December 2024Preparation of a New Shape-Stable Phase-Change Material Based on Expanded Perlite, Paraffin, Epoxy, Copper and High-Density Polyethylene
Phase change materials (PCMs) face challenges such as low thermal conductivity and leakage, often addressed through attempts at encapsulation or integration into polymer matrices or porous materials. This study uses expanded perlite to prepare a PCM composite. The perlite is treated with hydrochloric acid to remove impurities and improve its absorption, then impregnated with paraffin at 65 °C, with the addition of copper to enhance thermal conductivity. After drying, the material was coated with epoxy resin to prevent leakage and mixed with high-density polyethylene (HDPE) to improve its mechanical strength and facilitate integration with other materials. Characterization techniques, including differential scanning calorimetry (DSC), thermogravimetric analysis (TGA), and scanning electron microscopy (SEM), evaluate the structure and properties of the composite. TGA results show that acid treatment increases paraffin absorption to 80% by weight, while weight loss tests confirm the effectiveness of the epoxy coating against leaks. A decrease in melting temperatures was observed in all HDPE blends, ranging from 4.72 °C to 9.58 °C, likely due to the integrated elements interfering with the reorganization of the molecular chains of HDPE. Although the preparation improved thermal conductivity, thermal tests revealed that increasing the (perlite/PCM) phase in HDPE is essential for further optimization, highlighting the potential of the composite as an effective energy storage solution for sustainable systems.
Article
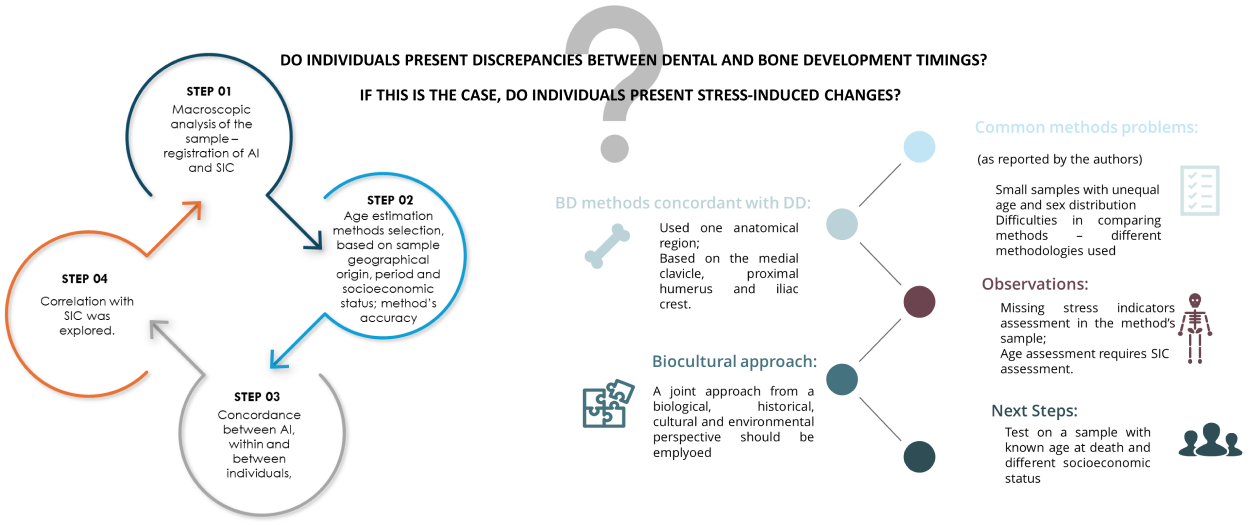
20 December 2024The Sum of One’s Parts: Exploring Bone and Dental Age Assessment in Age Estimation Methods
Age estimation (AE) is a fundamental aspect used to establish the biological profile of both living and deceased individuals. This study evaluates AE methods to determine if bone development (BD) methods yield similar results to dental development (DD) and whether methods using samples with similar geographic origins, socioeconomic status (SES), chronology, data specificity, and/or anatomical regions yield consistent results. We hypothesized that BD and DD methods differ in age estimations, although these differences would be minor when methods have similar variables. The sample consisted of 11 immature skeletons from the Hospital Real de Todos os Santos’ collection (18th-century, Lisbon, Portugal) and applied 56 AE methods. The results were compiled into individual-based diagrams, facilitating both within- and between-individual comparisons, including stress-induced changes. This showed that BD methods tended to underestimate age compared to DD methods. BD methods closely aligning with DD methods were mainly based on individuals from lower to middle SES, focusing on areas like the iliac crest and medial clavicle. Findings also suggest that physiological stress might influence AE outcomes. This study emphasizes the importance of combining BD and DD methods alongside a detailed pathological and/or chronic stress assessment of human remains when estimating AE to minimize interpretative errors. This care applies to any discipline aiming to profile living or dead individuals, highlighting the importance of controlling for confounding variables, such as disease, in any AE estimation.
Article
18 December 2024EU Energy Law: Insufficient for the 1.5-Degree Celsius Limit—The Examples of EU Emissions Trading and Hydrogen Policies
This article examines the extent to which the current EU climate protection law fulfils the 1.5-degree limit from Article 2 of the Paris Climate Agreement. To this end, a qualitative governance analysis is applied. On this methodological basis, the main instrument for fossil phasing-out—the emissions trading scheme—and the promotion of hydrogen are discussed as examples. The results show that the EU must further intensify its efforts on its territory and cooperate with other countries since the reformed ETS 1 and ETS 2, the SCF and the CBAM are not sufficiently effective to stay within the 1.5-degree limit of the Paris Agreement. This is also the case with regard to hydrogen policies. The primary focus of energy law on the ETS is therefore fundamentally convincing; however, it should be implemented more consistently, for example, in terms of the breadth of the approach, closing loopholes and the level of ambition.

Article
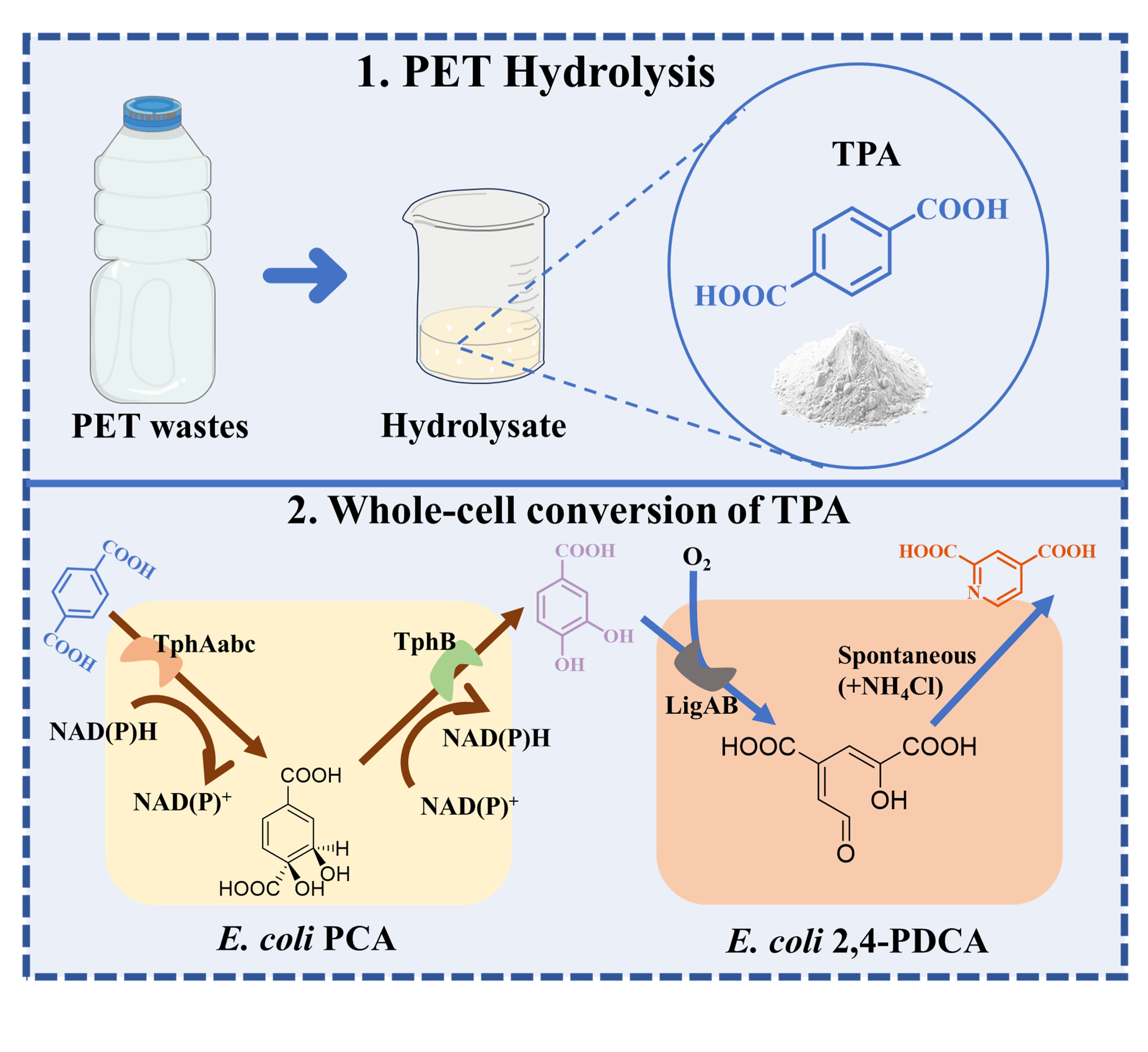
17 December 2024Upcycling of Waste Poly(ethylene terephthalate) into 2,4-Pyridine Dicarboxylic Acid by a Tandem Chemo-Microbial Process
This study presents a chemo-microbial cascade process for the upcycling of waste poly(ethylene terephthalate) (PET) into valuable compound 2,4-pyridine dicarboxylic acid (2,4-PDCA). Initially, waste PET undergoes efficient hydrolysis to terephthalic acid (TPA) with a high yield of 92.36%, catalyzed by p-toluenesulfonic acid (PTSA). The acid catalyst exhibits excellent reusability, maintaining activity over five cycles. Subsequently, a one-pot, two-step whole-cell conversion system utilizing genetically modified Escherichia coli strains (E. coli PCA and E. coli 2,4-PDCA) converts the generated TPA into 2,4-PDCA. By integrating the PET hydrolysis module with the 2,4-PDCA biosynthesis module, the study achieves an impressive overall efficiency of 94.01% in converting challenging PET waste into valuable 2,4-PDCA. Our research presents a rational design strategy for PET upcycling and 2,4-PDCA synthesis methods. This research provides a systematic approach to PET upcycling, demonstrating its feasibility and potential for industrial application.