Artiles
Article
20 November 2024Contextualization of Industry 4.0 Design Principles for the Imminent Industry 5.0 Scenario
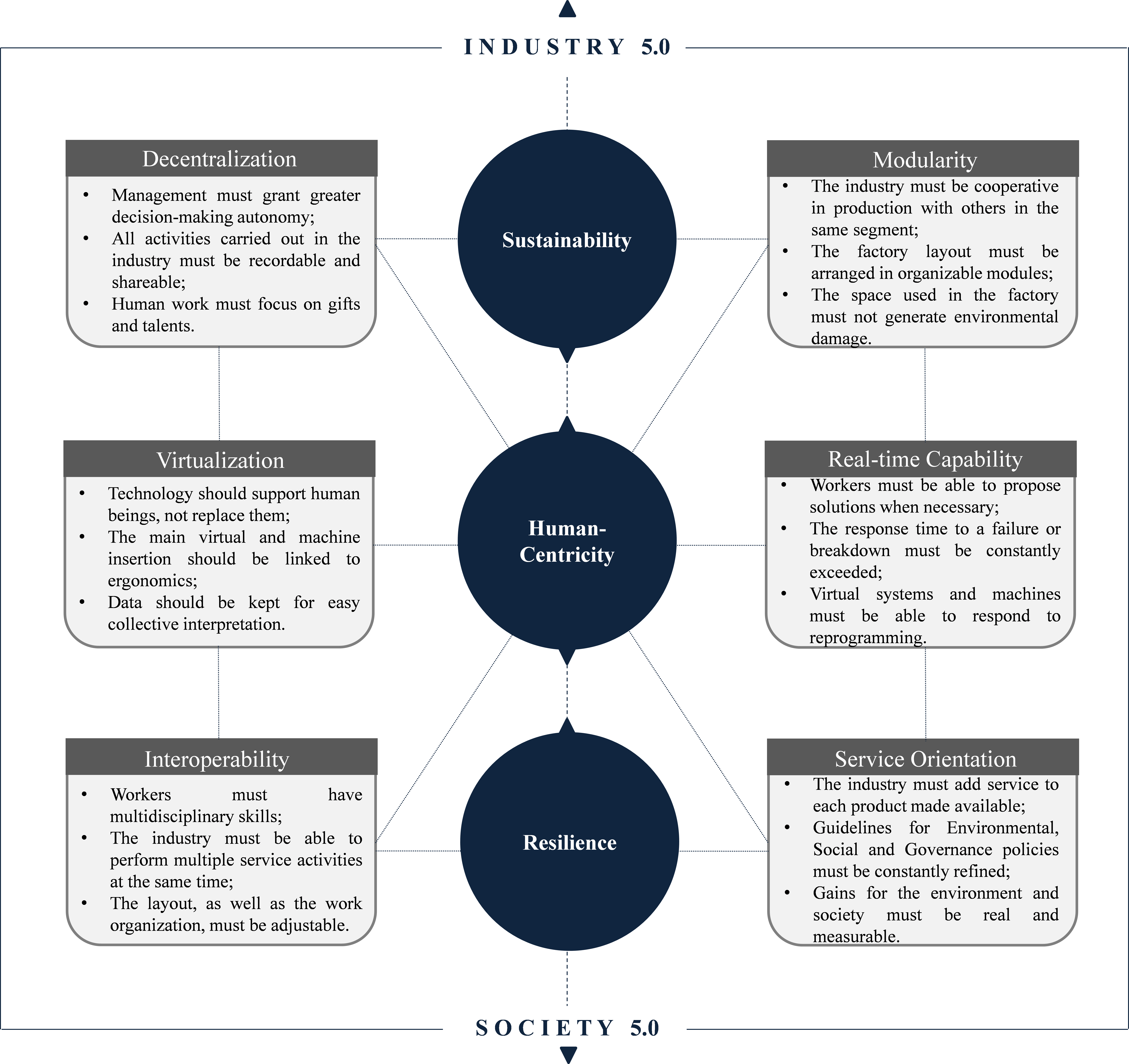
The Fourth Industrial Revolution, known as Industry 4.0 (I4.0), has introduced a completely disruptive pace compared to the rhythm of the three previous industrial revolutions. With a wide range of technologies, design principles, and a high potential to replace the human workforce, this industry presents aspects that urgently require greater attention. With a purpose close to meeting this need, Industry 5.0 (I5.0) emerges, a milestone not yet registered with historical facts but with great hopes for positive changes. While I4.0 maintains design principles for its complete activity, I5.0 has a supporting tripod for its operation. As I5.0 is still perceived as an evolutionary character of I4.0, it is expected that for the time being, it will use these same design principles for its activity and may later include new principles. Based on this context, this article seeks to contextualize, in a descriptive way, the functioning of design principles 4.0 for the imminent industrial context 5.0. The article uses a conceptual approach based on previously published literature on the subject of design principles in I4.0. Although the characteristics of I5.0 are not yet fully known, it is assumed that it has a more refined character than I4.0, so that points that presented a positive, significant, and already consolidated result are maintained for the new model. The distinctive feature of this article is its presentation of a textual analysis that breaks down the potential contributions of design principles in relation to the three core values of Industry 5.0: Sustainability, Human-Centricity, and Resilience.
Article
19 November 2024Calcite as a Mineralizer and Stabilizer for Low-Cost Zirconia-Mullite-Alumina Composites Synthesized from Siliceous Clay, Alumina and Zirconia
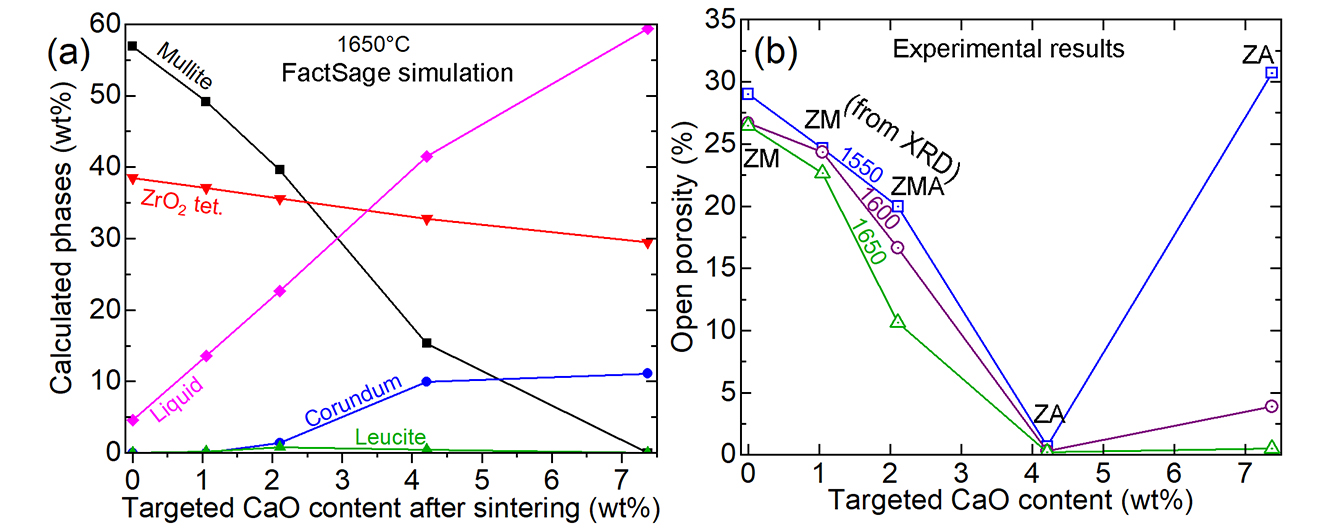
Fused zirconia-mullite (ZM) and zirconia-alumina (ZA) are expensive aggregates used in refractory formulations to enhance thermal shock tolerance and corrosion resistance, respectively. A cost-effective alternative approach was explored in this work to produce 37.4 wt% ZrO2 containing ZM utilizing conventional reaction sintering of siliceous clay, calcined alumina and monoclinic ZrO2. A series of chemical reactions ensued from 1200 °C, forming low quartz and cristobalite from the clay, in situ ZrSiO4, monoclinic ZrO2, α-Al2O3 and traces of leucite. 1600 °C was required to fully form mullite and monoclinic ZrO2 but it had 26.5% porosity even after firing at 1650 °C for 2 h. It consisted of small equiaxed primary mullite grains secondary mullite rods, and scattered and clustered, round ZrO2 grains. With 1.05% CaO addition, tetragonal ZrO2 formed, but 22.7% porosity remained despite the presence of 13.5% liquid phase having a low viscosity (0.6 Pa.s, from FactSage). With 2.11% CaO, porosity reduced to 10.7% but mullite partly dissolved, forming α-Al2O3 (ZMA aggregate). The added CaO mostly remained in the intergranular glassy phase rather than inside the ZrO2 grains but increased the thickness of the secondary mullite and the ZrO2 grains. Mullite was completely lost with 4.21% CaO doping but favorably formed cubic ZrO2 containing up to 0.26 at% Ca, interlinked α-Al2O3 rods and attained a low porosity of 0.2%. This ZA aggregate is limited to 1550 °C application temperature as excess liquid phase drained out beyond that. 7.37% CaO addition was detrimental as it formed an excessive anorthite-like liquid phase that percolated out at 1550 °C with 5.6% weight loss. Thus, in ZM-based calcium aluminate cement bonded refractory castables, the final CaO content should be restricted to below 2.1% to avoid partial dissolution of mullite.
Article
18 November 2024Developing a Climate Litigation Framework: China’s Contribution to International Environmental Law
Although “climate litigation” is not an indigenous term in China, localizing it is essential to support the development of an independent environmental legal knowledge system in China. Rooted in China’s judicial tradition, which emphasizes substantive rationality, traditional legal theories have primarily focused on environmental law. However, the contemporary practices in the rule of law have created an unclear trajectory for climate litigation. Research in this area has long been trapped in a paradigm that relies on lawsuits for ecological environmental damage compensation and environmental public interest litigation, leading to a significant disconnect between theoretical framworks and practical application. With the advancement of the "dual carbon" strategic goals—carbon peaking and carbon neutrality—it has become imperative to redefine the concept of climate litigation within the Chinese context. We need to establish a theoretical framework that aligns with the “dual carbon” objectives while providing theoretical and institutional support for climate litigation, ultimately contributing to the international discourse on climate justice. Additionally, Hong Kong’s proactive climate governance and robust ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) practices provide valuable insights for developing comprehensive climate litigation mechanisms. Based on this analysis, we propose concrete plans for building a climate litigation system in China, establishing a preventive relief system and a multi-source legal framework at the substantive level and developing climate judicial mechanisms for mitigation and adaptation at the procedural level.

Article
15 November 2024Long-Term Change in Human Impact and Environmental Perceptions: A 40-Year Case Study of an Environment-Focused Non-Governmental Organization
Non-governmental environmental organizations are diverse in scope, goals and doctrine, ranging from natural history societies to green parties. It was from the 1960s that they became widespread worldwide. To characterize a French NGO and assess the changing trends in its objectives over time, we have qualitatively and quantitatively analyzed the journal it has published without interruption for 40 years: 140 issues, 4500 pages, and almost 250 keywords. The initial scope of the NGO was focused on ‘humans and nature’: we do not protect the environment against humans but with humans, i.e., at the same time as humans, which is the very definition of sustainable development, with its three-fold focus: nature, economy and social justice. The primary issues included recognizing water as a shared resource for all people, promoting sustainable agriculture and transportation (such as railways), advancing peace efforts, and protecting nature. This approach emphasizes a rigorous, evolving scientific perspective that goes beyond a focus on a few charismatic species (‘deluxe biodiversity’), embracing biodiversity in its entirety. Over time, the discourse has kept track of the shifting priorities of most Green parties: less and less focused on nature (e.g., forests, ecosystems) and more and more on social issues (e.g., health, housing, transport). However, it differs in not focusing on the idées fixes of the Greens (e.g., rejection of civil nuclear power, GMOs).

Review
15 November 2024Intelligent Manufacturing Factory: A Bibliometric Analysis of Global Research Hotspots and Progress
Intelligent factories provide flexible and adaptive production processes, offering significant competitive advantages to manufacturers and are widely studied in industrial production. Information technology is recognized as a key factor influencing the production efficiency and intelligence of Intelligent factories. However, current research has primarily focused on the operational processes of intelligent factories, with limited analysis of information technology. To address this gap, this paper conducts a bibliometric analysis of information technology in intelligent factories, along with a review of its development and applications. Firstly, the data collection and visualization methods of bibliometrics are introduced. Secondly, bibliometric analyses are performed using platforms such as VOSviewer and Scimago to investigate co-authorship, co-citation, and contributions from countries and institutions in the field of information technology for intelligent factories. Finally, a framework for information technology in intelligent factories is established, summarizing its development in terms of information acquisition, transmission, processing, management, and control. This paper aims to assist scholars in understanding the development trends of intelligent factory technology and enhancing the informatization level of intelligent factories.
Review
15 November 2024Ion Channels in the Immune Response of Asthma
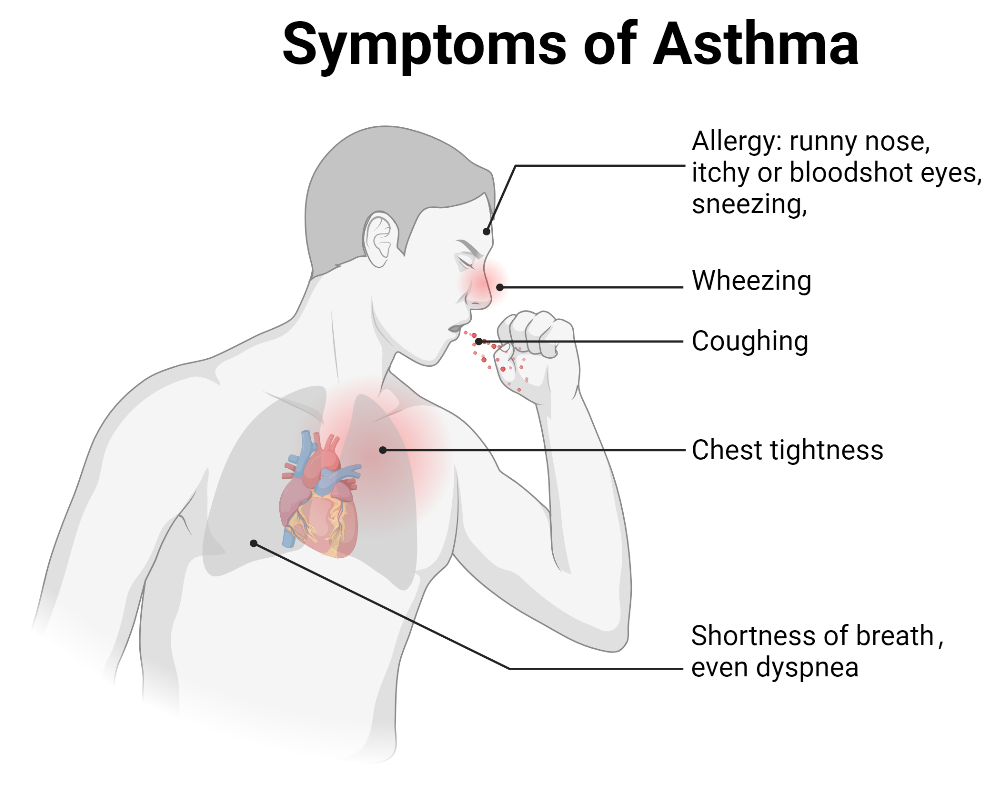
Asthma is a common respiratory disorder characterized by chronic inflammation of the lower airways, contributing to significant morbidity, mortality, and a substantial global economic burden. It is now understood as a heterogeneous condition, with ongoing research shedding light on its complex immunological underpinnings. Ion channels, which are specialized transmembrane proteins that facilitate ion movement based on electrochemical gradients, play a crucial role in the pathophysiology of asthma. Ion channels regulate essential processes like maintaining epithelial hydroelectrolyte balance and also play a role in modulating immune responses involved in asthma. We discuss the connection between ion channel activity and immune regulation in asthma, focusing on ion channel regulation of immune cell behavior, airway hyperresponsiveness, and inflammation in asthma. Understanding ion channels in asthma could lead to the development of targeted therapies modulating their activity, thereby enhancing disease management and patient outcomes.
Article
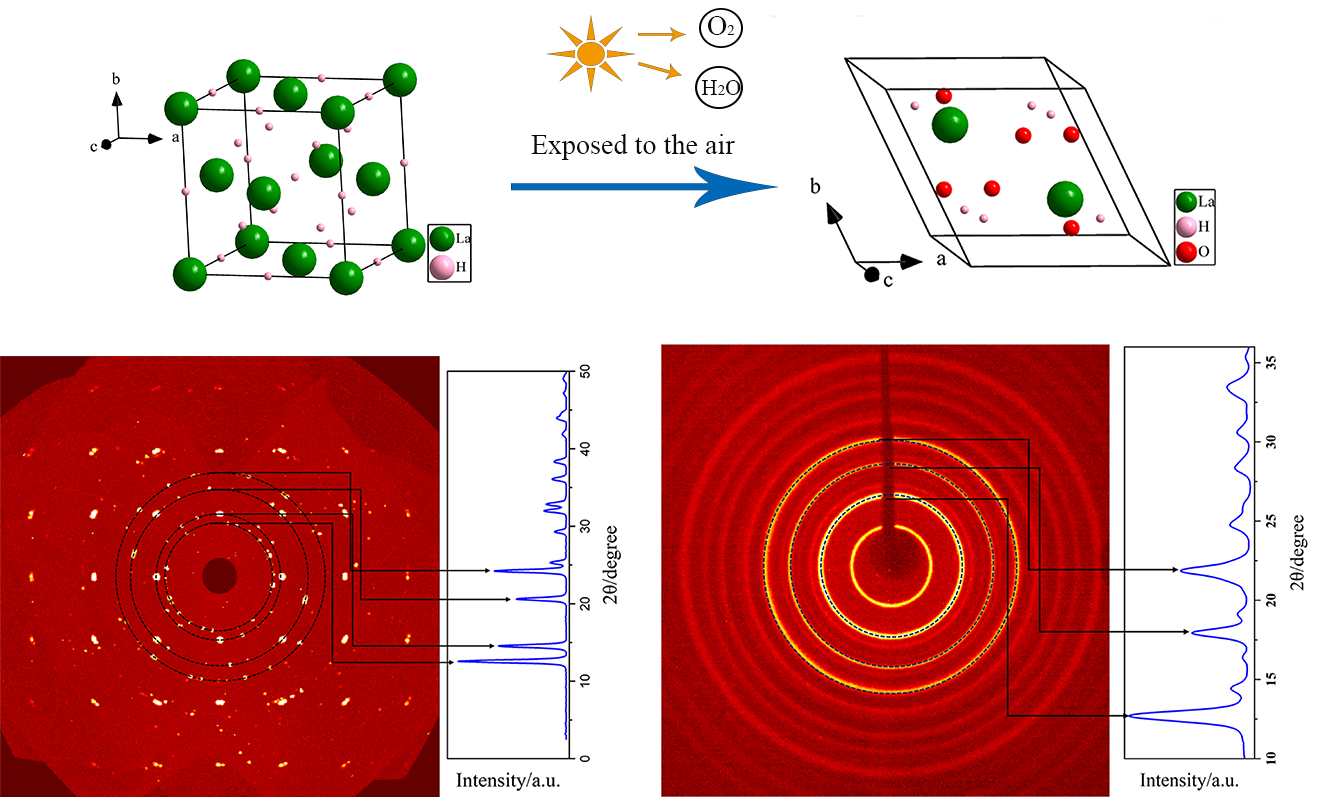
14 November 2024The Discovering of Rapid Formation La(OH)3 from LaH3
It was found that the single crystal of LaH3 specimen with $${Fm\overline{3}m}$$ (No.225) will decompose into powders within 24 h, which is later characterized to be La(OH)3 by single crystal X-ray diffraction (SXRD) measurements. The discovery motivates the examination of three possible transition paths by comparing formation enthalpy with first-principles calculations and employing a custom- designed hydrogen detection setup. Furthermore, the most suitable adsorption position of O2 molecules on the (111) surfaces has been investigated by comparing the adsorption enthalpy from different candidate positions by utilizing first-principles calculations, implying the pivotal role of O2 molecules played in the rapid formation of La(OH)3 along the optimal transition path.
Article
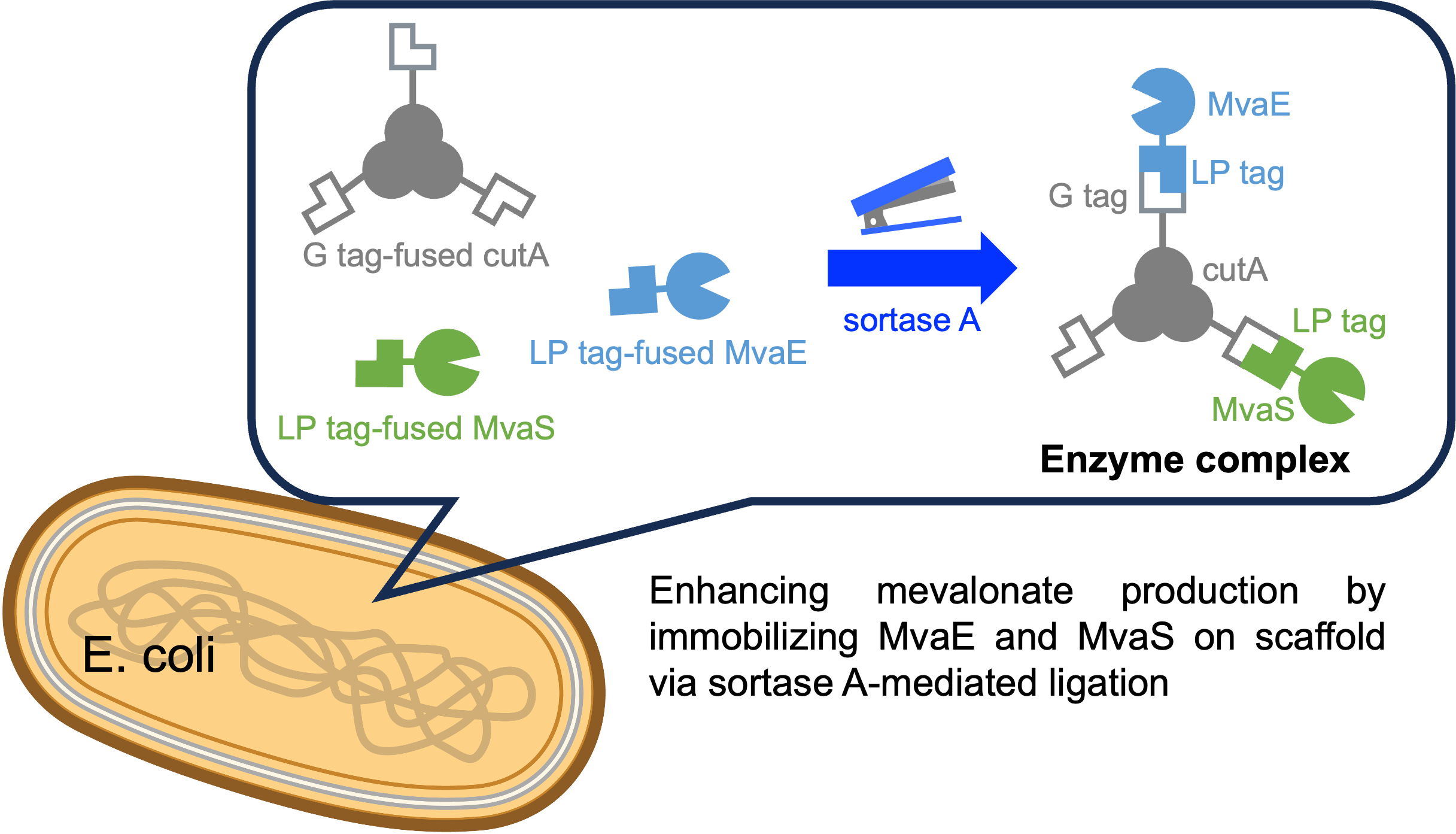
14 November 2024Sortase A-Mediated Enzyme Assembly on Multimeric Protein for Improving Mevalonate Production
Microorganisms have been extensively studied for their production of valuable chemicals. However, conventional gene fusion approaches often lack versatility and can result in enzyme inactivation. This study explored an alternative strategy for inducing metabolic channeling through sortase A-mediated ligation of metabolic enzymes. Sortase A recognizes specific amino acid sequences and selectively conjugates proteins at these sites. We focused on mevalonate production as a proof-of-concept to enhance the yield by assembling metabolic enzymes on a protein scaffold using sortase A. Although metabolic enzyme complexes were successfully formed using streptavidin as a scaffold, production did not improve. The use of CutA as a scaffold led to a 1.32-fold increase in production compared with that of the strain without the scaffold, demonstrating the efficacy of CutA in mevalonate production. These findings suggest that using sortase A to assemble metabolic enzymes onto a scaffold can effectively enhance microbial bioproduction.
Article
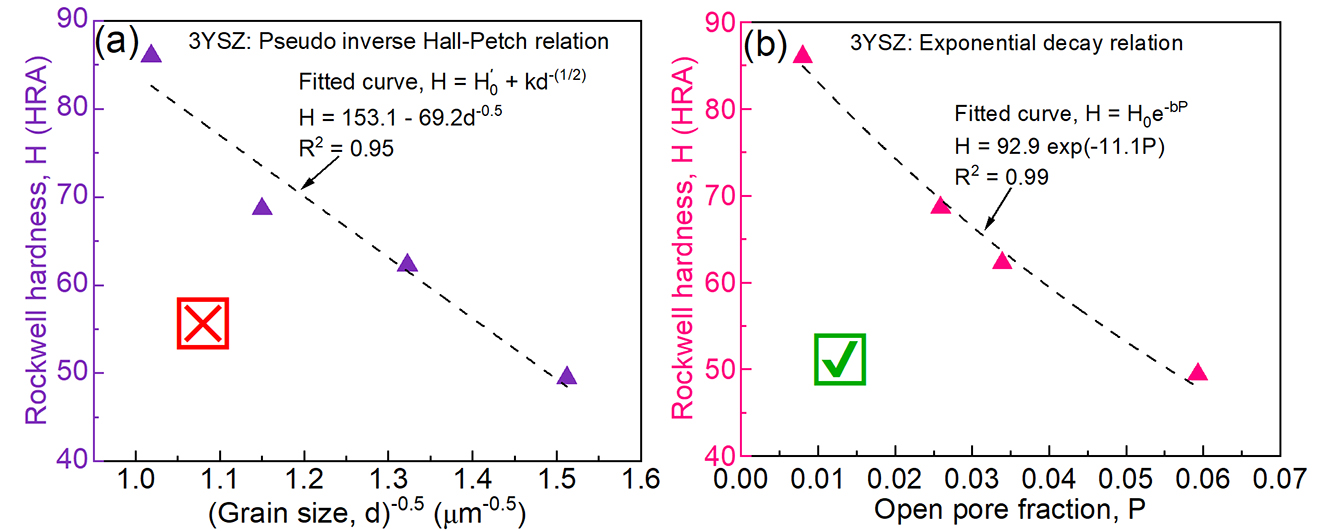
14 November 2024Hardness-Porosity-Grain Size Interrelationship in Conventionally Sintered 3 mol% Yttria Stabilized Zirconia
Considerable research has been done in the past on expensive, <50 nm particle size 3 mol% yttria-stabilized zirconia (3YSZ) using advanced sintering techniques. However, insights are still needed to reveal which factors among grain size and porosity, when both are changing simultaneously, more strongly control the hardness of conventionally sintered, relatively coarse, 250 nm 3YSZ powder, which can be used to make large industrial engineering ceramic parts at a lower cost. This investigation showed that elevating the sintering temperature from 1500 °C to 1650 °C increased the Rockwell hardness from 49.4 HRA to 86.0 HRA, which was concomitant with an increase in grain size and bulk density. A pseudo-inverse Hall-Petch relationship between hardness and grain size was observed given by H (in HRA) = 153.1 − 69.2/$$\small\sqrt{(\mathrm{grain}\,\mathrm{size})}$$ with a somewhat low R2 of 0.95, which was mainly due to the porosity being an additional important variable. Compared to grain size, the impact of open pore fraction (P) on hardness was stronger, inferred from a higher R2 of 0.99 while fitting the data into the well-known exponential decay equation, H = 92.9 exp(−11.1P). Finally, it was observed that the 3YSZ conventionally sintered at 1650 °C for 2 h had 0.8% open porosity, 6.08 g/cm3 bulk density, 960 nm grain size and consisted of only tetragonal ZrO2.
Review
13 November 2024Recent Advances in Developing Aldehyde-Accumulating Microbes and Future Perspective of Biosynthetic Applications
Aldehydes are a class of compounds that contain carbonyl groups in their side chains and are widely used in industries such as fragrances, flavoring compounds, and pharmaceutical intermediates. In recent years, there has been a substantial rise in the application of microbial synthesis to generate aldehyde compounds and their derivatives. This review will conduct an in-depth analysis of the literature related to the manipulation of microorganisms for aldehyde accumulation and the subsequent generation of aldehyde-derived products using metabolic engineering and synthetic biology principles. Furthermore, the review further highlights the prospects and future potential of employing these aldehyde-accumulating microorganisms to synthesize a diverse range of value-added chemicals.
