Found 297 results
Article
11 October 2023Fibrous SiC-based Mesoporous Solids for the Photocatalytic Degradation of Organic Pollutants under Artificial Light
SiC-based mesoporous solids with fibrous nanostructure were prepared by impregnation of a polycarbosilane precursor on annealed polyacrylonitrile (PAN) fibers and subsequent pyrolysis. The obtained material exhibits a mesoporous structure and has a specific surface area of ~20 m2/g. It has a semiconducting electronic character with a bandgap of 2.65 eV, i.e., in the visible range. Adsorption tests of methylene blue were performed on the material under dark conditions, which showed an adsorption amount of 78 wt%. The photocatalytic activity of the material was then evaluated for the degradation of the dye under artificial daylight irradiation over a period of 7 h. A degradation of 94 wt% was achieved. Regeneration and reuse of the material was also tested and resulted in 97 wt% degradation after reuse, indicating potential interest of the material as a contactor in environmental remediation devices.

Article
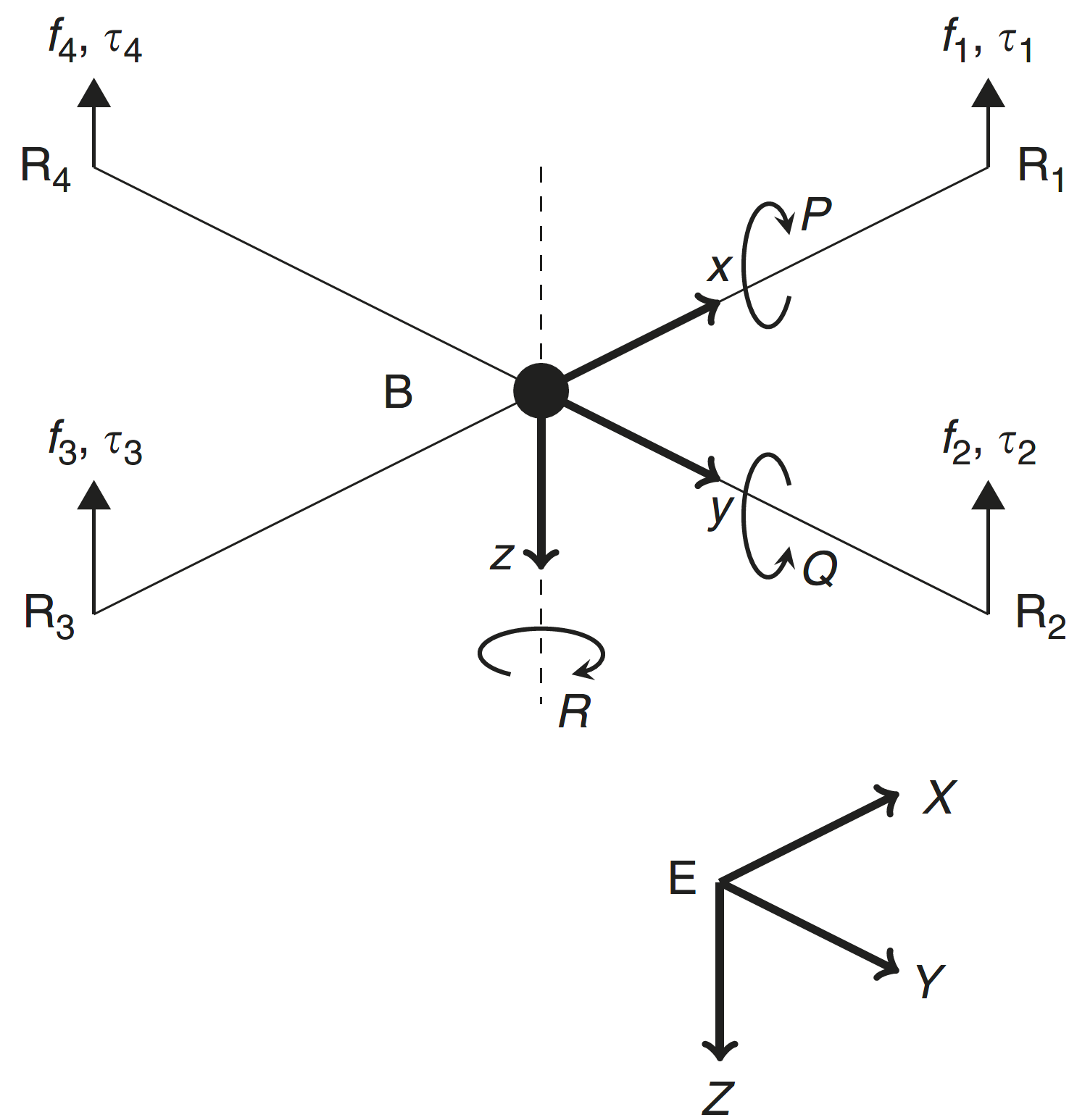
10 October 2023ℒ1 Adaptive Control of Quadrotor UAVs in Case of Inversion of the Torque Direction
This paper presents a method for fault tolerant control of quadrotor UAVs in case of inversion of the torque direction, a situation that might occur due to structural, hardware or software issues. The proposed design is based on multiple-model ℒ1 adaptive control. The controller is composed of a nominal reference model and a set of degraded reference models. The nominal model is that with desired dynamics that are optimal regarding some specific criteria. In a degraded model, the performance criteria are reduced. It is designed to ensure system robustness in the presence of critical failures. The controller is tested in simulations and it is shown that the multiple model ℒ1 adaptive controller stabilizes the system in case of inversion of the control input, while the ℒ1 adaptive controller with a single nominal model fails.
Article
07 October 2023Comprehensive Evaluation of Sustainable Treatment Technology of Oily Sludge Based on AHP-FCE
Oil is an unsustainable energy since it is non-renewable. However, oil may not be completely replaced in a short time, so the environmental problems caused by the oil development still require our attention. The oily sludge is a kind of hazardous waste produced during the oil development. To reduce the environmental impact caused by oily sludge, low-carbon and sustainable treatment technologies need to be selected. The incineration, chemical extraction and thermal desorption are common technologies for treatment of oily sludge. We calculated the carbon emissions of these technologies. Then the index evaluation system of oily sludge treatment technology was established with the environmental, economic, social, and technical factors. And the weight of evaluation index was determined by the analytic hierarchy process (AHP). Through the investigation of industry experts, we evaluated the treatment technologies by the fuzzy comprehensive evaluation method (FCE). The results showed that the carbon emissions of incineration are 42.70 t CO2-eq/t which is the highest. Meanwhile, it is 4.80 t CO2-eq/t and 0.10 t CO2-eq/t for chemical extraction and thermal desorption, respectively. The comprehensive scores of incineration, chemical extraction and thermal desorption were 4.59, 5.16 and 4.95, respectively. Therefore, the chemical extraction technology is an optimal treatment technology for oily sludge with the relatively low carbon emission and the highest comprehensive technical score. At the same time, the thermal desorption technology has strong application potential with the lowest carbon emissions. This result provides a reference for achieving clean and sustainable energy development processes.

Article
25 September 2023Depopulation Villages in Poland—Current Status and Possible Transition Scenarios
The picture of many localities undergoing depopulation will change in the coming years. A significant scale of migration and advanced ageing processes will result in an increase in the number of vacant buildings, or the removal of social infrastructure. The term ‘shrinkage’ tends to have negative connotations, but can lead to positive changes, e.g., an improvement in land structure under conditions of fragmented, dispersed agriculture. Depending on the quality of the natural environment and communication accessibility, other functions will develop there, including housing and recreation. However, a large part of the village may disappear completely.

Article
25 September 2023Anion Exchange Membrane Reinforced with Polyethylene Substrate for Alkaline Fuel Cell Applications
To enhance mechanical robustness of our in-house anion exchange membrane (QPAF-4), the reinforcement technique was applied using ozone-treated, porous polyethylene (PE) thin film (Toray SETELA) as a substrate. Homogenous and flexible reinforced membranes (QPAF-4-PE, 15–20 µm thick) were obtained by bar-coating method. The cross-sectional SEM image and EDS analysis revealed triple-layered (sandwich-like) structure without detectable pinholes. The QPAF-4-PE with ion exchange capacity (IEC) of 1.48 meq·g−1 exhibited lower water uptake (15 wt% at 90% relative humidity) and slightly lower hydroxide ion conductivity (71 mS·cm−1 at 80 ℃) than those of the pristine QPAF-4 (IEC = 1.84 meq·g−1, 25 wt% water uptake and 82 mS·cm−1 of the conductivity). The reinforced QPAF-4-PE exhibited slightly higher viscoelasticity (particularly, in MD direction) due to the suppressed water absorbability. Furthermore, the elongation at break increased by 9.8% in TD direction and 6.3% in MD direction. An H2/O2 fuel cell using QPAF-4-PE as membrane was investigated at different back-pressure, in which the cell with 100 kPa back-pressure onto the cathode side only achieved the maximum performance (176 mW·cm−2 at current density of 364 mA·cm−2) and the longest durability for (>200 h) at a constant current density of 100 mA·cm−2 maintaining 0.43 V of the cell voltage (67% remaining). The durability was eight times longer than that with ambient pressure and two times longer than that with back-pressure on both sides.

Perspective
13 September 2023Estimate of Economic Impact of EVs Li-ion Batteries Recovery
Nowadays, increasing attention is directed towards the sustainable use of raw materials. For a circular economy, recovery from spent devices represents a fundamental practice. With the transition to electric mobility, an increasing number of devices powered by lithium batteries are produced. Indeed, this is the fastest growing sector producing spent batteries, which are an important secondary source of critical raw materials, such as lithium, cobalt, graphite, and nickel. Therefore, this work aims to quantify the economic impact of recovering raw materials from lithium batteries used in the electric vehicles sector. Based on the chemical composition of the various lithium batteries and their market diffusion, the intrinsic economic value of this waste has been estimated to be around 6500 €/ton. Starting from the literature data on the global energy demand from lithium batteries and deriving the trend of their specific energy over time, the mass of material introduced into the market annually is estimated to reach 60 Mton/year by 2040. The annual amount of end-of-life lithium batteries was calculated by applying the Weibull distribution to describe the probability of failure, yielding 10 Mton/year by 2040. Finally, based on these results, the economic impact of the recovery market was assessed for two different scenarios.

Review
01 September 2023In Vitro BioTransformation (ivBT): Definitions, Opportunities, and Challenges
Great needs always motivate the birth and development of new disciplines and tools. Here we propose in vitro BioTransformation (ivBT) as a new biomanufacturing platform, between the two dominant platforms—microbial fermentation and enzymatic biocatalysis. ivBT mediated by in vitro synthetic enzymatic biosystems (ivSEBs) is an emerging biomanufacturing platform for the production of biocommodities (i.e., low-value and bulk biochemicals). ivSEB is the in vitro reconstruction of artificial (non-natural) enzymatic pathways with numerous natural enzymes, artificial enzymes, and/or (biomimetic or natural) coenzymes without living cell’s constraints, such as cell duplication, basic metabolisms, complicated regulation, bioenergetics, and so on. The two great needs (i.e., food security and the carbon-neutral renewable energy system) have motivated the birth and development of ivBT. Food security could be addressed by making artificial food from nonfood lignocellulose and artificial photosynthesis for starch synthesis from CO2. The carbon-neutral renewable energy system could be addressed by the construction of the electricity-hydrogen-carbohydrate cycle, where starch could be a high density of hydrogen carrier (up to 14.8% H2 wt/wt) and an electricity storage compound (greater than 3000 Wh/kg). Also, ivBT can make a number of biocommodities, such as inositol, healthy sweeteners (e.g., D-allulose, D-tagatose, D-mannose), advanced biofuels, polymer precursors, organic acids, and so on. The industrial biomanufacturing of the first several biocommodities (e.g., myo-inositol, D-tagatose, D-mannose, and cellulosic starch) would wipe off any prejudice and doubt on ivBT. Huge potential markets of biocommodities with more than tens of trillions of Chinese Yuan would motivate scientists and engineers to address the remaining technical challenges and develop new tools within the next decade.

Review
28 August 2023Dynamic Metabolic Control: From the Perspective of Regulation Logic
Establishing microbial cell factories has become a sustainable and increasingly promising approach for the synthesis of valuable chemicals. However, introducing heterologous pathways into these cell factories can disrupt the endogenous cellular metabolism, leading to suboptimal production performance. To address this challenge, dynamic pathway regulation has been developed and proven effective in improving microbial biosynthesis. In this review, we summarized typical dynamic regulation strategies based on their control logic. The applicable scenarios for each control logic were highlighted and perspectives for future research direction in this area were discussed.

Review
15 August 2023Green Composites Using Naturally Occurring Fibers: A Comprehensive Review
Depletion of non-renewable resources and health hazards of petroleum-based polymers and plastics has enforced the development of eco-friendly materials. The use of conventional plastics has to be minimized and can be replaced with environmentally friendly and sustainable bio-based polymers or biopolymers due to extensive environmental impact. A major share of petroleum-based polymers is used for polymeric composites with research focus on green composites and biocomposites containing renewable/bioderived matrix polymer and fillers from naturally occurring fibers. Biocomposites hold great promise to replace petroleum-based polymer composites owing to their lower cost, non-toxicity, abundance of raw material, renewability, and high specific strength. All these merits of biocomposites have led to an increment in the development of new biocomposites with enhanced properties, wide applicability and ever demanding criteria. The recently published review studies detailed the raw materials used, fabrication techniques, characterization, and applications including biodegradation and rheological studies performed in recent years. This review covers all the important properties of biocomposites along with detailed description of synthesis, properties, characterizations and applicability of these green composites in several areas. The review also focuses on their raw materials, types, recent biocomposites, processing techniques, characterizations, applications, and current challenges with future aspects.

