Found 297 results
Article
14 March 2025A Conceptual Design of Industrial Asset Maintenance System by Autonomous Agents Enhanced with ChatGPT
This article introduces OPRA (Observation-Prompt-Response-Action) and its multi-agent extension, COPRA (Collaborative OPRA), as frameworks offering alternatives to traditional agent architectures in intelligent manufacturing systems. Designed for adaptive decision-making in dynamic environments, OPRA enables agents to request external knowledge—such as insights from large language models—to bridge gaps in understanding and guide optimal actions in real-time. When predefined rules or operational guidelines are absent, especially in contexts marked by uncertainty, complexity, or novelty, the OPRA framework empowers agents to query external knowledge systems (e.g., ChatGPT), supporting decisions that traditional algorithms or static rules cannot adequately address. COPRA extends this approach to multi-agent scenarios, where agents collaboratively share insights from prompt-driven responses to achieve coordinated, efficient actions. These frameworks offer enhanced flexibility and responsiveness, which are critical for complex, partially observable manufacturing tasks. By integrating real-time knowledge, they reduce the need for extensive training data and improve operational resilience, making them a promising approach to sustainable manufacturing. Our study highlights the added value OPRA provides over traditional agent architectures, particularly in its ability to adapt on-the-fly through knowledge-driven prompts and reduce complexity by relying on external expertise. Motivational scenarios are discussed to demonstrate OPRA’s potential in critical areas such as predictive maintenance.
Review
13 March 2025Review on Vibration Control of Wafer Handling Robot
The wafer handling robot serves as the pivotal component of the wafer transfer system, wherein its operational speed and motion precision exert a direct influence on both the yield and productivity of wafer processing. With the semiconductor manufacturing process advancing towards nanoscale linewidths and heightened throughput, the time-varying stiffness characteristics of the flexible joints in wafer handling robots, along with the resultant end vibration issues, have emerged as critical challenges that constrain overall performance. A comprehensive understanding of the stiffness change mechanisms, coupled with enhancements in control methodologies, plays an indispensable role in the effective vibration control of wafer handling robots. To facilitate research in pertinent areas, this paper systematically reviews the cutting-edge methods for vibration suppression in variable stiffness flexible joint wafer handling robots, concentrating on the following core aspects: The impacts of diverse dynamic stiffness identification methodologies on the accuracy of stiffness identification are thoroughly examined; This paper also explores the potential of collaborative optimization strategies involving trajectory planning, control methodologies, and lightweight intelligent algorithms in enhancing real-time control. Furthermore, it evaluates the application scenarios and feasibility of passive vibration absorbers and semi-active adjustable dampers within the context of broadband vibration suppression technologies. In conclusion, this paper synthesizes and critically discusses the advantages and limitations inherent in various research findings, while also constructing a “model-control-vibration suppression” closed-loop optimization system aimed at facilitating ultra-precision vibration control of wafer handling robots under conditions of high dynamic operation. By elucidating the bottlenecks present in existing technologies alongside the trajectory for future interdisciplinary integration, this work provides theoretical support for the intelligent advancement of wafer handling robots and fosters the expedited and reliable development of wafer transfer systems.

Article
12 March 2025How Do Gender-Based Employment, Agricultural Machinery, and Fertilizers Influence Regional Agricultural Productivity? Panel Analyses for South and Southeast Asian Countries
The analysis delves into key strategies for enhancing agricultural productivity in Southeast Asia and South Asia. It underscores the vital role of mechanization, sustainable input practices, and gender-inclusive policies. Customized interventions in these realms hold promise for significantly amplifying agricultural performance in the region. Fertilizer and machinery productivity are pivotal factors that correlate strongly with overall agricultural productivity, as revealed by regression analyses. Notably, male employment in agriculture and agricultural machinery exhibits positive and substantial impacts on agricultural productivity, while female employment and fertilizer consumption indicators show significant yet negative associations. The study highlights systemic issues such as unequal resource access and differing gender roles in agriculture that may impede the immediate productivity gains from increased female labor force participation. Mechanization and efficient fertilizer utilization emerge as critical drivers of enhanced agricultural output, with consistent coefficients across models. Male employment consistently demonstrates a positive influence on productivity, emphasizing the significance of labor force engagement in agriculture. Moreover, the study underscores the imperative of judicious fertilizer management to avert environmental degradation and diminishing returns. The findings affirm the efficacy of the random effects model, supported by the Hausman test, which indicates congruence in results between fixed and random effects models. This methodological choice ensures robust and reliable conclusions regarding the relationships between male and female employment, machinery, fertilizer consumption, and agricultural productivity in South and Southeast Asia.
Article
12 March 2025Cultural and Sex Differences in Emerging Adults: Identity Uncertainty, Psychological Symptoms and Adjustment at University
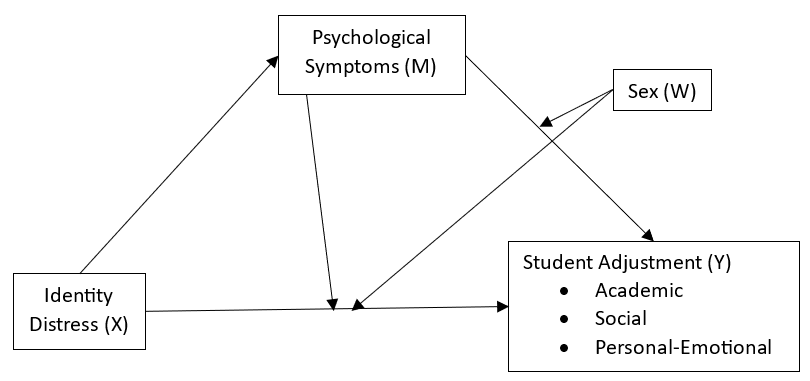
From the perspective of emerging adulthood, we investigated the role of culture and sex in associations between uncertainty and distress in identity development, psychological symptoms, and functioning at university among students in Canada, Spain, and Ecuador. The countries were categorized as individualistic or collectivistic according to Hofstede’s cultural dimensions. Participants included 661 students (median = 18 years, 76.6% female) in Canada (51.6%), Spain (16.2%), and Ecuador (32.2%). They completed the Identity Distress Scale, College Assessment of Psychological Problems Scale, and Student Adjustment to College Questionnaire with online surveys. Spanish students reported the greatest identity distress. Elevated academic adjustment was found for Ecuadorian students, who along with Spanish students exceeded those in Canada on social adjustment. Psychological symptoms mediated linkages between identity distress and academic and social adjustment for Canadian and Spanish women. Conversely, mediation was supported for the personal-emotional functioning of all students. Unexpected differences were found between males and females for identity distress and psychological difficulties among students in the individualistic countries. The findings underscore the need for the attention of researchers and counselors to potential variations in culture, sex, and other relevant personal and contextual factors and how they influence the identity development and well-being of university students worldwide.
Article
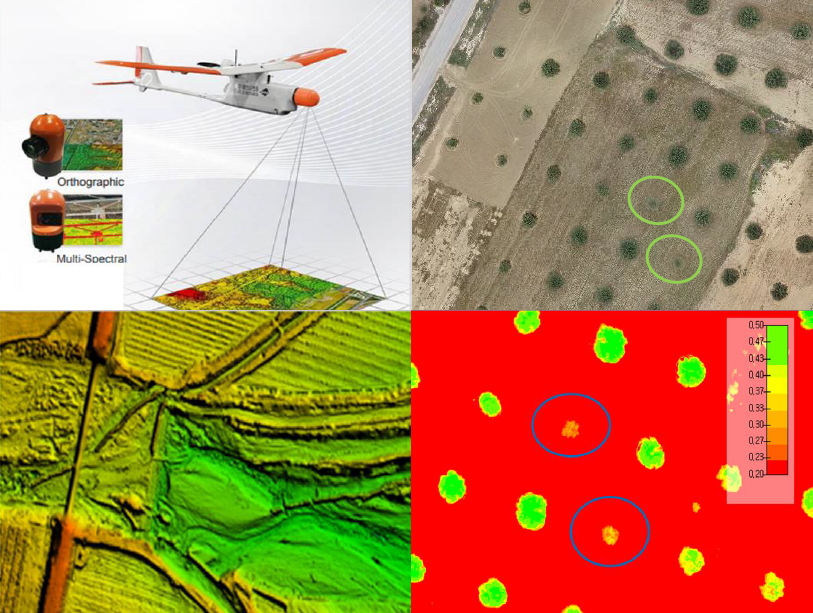
10 March 2025Leveraging Drone Technology for Precision Agriculture: A Comprehensive Case Study in Sidi Bouzid, Tunisia
The integration of drone technology in precision agriculture offers promising solutions for enhancing crop monitoring, optimizing resource management, and improving sustainability. This study investigates the application of UAV-based remote sensing in Sidi Bouzid, Tunisia, focusing on olive tree cultivation in a semi-arid environment. REMO-M professional drones equipped with RGB and multispectral sensors were deployed to collect high-resolution imagery, enabling advanced geospatial analysis. A comprehensive methodology was implemented, including precise flight planning, image processing, GIS-based mapping, and NDVI assessments to evaluate vegetation health. The results demonstrate the significant contribution of UAV imagery in generating accurate land use classifications, detecting plant health variations, and optimizing water resource distribution. NDVI analysis revealed clear distinctions in vegetation vigor, highlighting areas affected by water stress and nutrient deficiencies. Compared to traditional monitoring methods, drone-based assessments provided high spatial resolution and real-time data, facilitating early detection of agronomic issues. These findings underscore the pivotal role of UAV technology in advancing precision agriculture, particularly in semi-arid regions where climate variability poses challenges to sustainable farming. The study provides a replicable framework for integrating drone-based monitoring into agricultural decision-making, offering strategies to improve productivity, water efficiency, and environmental resilience. The research contributes to the growing body of knowledge on agricultural technology adoption in Tunisia and similar contexts, supporting data-driven approaches to climate-smart agriculture.

Communication
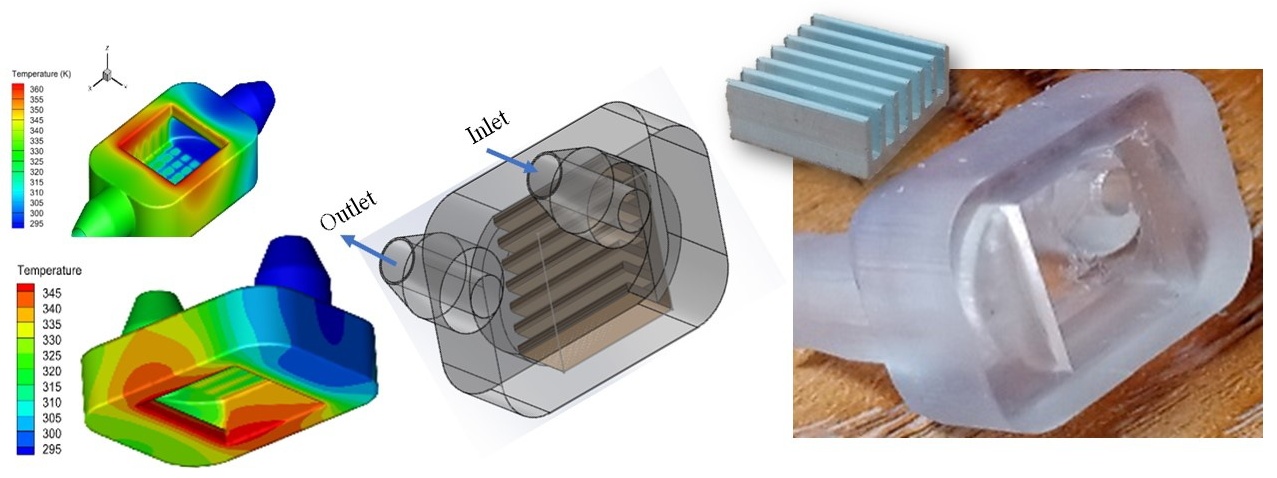
10 March 2025Design Effect of a Mini Channels Heat Sink Using Additive Manufacturing
The present work aims to examine the influence of designing mini channel heat sinks using Stereolithography (SLA) 3D printing. Stereolithography (SLA) is a common additive manufacturing technique. The internal mini channels of the heat sink are made of aluminium materials and the outer cover is made of commercial polymer. Three models of the mini channel heat sinks are considered. A constant heat flow is applied to the bottom wall of the heat sink, and water is used as a coolant. The flow and heat transfer were studied for different cooling speeds. The physical properties of the fluid provided good thermal performance for the heat sink, especially at increased flow rates. The acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) copolymer resin has shown its good insulator for the heat sink and has improved the performance of the heat sink. This study demonstrates that the ABS copolymer resin enhances the cooling of electronic components.
Review
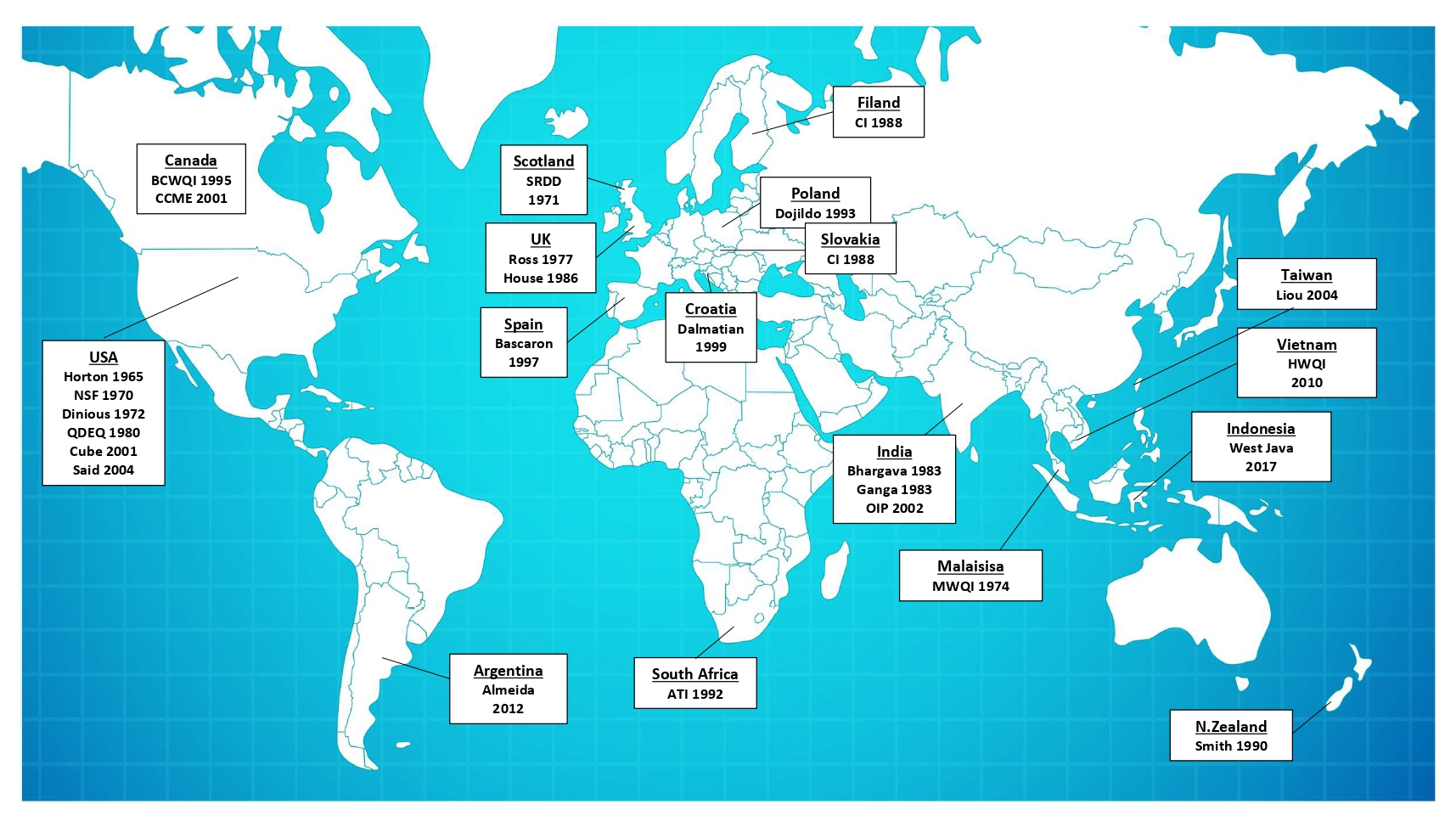
10 March 2025A Review on Water Quality Indices
Water, as vital natural resource, is indispensable for human activities, both directly and indirectly. It significantly contributes to a country’s economic development, encompassing above-ground and underground water resources. However, ongoing pollution from surface contaminants is causing concerning degradation in both confined and unconfined aquifers, warranting the need for addressing this issue. Water quality indices (WQIs) serve this purpose by simplifying complex water quality data, providing a single value for easier interpretation. Surface water quality indices have achieved global recognition, while the development of groundwater quality indices is an evolving field. WQIs are established based on specific water quality criteria set by national and international organizations, which consider various parameters based on the intended use of water bodies. Consequently, numerous WQI models exist, including National Sanitation Foundation (NSFWQI), Oregon (OWQI), British Columbia (BCWQI), Canadian Council of Ministers of the Environments (CCMEWQI), and country-specific variants tailored to the unique requirements of individual regions such as Vietnam, India, Indonesia, Spain, Canada, Malaysia, and others, all in accordance with the specific characteristics of the water system under assessment.
Article
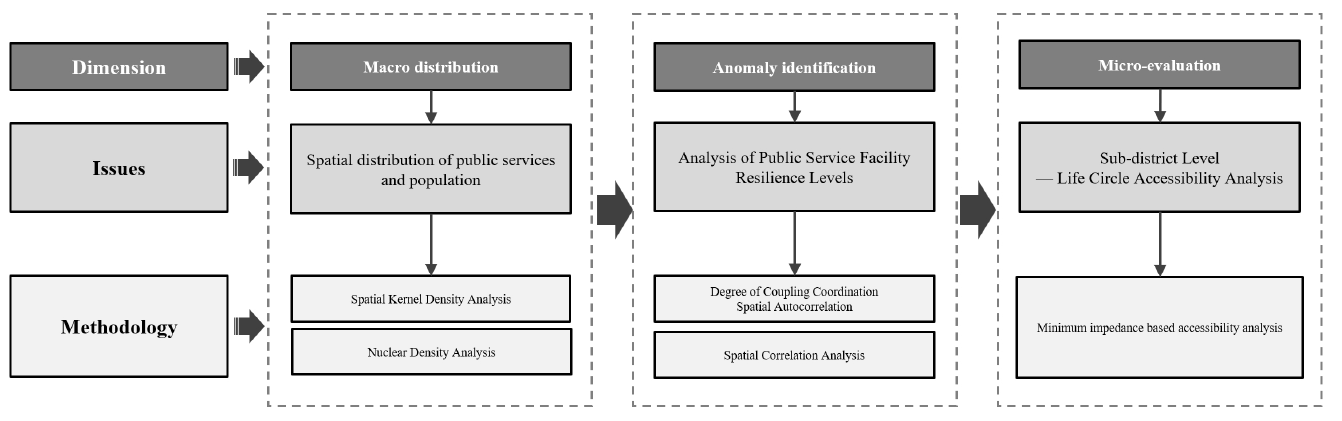
07 March 2025Constructing an Urban Spatial Resilience Assessment Framework Based on Public Service Facilities: A Case Study of Beijing
This paper takes Beijing as a research object to develop a framework for assessing urban public service facilities’ resilience, incorporating both macro and micro perspectives. Initially, the study utilizes spatial matching theory and coupling coordination models at the district and sub-district levels to analyze the spatial coupling between public service facility layouts and population distribution, thereby identifying regions exhibiting discrepancies in service supply and demand. Building on this foundation, the research further investigates at the neighborhood level the alignment between different types of public service facilities and residents’ daily activity patterns through the living circle theory and accessibility analysis models. From a macro perspective, research findings indicate that the layout of Beijing’s public service facilities exhibits a radial structure of centralized clustering and polycentric dispersion and that the resilience of these facilities diminishes from the city center outward. Microanalysis in three outlier sub-districts of Chaoyang District reveals that the accessibility to cultural and social welfare facilities in Daitou Sub-district is below the regional average and exceeds the typical 15-min walking distance accessible to the average person. Based on these findings, the paper proposes specific policy recommendations, including prioritizing the establishment of multifunctional public service facilities in densely populated and underserved peripheral areas and reserving adequate land for facilities in newly developing areas to ensure the sustainability of urban growth. Additionally, it is recommended that urban planners utilize dynamic data updating mechanisms to adjust the distribution of public service facilities, thereby better accommodating changes in population structure. This study not only highlights the dual role of public service facilities in enhancing urban resilience and living quality but also provides theoretical support and empirical evidence for creating a human-centered urban resilience spatial structure.
Review
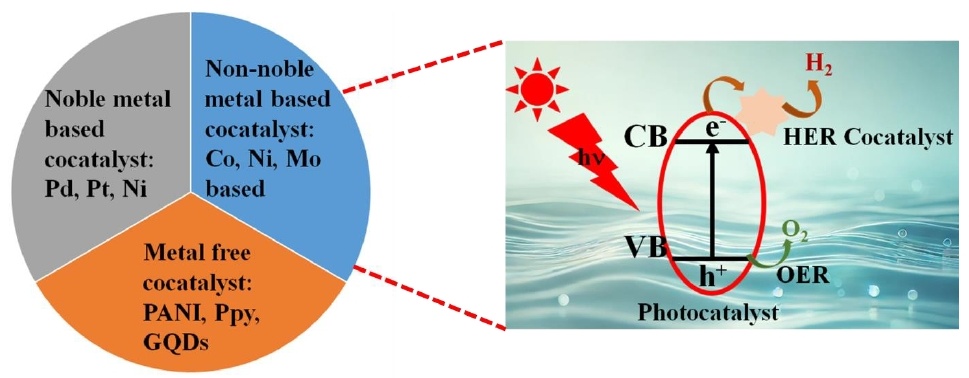
07 March 2025Unravelling the Role of Hydrogen Evolution Reaction Co-Catalysts in Photocatalytic Water Splitting: Mechanistic Insights and Material Strategies
The reliance on fossil fuels has led to a substantial increase in greenhouse gas emissions, presenting a critical environmental challenge. Addressing this issue necessitates the adoption of alternative renewable energy sources, with green hydrogen emerging as a promising candidate due to its high gravimetric energy density and absence of harmful emissions. Among the various hydrogen production techniques, photocatalytic technology has garnered significant attention for its dual potential to produce green hydrogen and degrade pollutants, thereby addressing both energy and climate crises. Efforts to scale photocatalytic technology for industrial applications have identified cocatalyst integration as a pivotal strategy, as it enhances reaction kinetics by lowering the activation energy and mitigating charge carrier recombination. This review comprehensively examines the hydrogen economy, the underlying principles of photocatalysis, recent technological advancements, key factors influencing photocatalytic reactions, the role of catalysts in hydrogen evolution reaction (HER) surface mechanisms, strategies for cocatalyst optimization, and future directions for the field.
Review
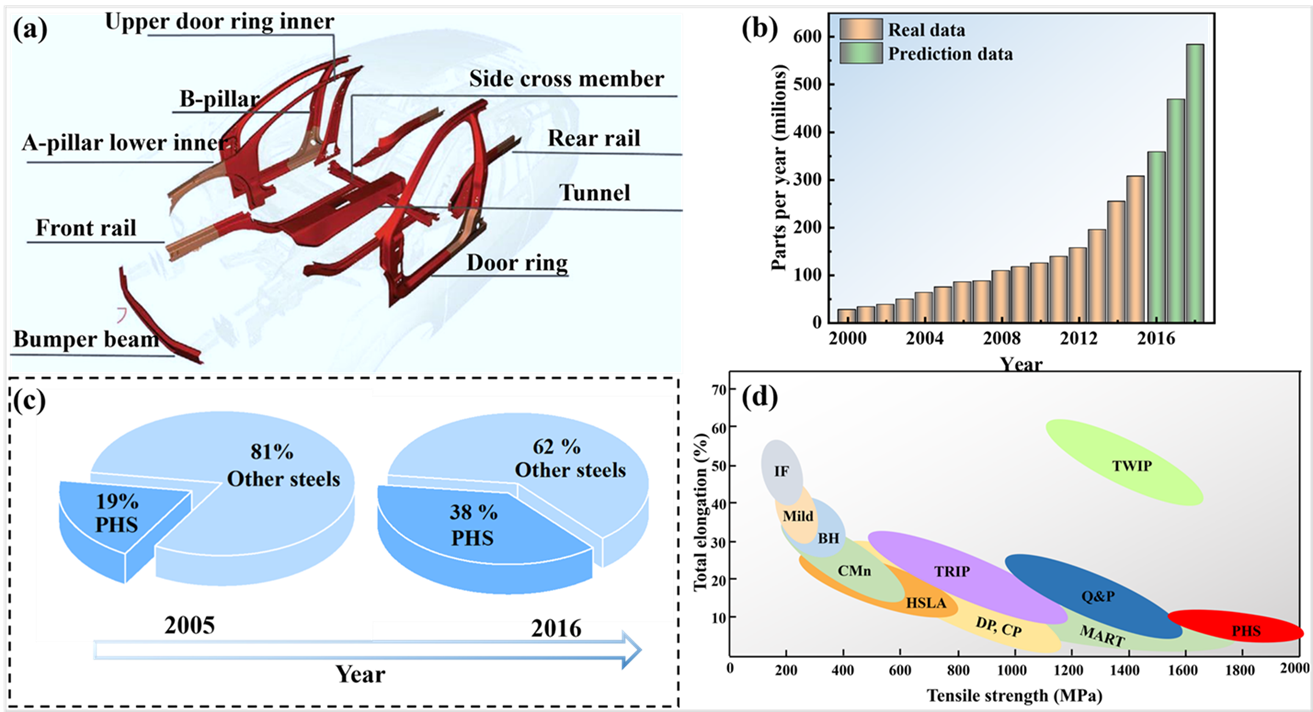
06 March 2025A Comprehensive Review towards Oxidation Resistant Press-Hardened Steels
As an important lightweight material, press-hardened steels (PHS) are now widely used in the car body-in-white. However, severe oxidation of conventional Mn–B bare sheets not only damages production molds, but also prevents subsequent welding and painting, leading to a significant increase in production costs. The aim of this review is to systematically summarize the current solutions to overcome the problem of high-temperature oxidation of conventional Mn–B PHS and to highlight future directions for improvement. The review begins with a brief background on PHS, followed by a detailed description of measures to improve the oxidation resistance of conventional Mn–B PHS and the development of novel PHS with superior oxidation resistance. The oxidation resistance solutions for conventional Mn–B PHS mainly include the use of coatings and pre-deposited films. In contrast, the oxidation resistant PHS mainly includes the use of the oxidation resistant elements Cr, Si, Al or rare earth elements to improve the steel’s own high-temperature oxidation resistance.