Found 297 results
Article
29 April 2025Application of recovered Carbon Black (rCB) by Waste Tire Pyrolysis as an Alternative Filler in Elastomer Products
The increasing global accumulation of End-of-Life (EoL) tires and the growing demand for fossil industrial Carbon Black (CB) call for sustainable alternative solutions. In this context, tire pyrolysis and the resulting recycled raw material recovered Carbon Black (rCB), are considered potential alternatives. In the study, various rCBs were incorporated into new elastomer compounds using a laboratory internal mixer and their properties were investigated. The compounds were selected based on examples of applications such as bicycle inner tubes and hydraulic membranes. By comparing the in-rubber properties of rCB-based compounds with CB reference compounds, an initial assessment of the potential use of rCB for the chosen products was derived. Compared to industrial carbon black, the use of rCB leads to a reduction in performance. Although increasing the filler content partially compensated for the mineral content in rCB and led to a slight improvement, it could not fully offset the performance loss.

Article
28 April 2025Production and Characterization of Recovered Carbon Black (rCB) by Waste Tire Pyrolysis as a Potential Carbon Black (CB) Substitute
Recovered Carbon Black (rCB) from scrap tire pyrolysis offers a potential alternative to fossil-based virgin Carbon Black (CB) in the context of a circular economy. This study investigated the influence of pyrolysis process parameters on rCB yield and quality at laboratory and semi-industrial scales. The resulting rCBs were characterized and found to have surface and structural properties comparable to N500 and N600 series CBs, but with higher mineral and volatile contents. The quality of rCB is influenced by the feedstock composition, particularly the ratio of organic to inorganic components as well as key process parameters such as heating rate, pyrolysis temperature and residence time. Higher heating rates accelerate degradation and shift product distribution toward increased oil yield and reduced rCB formation, while higher pyrolysis temperatures lead to lower volatile content in rCB. Additionally, reactor and process design affect heat distribution, transfer efficiency, and mixing behavior, further shaping rCB properties. However, further testing is required to evaluate the actual in-rubber properties of rCBs. Therefore, additional tests are planned, incorporating rCB into butyl and nitrile rubber-based elastomer compounds, which will be addressed in a follow-up study. In addition, data from the current experiments will support a comprehensive Life Cycle Assessment (LCA) to evaluate the environmental impacts of tire pyrolysis and rCB production compared to other recycling methods, with details to follow in a future publication.
Article
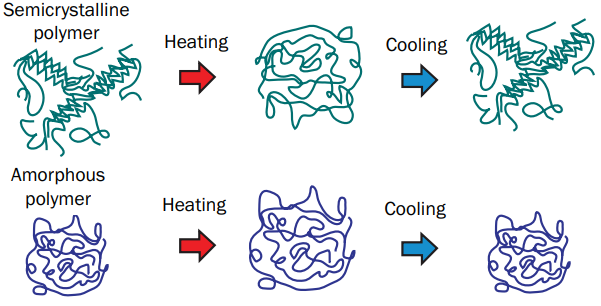
27 April 2025Steel and Aluminium Moulds: Comparative Analysis of Optimal Parameters to Inject Amorphous and Semicrystalline Polymers
The thermoplastic injection moulding process is very important in the plastics industry, as it enables automated production, supports high productivity and allows the production of plastic parts with complex geometries. It is possible to split into two large groups of polymers: amorphous and semicrystalline. Cooling rate and other injection moulding parameters have a great influence on the final properties of the plastic part. Regarding the use of aluminium as cavity material in injection moulds, new variables must be included in the analysis, since its thermal properties are significantly different from those presented by steels, which are traditionally used. In this way, the purpose of this study was to evaluate the effect of aluminium and steel cavities on different types of thermoplastics belonging to the two classes of polymers by assessing the injection parameters of a high-production part (automotive cup holder). In terms of productivity factors, moulds made of aluminium using semicrystalline polymers showed more significant reductions in cycle time compared to amorphous materials. Specifically, polypropylene exhibited a cycle time reduction between 40.6% and 52.5% when compared to steel moulds, while polyamide showed an even more substantial reduction, ranging between 56% and 63.5%. As for warpage, the amorphous materials displayed the lowest values for both types of moulds, but they also exhibited greater variations in isothermal simulations compared to semicrystalline materials. In relation to the mould materials, aluminium mould exhibited the lowest warping results and smaller variations compared to the isothermal analyses for all polymers.
Article
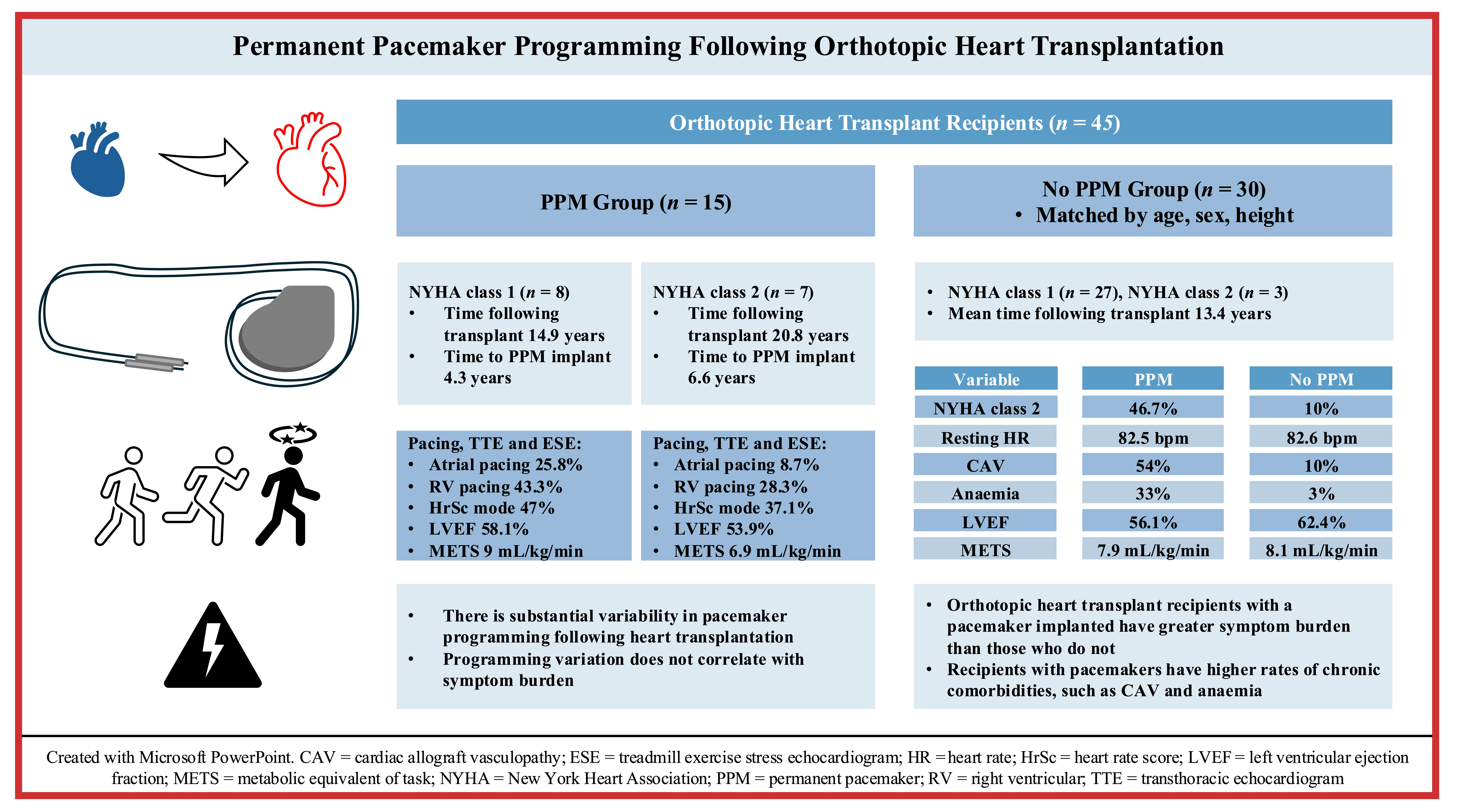
27 April 2025The Impact of Pacemaker Programming on Morbidity in Heart Transplant Recipients
Pacemaker programming recommendations in patients post-heart transplant include a higher lower rate limit, activating rate response mode, maximising battery longevity and minimising ventricular pacing in patients without atrioventricular block. This study sought to investigate how variability in pacemaker programming following orthotopic heart transplant affects morbidity. We conducted a retrospective analysis of heart transplant recipients at a single transplant centre between 1991 and 2023. Patients requiring pacemaker implantation following transplantation were matched with non-pacemaker recipients by age, sex and height. Patient and device characteristics were reviewed. Clinical outcomes, programming and physiological parameters were compared within the pacemaker group and between subject and comparator groups. Forty-five heart transplant recipients were included: 15 with pacemakers and 30 without. Within the pacemaker group, 20% were programmed with LRL > 60 bpm, rate-response mode in 47% and algorithms minimising ventricular pacing in 27%. Fifty-three percent were NYHA class I, and 46% NYHA class II; resting heart rate was similar between the groups (85 (SD14.9) and 79 (SD8) bpm: p = 0.33). NYHA class I group achieved a higher workload (METS 9 (SD2.7) vs. 6.9 (SD1) mL/kg/min: p = 0.21), and peak heart rate (135 (18.8) vs. 123 (14.8) bpm: p = 0.29) during exercise stress echocardiogram (ESE). The pacemaker group was more symptomatic than the comparator group (NYHA class II 46% vs. 10%: p = 0.016) and exhibited higher rates of cardiac allograft vasculopathy (53% vs. 10%: p = 0.005). There is substantial variability in pacemaker programming in heart transplant recipients. Patients who require a pacemaker have a greater symptom and comorbidity burden than those without. No identifiable physiological or programming differences stratified the greater morbidity within the pacemaker cohort.
Review
27 April 2025Efficient Communication, the Lexicon, and Grammar
The driving forces behind language variation and change have long been a subject of debate. One prominent approach takes a functionalist perspective and posits that the need for efficient communication shapes lexical and grammatical patterns. This paper reviews five recent studies that offer further support for the plausibility of the communicative efficiency principle while also providing new insights into other factors that contribute to efficient linguistic structures. The key findings from these studies can be summarized as follows: (1) the principle of communicative efficiency offers plausible explanations for both lexical and grammatical phenomena, addressing both synchronic variations and diachronic changes in language evolution; (2) linguistic systems achieve efficiency through multiple mechanisms such as creation bias and selective pressures favoring efficient communication; (3) in addition to communicative efficiency, language evolution is also shaped by language history, with existing structures influencing subsequent ones. By synthesizing these studies, this paper underscores the efficiency account as a plausible and inclusive explanatory framework. It also stresses the need to rigorously delineate the role of communicative efficiency in language evolution, cautioning against automatically conflating the presence of efficient structures with intentional optimization for communicative goals.

Article
25 April 2025Human Behavioral Ecology: Opportunities for Theoretically Driven Research on Human Behavioral Variation in China
Human behavioral ecology is an evolutionary framework that attempts to understand how adaptive human behavior maps on to variation in social, cultural, and ecological environments. It emerged as a coherent framework in the United States and the U.K. in the 1980s and has flourished as an explanatory framework ever since. The concentration of HBE scholarship in English-speaking countries has led to missed opportunities to engage other partners in testing and expanding human behavioral ecological models of human behavioral and life history variation. In this review, we provide a brief review of human behavioral ecology and describe opportunities for related scholarship in the Chinese context. We introduce human behavioral ecology holistically, including its history, methodological frameworks, pet topics, and recent integration with related fields, with a special emphasis on its recent integration with Chinese social, archaeological, and life sciences scholarship. We address potential criticisms of human behavioral ecology and how to ensure a robust and careful application of human behavioral ecology principles in the study of human behavior in China, past and present. We conclude with excitement as the remarkable variation in the Chinese behavioral landscape offers unparalleled opportunities for innovative and integrative studies.
Article
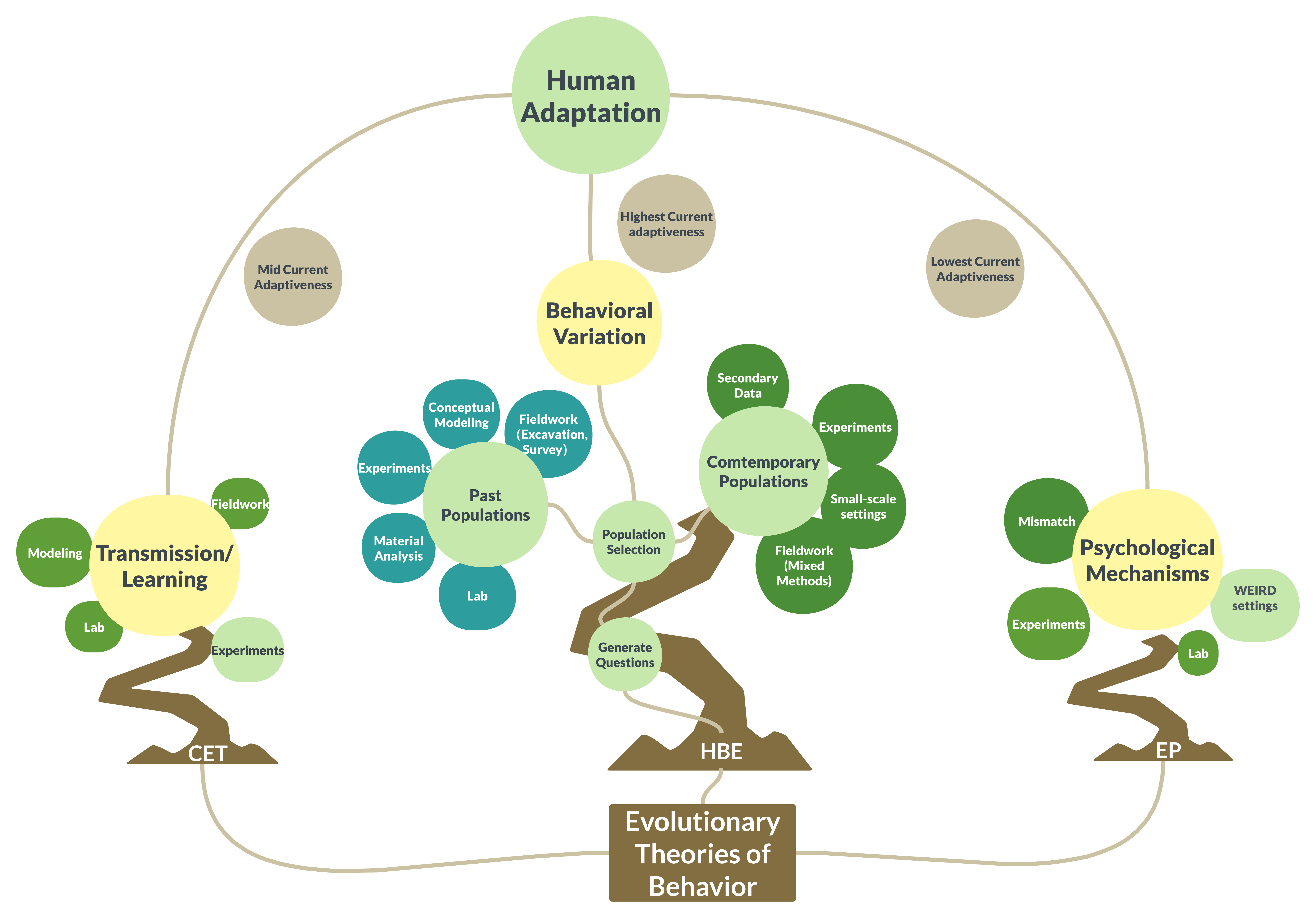
25 April 2025The Crystal Structure of Apatite and Copper-Doped Apatite
The recent claim of superconductivity above room temperature in Pb10−xCux(PO4)6O, where 0.9 < x < 1 (referred to as LK-99), has generated significant interest. In this study, we first investigated the detailed crystal structures of four natural apatite by single crystal X-ray diffraction (SXRD) combined with a scanning electron microscope (SEM) equipped with energy dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDX) measurement. Secondly, pilot experiments of doping copper (Cu) atoms into the apatite lattice were carried out by high-temperature mixed pure copper and natural apatite powders. Finally, copper-doped lead apatite has been synthesized via a three-step solid-state reaction method, and its crystal structure has been determined using SXRD, SEM/EDX, and transmission electron microscopy (TEM).
Article
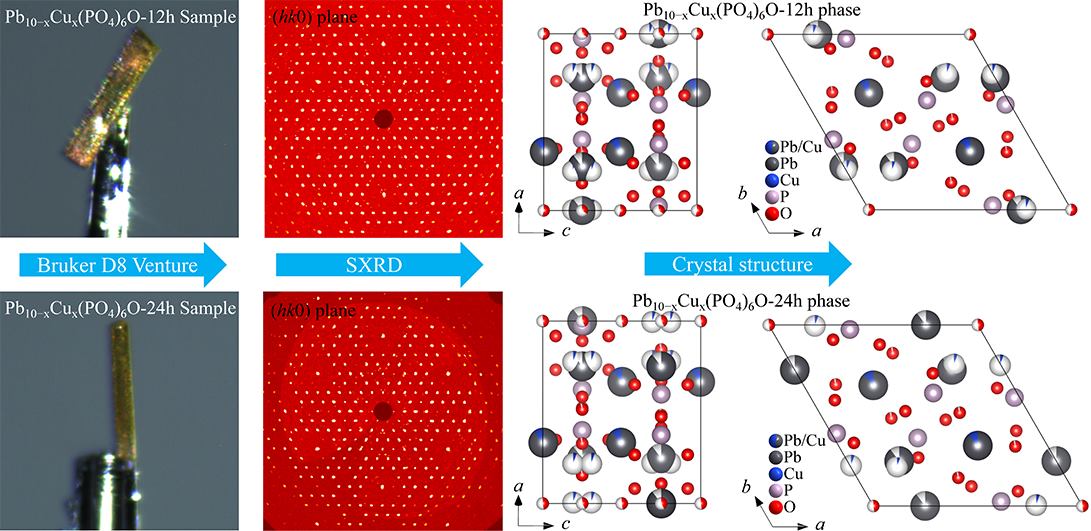
23 April 2025Socio-Economic and Environmental Impacts of Jamrani Irrigation Dam Project, Kumaon Himalaya, India
This paper examines the economic and environmental impacts of the proposed Jamrani Irrigation Dam Project on the upstream and downstream areas. This study is primarily empirical, and a case study of six villages was conducted. A total of 415 households are being affected—fully and partially, due to the construction of the dam, out of which 122 heads of households were interviewed. A structured questionnaire was constructed, and the heads of households were asked about the socio-economic and environmental impacts of the proposed dam project. Furthermore, a detailed perception study of these households was conducted. Secondary data related to the size of the dam project, various land uses being affected by the dam, its socio-economic and environmental impact, and the most beneficial sectors were collected from the irrigation department, Government of Uttarakhand’s report 2020. In addition, socio-economic data from 415 households were collected from the same source. This study reveals that the dam project will have many favourable economic impacts in terms of supplying ample water for drinking and irrigation, electricity generation, development of infrastructural facilities and tourism, and the Gaula River flood control. On the other hand, the dam project will lead to land degradation, depletion of faunal and floral resources, soil erosion, and finally, the rehabilitation of the affected people. This study suggests that the proper use of technology and a suitable rehabilitation policy will make the project successful.
Review
22 April 2025Counterfeit Drug Investigations: Techniques, Challenges, and the Role of Abductive Reasoning
Variable types of investigations exist regarding counterfeit drug detection, disruption, and regulation. Counterfeit drugs are spurious drugs, falsely labelled, falsified, substandard, unregistered/unlicensed, and infringe trademarks. Counterfeit drugs can mimic both legitimate and illegitimate drugs and are often distributed in virtual environments, such as illicit online pharmacies, the surface web, and the dark web. Counterfeit drug operators and operations are the typically corrupt and/or criminal individuals, groups, and techniques by which counterfeit drugs are produced and distributed. The manufacture and distribution of counterfeit drugs are ever-changing, which results in the need for investigative techniques that are equally adaptable and collaborative. Counterfeit drug investigations can be defined according to four categories: medical investigations in hospitals and through autopsies, chemical and non-chemical drug investigations in forensic toxicology laboratories, various track-and-trace technologies used in pharmaceutical industry investigations, and national and global coordinated investigations. Due to the diverse counterfeit drug investigations present, the logic and practice of abduction are highlighted as a primary part of the investigative element to counter ongoing efforts by offenders to evade detection. Abductive rationalities are prioritized in that they are contrary to an increasing reliance on technoscientific modes of data production alone. Rather, abductive reasoning plays a central role in counterfeit drug investigations at the levels of instigating and directing investigations, as well as interpreting and responding to evidential findings.
Article
18 April 2025Factors Influencing the Incomes of Chinese Herdsmen in the Context of Grassland Ecological Compensation: A Meta-Analysis
This original paper, within the context of grassland ecological protection subsidies and reward policies, draws on 27 empirical studies conducted between 2011 and 2024 to conduct a meta-analysis of the factors influencing Chinese herdsmen’s incomes concerning heterogeneity and its sources. The results reveal 16 variables that have a significant positive impact on herdsmen’s incomes. These include herdsmen’s gender, age, ethnicity, level of education, household size, labor force, membership in cooperatives, subsidy amount, livestock quantity, living and production expenses, fixed assets, grassland area, per capita grassland area, grassland quality, and location. Among them, the quantity of livestock shows the greatest effect. Significant heterogeneity is evident across six variables: Subsidy amount, livestock quantity, grassland area, labor force, production expenses, and per capita grassland area. The heterogeneity in subsidy amount and grassland area originates from the use of different statistical methods, while the heterogeneity in livestock quantity is attributable to differences in the type of literature; per capita, grassland area heterogeneity is caused by differences in the geographical regions under analysis.