Artiles
Article
25 October 2024Supply Chain of Grey-Blue Hydrogen from Natural Gas: A Study on Energy Efficiency and Emissions of Processes
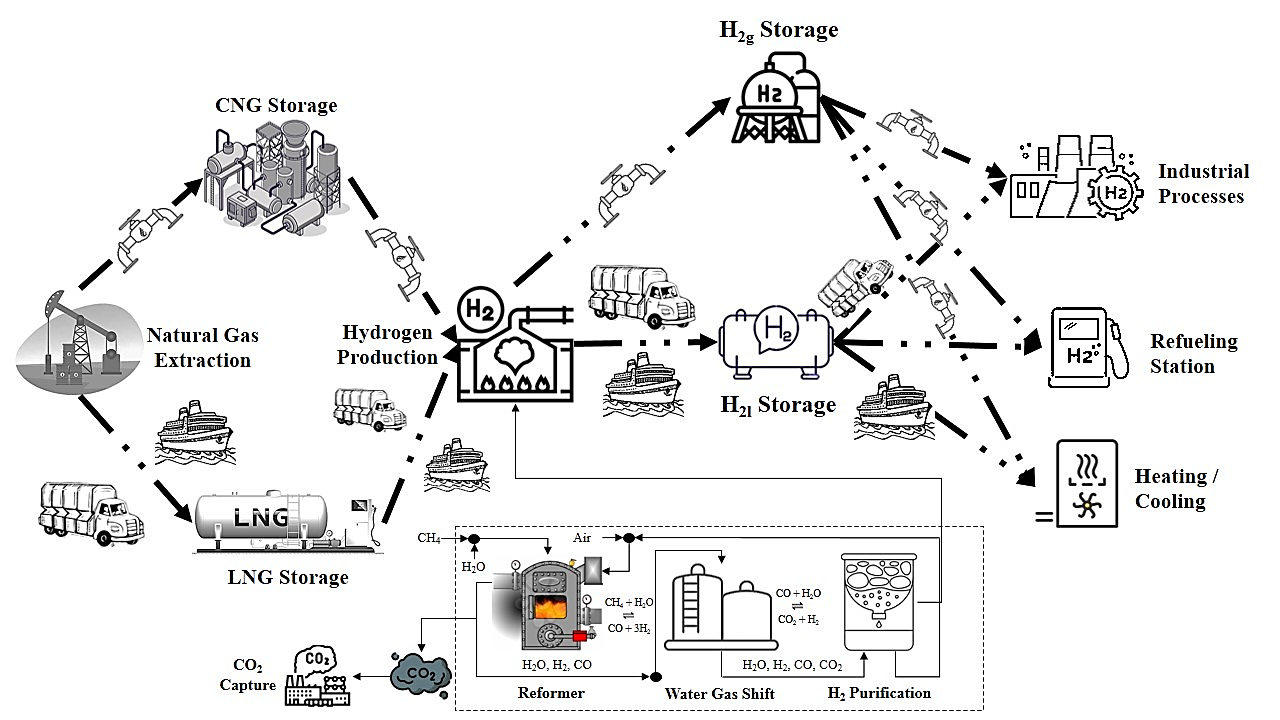
Hydrogen energy offers a significant potential for reducing carbon emissions and integrating clean energy across sectors such as heavy-duty vehicles, energy-intensive industries, and building heating. This study analyzes the energy efficiency and emissions of grey and blue hydrogen supply chains, identifying key issues such as high energy consumption and losses in transportation, steam methane reforming, and liquid hydrogen storage. Truck transportation emerges as the highest emitter, with emissions ranging from 0.140 to 0.150 kg CO2e per kg of hydrogen. Using a bi-objective Dijkstra Algorithm, the study identifies the most energy-emissions-efficient pathways and reveals a trade-off between energy efficiency and greenhouse gas emissions. Grey hydrogen shows higher energy efficiency (38.0%) but higher emissions (0.1689 kg CO2e per kg of hydrogen). In contrast, with 60% and 90% carbon capture and storage, blue hydrogen has slightly lower energy efficiencies (37.5% and 36.9%) but reduced emissions (0.1564 and 0.1514 kg CO2e per kg of hydrogen). Liquefied natural gas and hydrogen offer high energy efficiency but increase emissions, while compressed natural gas and hydrogen slightly reduce efficiency but nearly halve emissions. Hence, compressed options are preferable for an energy-emissions-efficient shortest path.
Article
23 October 2024Federated Transfer Learning-Based Paper Breakage Fault Diagnosis
The diagnosis of paper breakage faults during the papermaking process is of great significance for improving product quality and maintaining stability in the production process. This paper develops a cross-condition transfer learning fault diagnosis model. This study proposes a fault diagnosis method based on transfer learning to address the issue of single-condition diagnostic models performing poorly when applied to different conditions..This method uses both parameter transfer and feature transfer to diagnose faults across different conditions. At the same time, in response to the issue of insufficient small sample operating data, we introduce federated learning technology to explore the impact of model compression rates on the diagnostic accuracy of the federated global model during the federated model training process. The results indicate that compared to single operating condition models, fault diagnosis performance based on transfer learning across different operating conditions has improved. The diagnostic model based on feature transfer performs even better, achieving accuracy rates of 98.31%, 94.64%, and 96.43% under different transfer tasks, allowing for accurate classification of the majority of samples. Additionally, the federated learning method provides an effective solution for fault diagnosis in small sample operating conditions, and an appropriate model compression rate can ensure diagnostic accuracy while protecting data privacy.
Review
23 October 2024Chemical Recycling and Upcycling of Waste Plastics: A Review
The indiscriminate disposal of plastic waste represents a significant environmental hazard. Conventional remediation techniques, such as landfilling and incineration, also encounter limitations and are unable to adequately address the pollution issue. Chemical recycling and upcycling represent an effective method for the degradation of plastics into oligomers and subsequent transformation into other product substances. This review provides an overview of the various chemical treatment methods currently in use, from the earliest thermal degradation techniques to the emerging strategies. The conventional techniques for thermal degradation of discarded plastics frequently encounter difficulties due to the necessity for elevated temperatures, substantial energy consumption, and the generation of a heterogeneous product mixture. Significant advances have been made in the fields of catalytic solvolysis, hydrotreating, and oxidative cleavage for the recycling and upcycling of plastics under mild conditions. This review provides a comprehensive overview of the chemical treatment methods currently employed for plastics, with a particular focus on the principles and current developments, as well as the reaction mechanisms involved. Additionally, it offers a detailed introduction to various advanced catalytic technologies and the catalysts utilized. Finally, it presents prospective outlooks for different methods, based on their current development status and the gap between actual needs.

Communication
23 October 2024Modeling Viscosity in Starch-Polymer Suspensions: A Comparative Analysis of Swarm Algorithm-Aided ANN Optimization
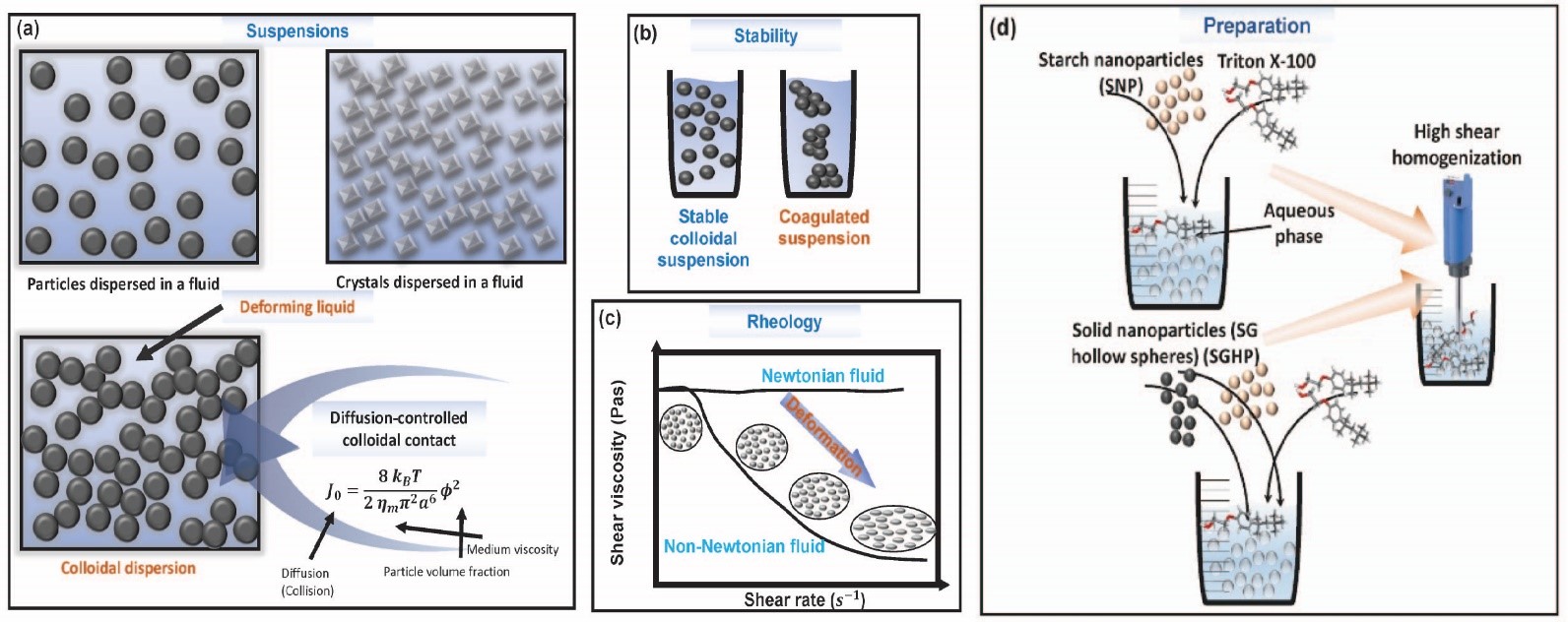
The analysis of rheological properties of suspensions requires the use of models such as Einstein’s formulation for viscosity in dilute conditions, but its effectiveness diminishes in the context of concentrated suspensions. This study investigates the rheology of suspensions containing solid particles in aqueous media thickened with starch nanoparticles (SNP). The goal is to model the viscosity of these mixtures across a range of shear rates and varying amounts of SNP and SG hollow spheres (SGHP). Artificial neural networks (ANN) combined with swarm intelligence algorithms were used for viscosity modeling, utilizing 1104 data points. Key features include SNP proportion, SGHP content, log-transformed shear rate (LogSR), and log-transformed viscosity (LogViscosity) as an output. Three swarm algorithms—AntLion Optimizer (ALO), Particle Swarm Optimizer (PSO), and Dragonfly Algorithm (DA)—were evaluated for optimizing ANN hyperparameters. The ALO algorithm proved most effective, demonstrating strong convergence, exploration, and exploitation. Comparative analysis of ANN models revealed the superior performance of ANN-ALO, with an R2 of 0.9861, mean absolute error (MAE) of 0.1013, root mean absolute error (RMSE) of 0.1356, and mean absolute percentage error (MAPE) of 3.198%. While all models showed high predictive accuracy, the ANN-PSO model had more limitations. These findings enhance understanding of starch suspension rheology, offering potential applications in materials science.
Review
23 October 2024The Notch3 Pathway in Organ Fibrosis
Fibrosis occurs in many organs, including the lung, heart, skin, liver or kidney, and is characterized by progressive tissue scarring in response to repetitive or chronic non-resolving injury, ultimately leading to organ failure and death. It is, in fact, a major cause of morbidity and mortality worldwide, being estimated to account for 45% of deaths in the world. Despite this fact, little progress has been made therapeutically, and fibrosis remains a major clinical and therapeutic challenge. Although significant advances in our understanding of cellular and molecular mechanisms driving tissue fibrosis have been made, the lack of an efficient treatment reflects the limited insight into the pathophysiological mechanisms underlying the initiation and progression of the fibrotic process. Thus, there is an urgent need for better understanding of tissue fibrosis and repair mechanisms that later lead to the development of new therapeutic approaches to fight fibrosis. The Notch pathway is a highly conserved signaling pathway that has been linked to tissue fibrosis in many organs and promises to open new therapeutic opportunities. This manuscript reviews the relevance of Notch signaling in the development and progression of tissue fibrosis in several organs with a special focus on the Notch3 pathway due to the unique features of this receptor.

Review
22 October 2024Engineering of Cu-Based Quaternary Sulfide Nanomaterials for Photocatalytic Applications
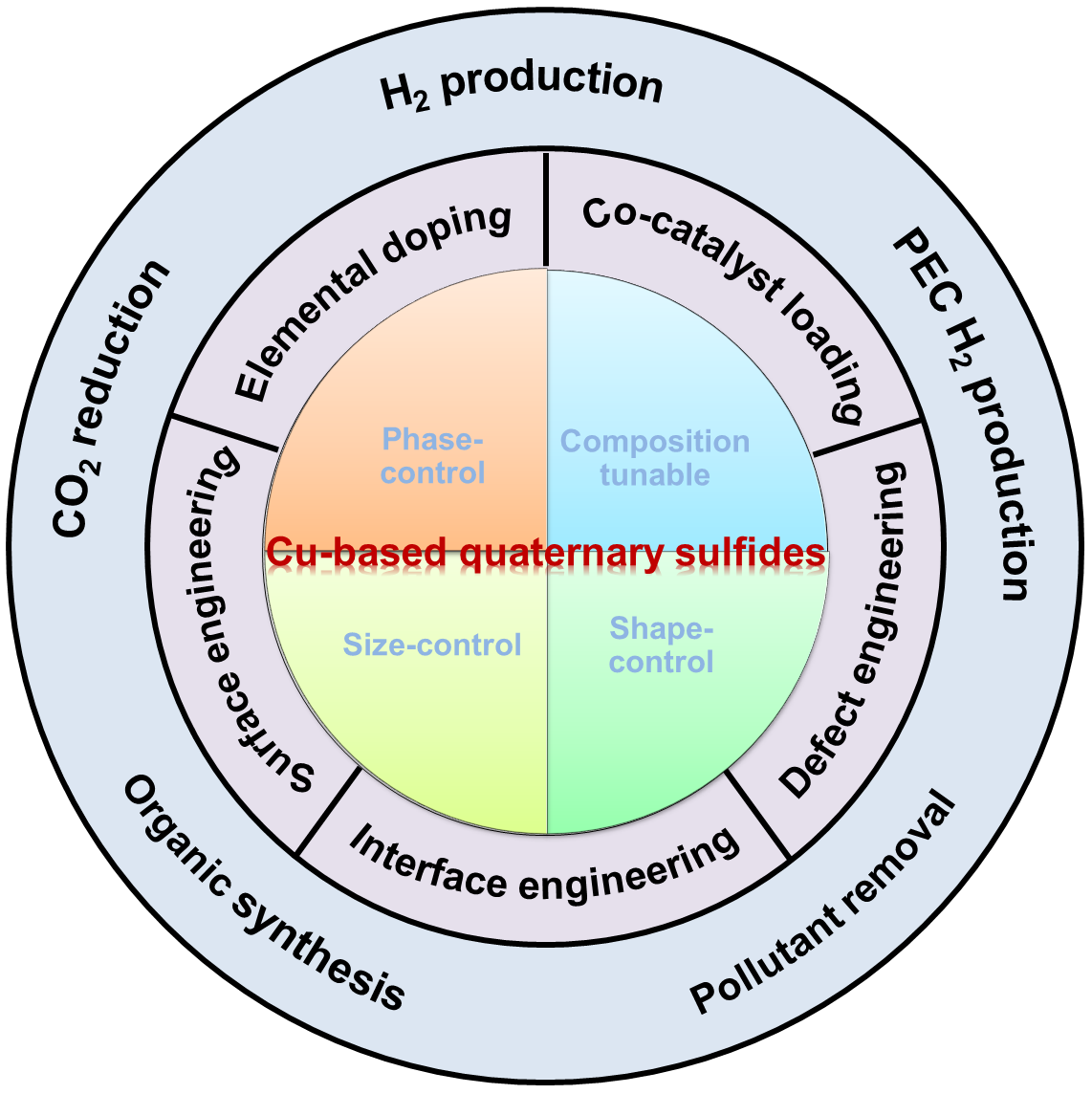
Semiconductor nanomaterials have been widely used as light-responsive photocatalysts for solar-to-fuel conversion over the past decade. However, the wide band gap of the most reported photocatalysts stems from light absorption in the visible region and results in low solar conversion efficiency. Therefore, it is necessary to develop new semiconductor nanomaterials with high absorption coefficients over the visible region as photocatalysts. The most promising candidates include Cu-based quaternary sulfide nanomaterials (CQSNs), such as Cu-II-III-S (e.g., CuZnInS, CuZnGaS), Cu-II-IV-S (e.g., Cu2ZnSnS4, Cu2ZnGeS4), and I-III-IV-S (e.g., CuInSnS4, Cu3GaSnS5). This review provides a comprehensive overview of the recent progress in developing CQSNs for various photocatalytic applications. Firstly, we present an overview of the synthesis of CQSNs with precise control over crystal phase, composition, size, and shape using solution-based methods. Then, the enhancement of photocatalytic performance was presented via the engineering of CQSNs, which included surface engineering, elemental doping, cocatalyst loading, vacancy engineering, and interface engineering. Subsequently, we further introduce the photocatalytic applications in the fields of photocatalytic and photoelectrochemical hydrogen conversion, CO2 reduction, organic synthesis, and pollutant degradation. Lastly, this review ends with views on the current challenges and opportunities of CQSNs in future studies.
Article
18 October 2024Multi-Objective Distributed Real-Time Trajectory Planning for Gliding Aircraft Cluster
A new combat strategy that enables coordinated operations of gliding aircraft clusters for multi-target strikes imposes higher demands on the coordination, real-time responsiveness, and strike accuracy of gliding aircraft clusters. Due to the high speed and large inertia characteristics of gliding aircraft, traditional trajectory planning methods often face challenges such as long computation times and difficulty in responding to dynamic environments in real-time when dealing with large-scale gliding aircraft clusters. This paper proposes a distributed cooperative trajectory planning method for multi-target strikes by gliding aircraft clusters to address this issue. By introducing a multi-objective distributed real-time trajectory planning approach based on Multi-Agent Deep Deterministic Policy Gradients (MADDPG), the gliding aircraft execute distributed cooperative trajectory planning based on the trained model. Due to its robust real-time performance, the gliding aircraft do not need to recalculate trajectories for different initial positions of the cluster. Simulation results show that the average error between the gliding aircraft cluster and the target point is 2.1 km, with a minimum error of 0.06 km and a hit rate of 96.6%, verifying the significant advantages of this method in real-time planning capability and strike accuracy.

Article
15 October 2024Stable Boundaries of Phragmites australis Marsh Development after Peat Mining in a Northern Japan Bog
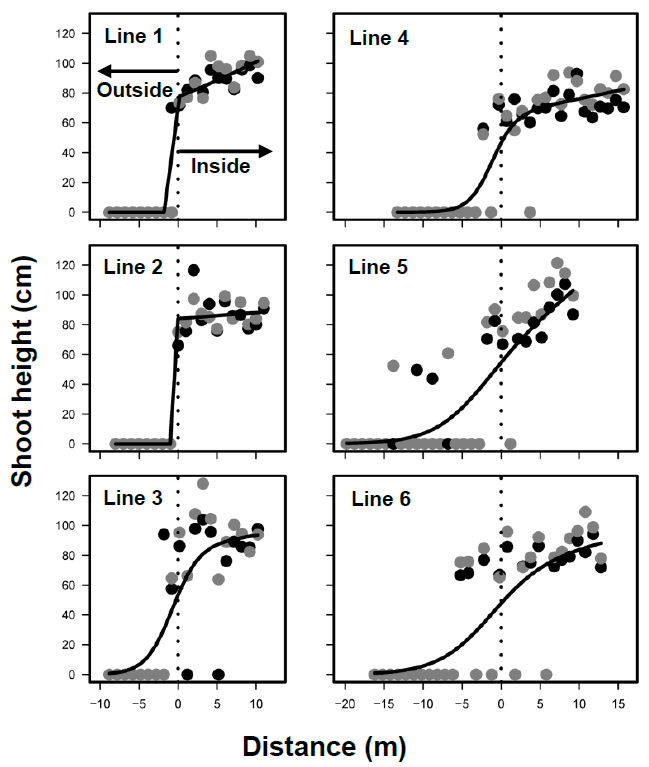
Since Phragmites australis often develop marshes soon after human disturbances, such as peat mining in bogs, the establishment patterns should be clarified for restoration purposes. The inside and outside boundaries of P. australis marshes were investigated following peat mining in Sarobetsu mire, northern Japan, in 2016 and 2017. The boundaries of marshes did not move during the two years, due mostly to the slow expansion of shoots. Various vegetation types developed outside of the marsh. P. australis coexisted with neither ericaceous nor carnivorous plants, which favor Sphagnum bogs. The succession in the marsh did not progress the original bogs. P. australis dispersed seeds mostly within the marshes, suggesting limited dispersal, and developed transient seed bank. Therefore, seed dispersal (sexual reproduction) and rhizomes (vegetative reproduction) contributed to population maintenance rather than population enlargement during the studied period. Peat moisture was higher in the marsh, whereas photosynthetic active radiation was lower. Water levels did not differ between inside and outside the marshes. Chemical properties in peat water were not different between inside and outside the marshes. Therefore, water chemistry and levels did not adequately explain the marsh development. These results suggest that, for wetland restoration, environmental manipulation is ineffective in reducing P. australis and unpredictable or stochastic events alter the dynamics of P. australis marshes.
Article
15 October 2024Binder Jetting 3D Printing Utilizing Waste Algae Powder: A Feasibility Study
This paper reports, for the first time in the literature, a preliminary study to investigate the feasibility of utilizing waste algae powder (byproducts of biofuel manufacturing from algae) in binder jetting 3D printing to produce environmentally friendly products. In this study, the algae powder’s morphology and particle size distribution were characterized using scanning electron microscopy and particle size analyzer, respectively, and the flowability was assessed through apparent density and repose angle. The algae powder successfully printed the cylindrical, cubic, and gyroid parts on a binder jetting 3D printer. Results show that it is feasible to print parts with binder jetting 3D printing utilizing waste algae powder. The use of waste algae powder in additive manufacturing offers a novel approach to upcycling waste algae powder into valuable products for various applications such as packaging and construction.

