Artiles
Commentary
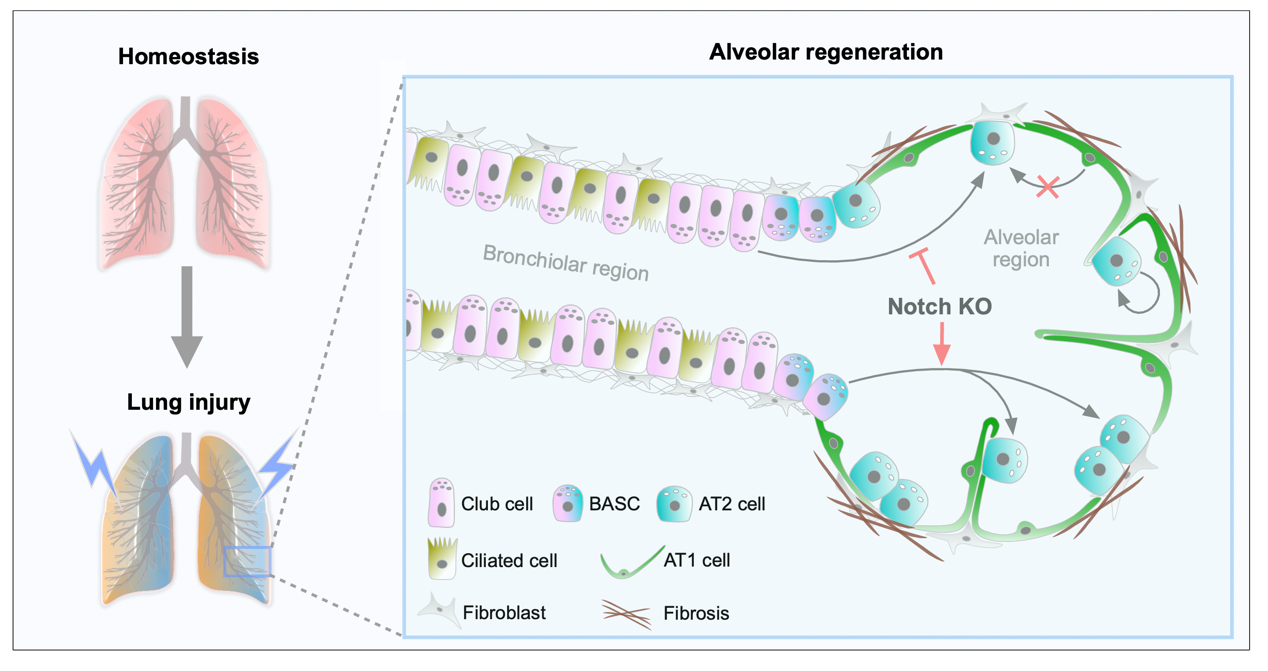
12 June 2024Dual Genetic Tracing Reveals the Origin of Alveolar Stem Cells after Lung Injury
As alveolar epithelial stem cells, alveolar type II (AT2) cells play a pivotal role in sustaining alveolar homeostasis and facilitating repair processes. However, the sources of AT2 cell regeneration have remained contentious due to the non-specific labeling limitations of traditional single recombinase-based lineage tracing techniques. To address this issue, we employed dual recombination systems to develop more precise lineage tracing methodologies, effectively bypassing the shortcomings of conventional approaches and enabling specific labeling of lung epithelial cells. Our findings demonstrate that, following lung injury, regenerated AT2 cells do not originate from alveolar type I (AT1) cells, but instead derive from bronchiolar club cells and bronchioalveolar stem cells (BASCs), alongside the self-renewal of resident AT2 cells. Furthermore, we discovered that the transition of club cells and BASCs into AT2 cells is distinctly modulated by the Notch signaling pathway. This study not only provides novel insights into lung regeneration, but the innovative lineage tracing technology developed herein also holds promise as a technical support for research in diverse fields.
Article
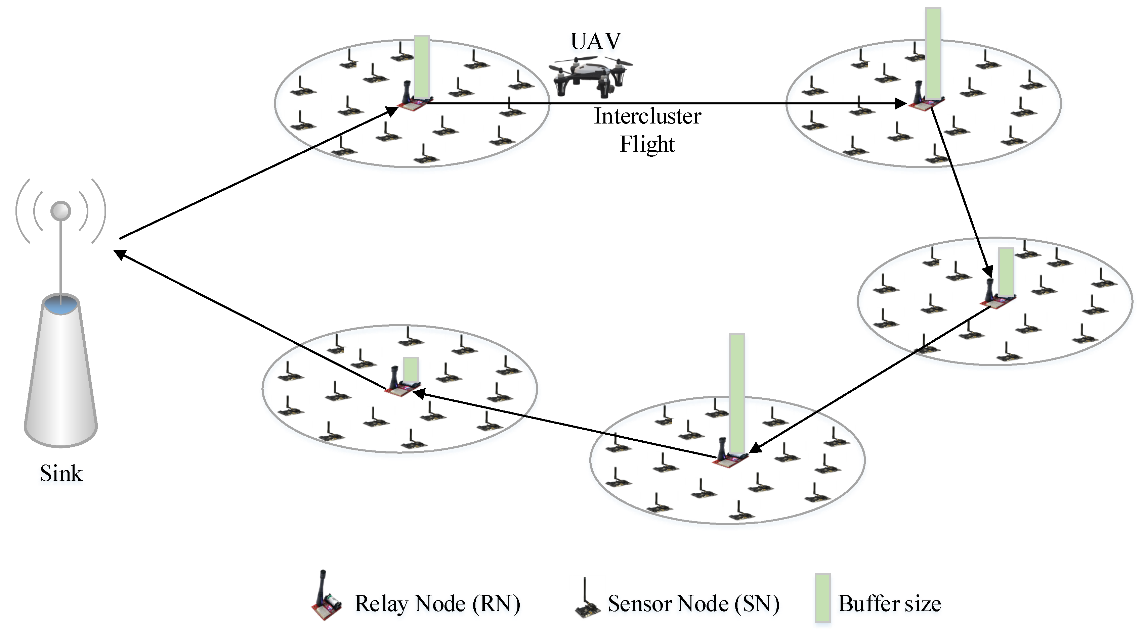
12 June 2024Optimized Real Time Single-Drone Path Planning for Harvesting Information from a Wireless Sensor Network
We consider a remote sensing system in which fixed sensors are placed in a region, and a single drone flies over the region to collect information from cluster heads. We assume that the drone has a fixed maximum range and that the energy consumption for information transmission from the cluster heads increases with distance according to a power law. Given these assumptions, we derive local optimum conditions for a drone path that either minimizes the total or maximum energy required by the cluster heads to transmit information to the drone. We show how a homotopy approach can produce a family of solutions for different drone path lengths so that a locally optimal solution can be found for any drone range. We implement the homotopy solution in Python and demonstrate the tradeoff between drone range and cluster head power consumption for several geometries. Execution time is sufficiently rapid for the computation to be performed in real time so that the drone path can be recalculated on the fly. The solution is shown to be globally optimal for sufficiently long drone path lengths. A proof of concept implementation in Python is available on GitHub. For future work, we indicate how the solution can be modified to accommodate moving sensors.
Article
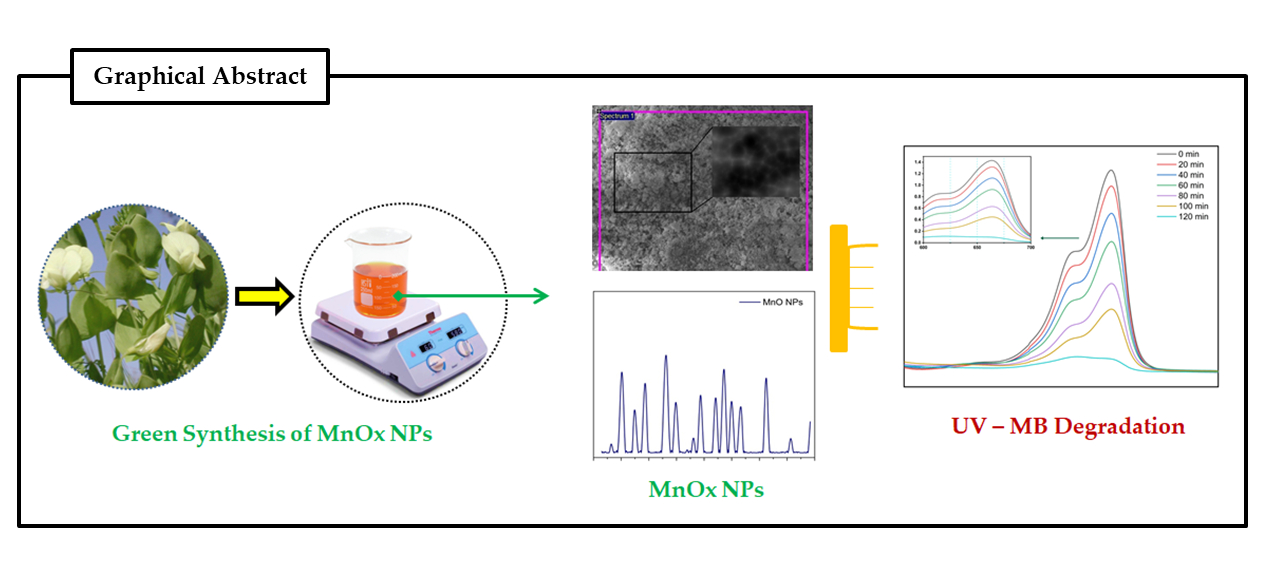
11 June 2024Lathyrus aphaca Extract MnO Nanoparticles: Synthesis, Characterization, and Photocatalytic Degradation of Methylene Blue Dye
Our environment has been impacted by man-made pollutants mainly industries make substantial use of synthetic dyes which exhibit cytotoxicity and have significant environmental consequences. Effective photocatalyst-based approaches for degrading synthetic dyes into less toxic chemical are of great interest. Synthesizing nanoparticles (NPs) using biological approaches, particularly plant-based approaches offer advantages, decreasing the risk of NPs losing biocompatibility during synthesis, cost-effectiveness, and eco-friendliness. In this study, we employed a green synthesis method to produce manganese oxide nanoparticles (MnO NPs) utilizing leaf extract from the Lathyrus aphaca plant. The synthesized MnOx NPs were characterized through various techniques; X-ray diffraction (XRD), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDX), Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), and UV–visible spectroscopy. XRD analysis showed distinct peaks, indicated the presence crystallographic planes within the MnO2 nanoparticles, thus confirming their crystalline structure. FTIR, showed the presence of the O-O stretching mode at a frequency of 719 cm−1, the presence of MnO6 oxides of manganese, and peak at 548 cm−1 corresponded to the Mn-O stretching mode. Furthermore, the green-synthesized manganese oxide nanoparticles exhibited promising photocatalytic and adsorption capabilities against Methylene Blue (MB) dye, leading to approximately 93% degradation of MB when treated with the green-synthesized MnO nanoparticles derived from plant extract. This highlights the efficacy and potential of these nanoparticles in environmental remediation applications, particularly in the degradation of methylene blue contaminants.
Case Report
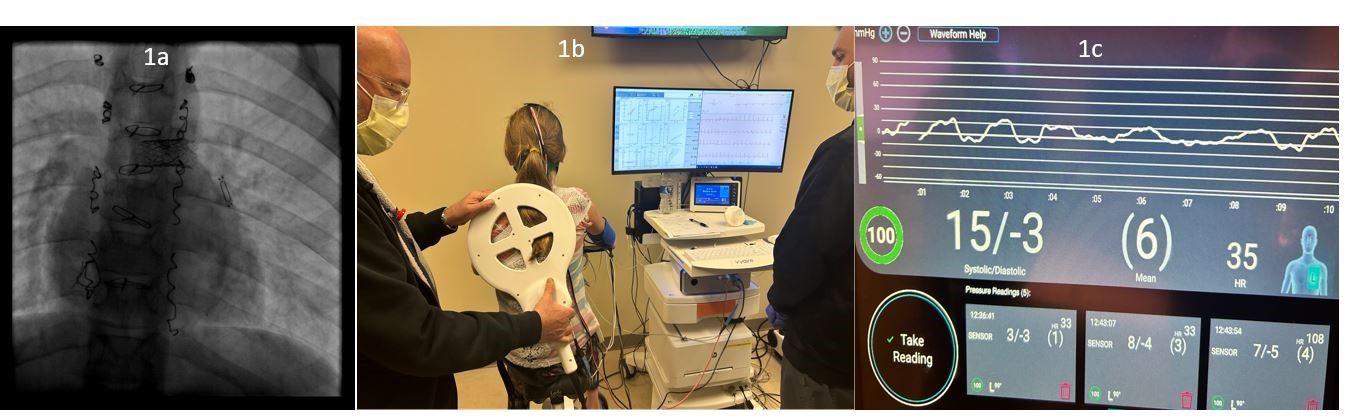
11 June 2024Early Experience Using Implanted Hemodynamic Monitor (CardioMEMs) for Hemodynamic Assessment during Exercise in Pediatric Patients with Fontan Circulation
Assessment of Fontan pressures during exercise has been previously challenging. We report our experience with 4 children, in whom implanted hemodynamic monitor was utilized to assess Fontan pressures during exercise. Data was used to modify treatment in one case. The device provided useful insight into exercise-related changes in Fontan patients.
Article
05 June 2024An Architecture for Early Wildfire Detection and Spread Estimation Using Unmanned Aerial Vehicles, Base Stations, and Space Assets
This paper presents, an autonomous and scalable monitoring system for early detection and spread estimation of wildfires by leveraging low-cost UAVs, satellite data and ground sensors. An array of ground sensors, such as fixed towers equipped with infrared cameras and IoT sensors strategically placed in areas with a high probability of wildfire, will work in tandem with the space domain as well as the air domain to generate an accurate and comprehensive flow of information. This system-of-systems approach aims to take advantage of the key benefits across all systems while ensuring seamless cooperation. Having scalability and effectiveness in mind, the system is designed to work with low-cost COTS UAVs that leverage infrared and RGB sensors which will act as the primary situational awareness generator on demand. AI task allocation algorithms and swarming-oriented area coverage methods are at the heart of the system, effectively managing the aerial assets High-level mission planning takes place in the GCS, where information from all sensors is gathered and compiled into a user-understandable schema. In addition, the GCS issues warnings for events such as the detection of fire and hardware failures, live video feed and lower-level control of the swarm and IoT sensors when requested. By performing intelligent sensor fusion, this solution will offer unparalleled reaction times to wildfires while also being resilient and reconfigurable should any hardware failures arise by incorporating state of the art swarming capabilities.
Editorial
04 June 2024
Article
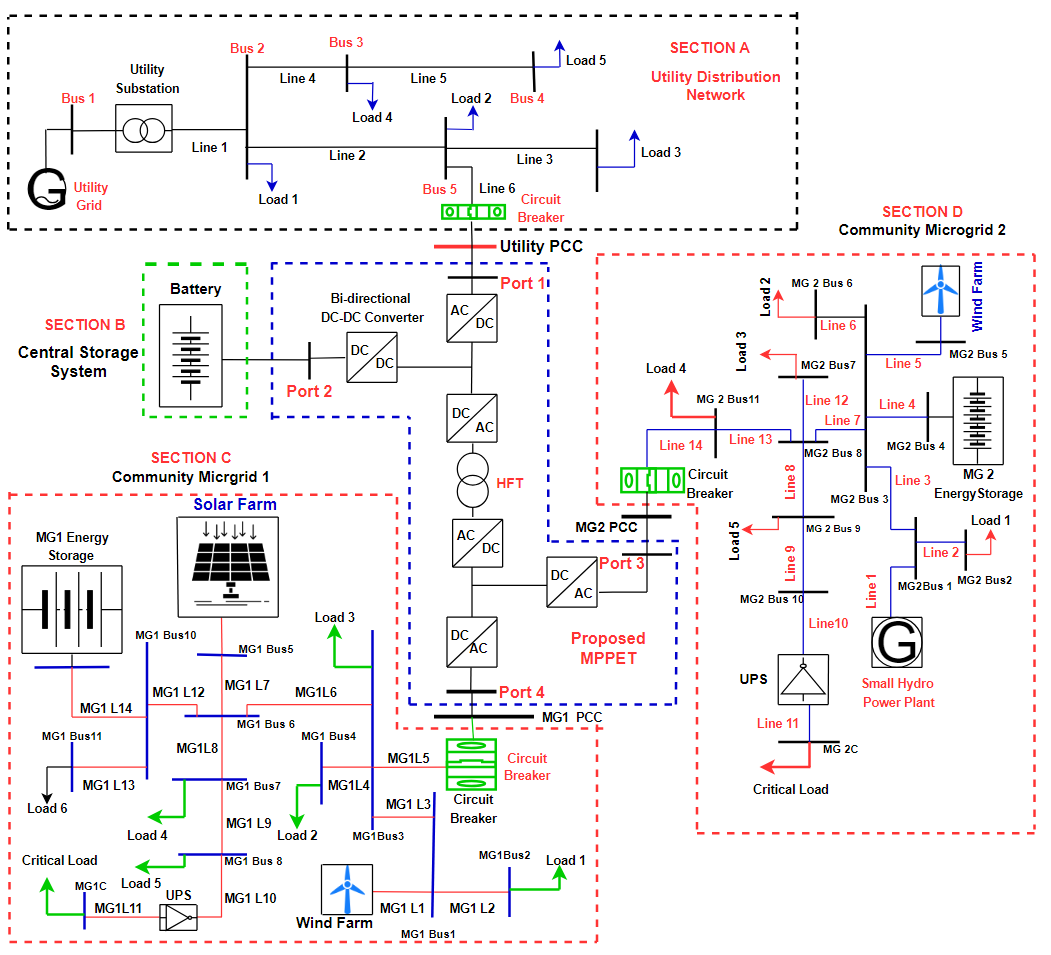
04 June 2024Investigating and Analyzing the Impact of a Bidirectional Multiport Power Electronic Transformer Interface on the Power Quality and Stability of Interconnected Microgrids
This paper investigates the potential benefits of a bidirectional multi-port power electronic transformer (MPPET) to interface multiple microgrids with utility distribution networks in terms of power quality and stability. The main concept is based on the interaction between the utility grid, the connected microgrids, and the MPPET in controlling the disturbances that lead to grid instability and power quality issues. The proposed MPPET does not require any serious communication infrastructure for operation. In addition, the MPPET can respond to reverse power flow caused by excess power generation on the grid. Due to the intermittent nature of the renewable energy sources and the different stages involved in the design of the proposed MPPET, the system is liable to internal DC voltage fluctuation, causing grid instability; thus, an energy storage system (ESS) is incorporated to avert the challenges. The networks under investigation and the proposed MPPET are designed and simulated using MATLAB and Simulink software. The electrical isolation capability of the proposed bidirectional MPPET is verified through simulation. Several case studies have been carried out to evaluate the behavior of the system under different operating conditions and to check the feasibility of MPPET for power quality improvements. It was observed that the MPPET is proficient in regulating power quality issues, thus enhancing grid stability. It is also varied that the proposed MPPET prevents the escalation of the impact of faults or disturbances all over the grid. At the same time, it is verified that the proposed bidirectional energy storage systems enhance energy transfer between the utility grid and microgrids, which improves the system’s stability.
Article
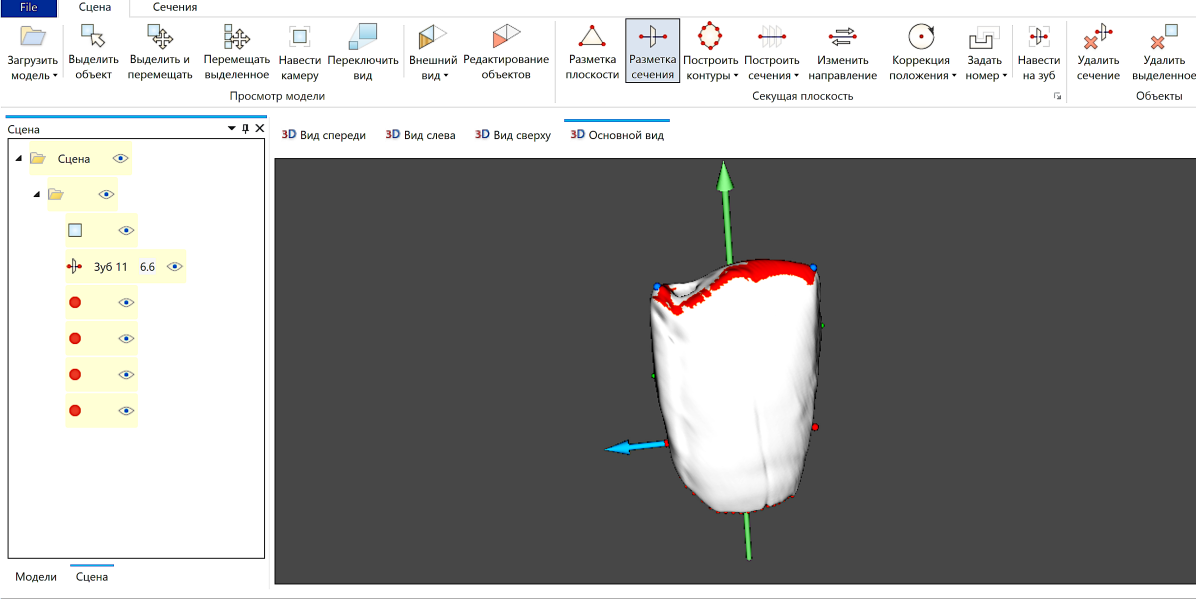
04 June 2024Initial Stages of Development of an Automated Measurement Technique on Incisors
Teeth are an important object of studies in many scientific disciplines and, among various study techniques, measurements have one of the most promising prospects for further improvements supported by progress in computer sciences, imaging and image processing. Our recent work on automated odontometric algorithms for premolars and molars has gradually come to develop similar methods for another group of teeth—incisors. Using 3D reconstructions of teeth obtained through micro-focus tomographic scanning, we propose landmarks, which correspond to main morphological features of incisors and enable their formal description. In this article we present an orientation and measurement technique, based on an interpretation of incisor morphology, as a system which is able to perform in a fully automated mode. Since the primary objective of the current paper is to introduce methodological improvements, data on measurements and their results are shown at the most basic level.
Article
31 May 2024Advancing Green Infrastructure Solutions in Rural Regions: Economic Impacts and Capacity Challenges in Southwest Ontario, Canada
Green infrastructure (GI) is a growing topic in urban planning, asset management, and climate change adaptation. However, rural regions have been under-represented in the discourse. This paper explores the benefits and challenges associated with the implementation and management of GI through a regional study of rural communities in southwestern Ontario. Our focus concerns the inter-relationships between GI, economic resilience, and the development of rural places. Findings show rural communities benefit from GI initiatives like natural stormwater management, park naturalization, and natural heritage restoration, which provide low-cost municipal services, conserve agricultural soils, and contribute to the amenity appeal of rural places. Challenges surrounding awareness, organizational capacity, and environmental regulation have slowed the uptake of GI and led to inconsistencies across jurisdictions. A mix of supportive policies, funding of demonstration projects with economic monitoring, and training to build professional capacity will advance the use and efficacy of GI across rural regions.
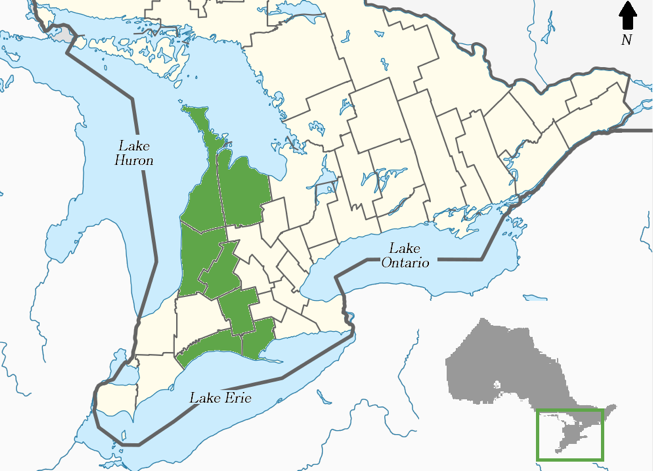
Article
31 May 2024Solid Waste Recycling in Textile Processing Industries: A Case Study of India’s Clothing Hubs
This study investigated the type and amount of solid waste generation from textile wet processing industries and analyzed the disposal and recycling strategies implemented for its utilization. The method involved industrial interactions with textile processing mills. Data was gathered based on a field survey of manufacturing units and their compliance management teams. The solid waste generated in textile processing stages against input raw materials and fuel sources was recorded. The challenges in recycling solid waste are identified and further scope for its valorization is suggested. The results indicate that significant solid waste produced during the wet processing of textiles arises from waste fabric cuttings, combustion of fuels used in processing stages, and sludge generated from the post-effluent treatment. Around 80% of solid waste generated during the wet processing of textiles can find applications in the construction industry. Effective management of solid waste and its potential applications in construction are elaborated in detail.
