Artiles
Article
26 February 2025Life Cycle Assessment of Tensile Specimens of Stainless Steel Obtained by Additive Manufacturing versus Conventional Manufacturing
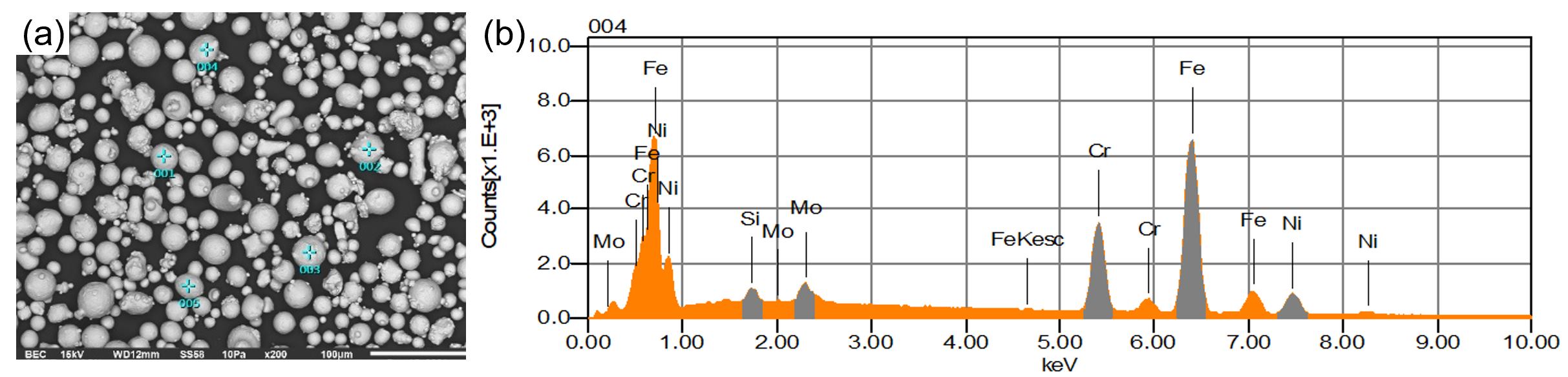
Life Cycle Assessment (LCA) of additive manufacturing (AM) evaluates the environmental impacts associated with each stage of the process, from raw material extraction to end-of-life disposal. Unlike conventional manufacturing, AM offers significant advantages, such as reduced material waste, optimized designs for lightweight structures, and localized production, which can decrease transportation emissions. However, its environmental benefits are context-dependent, as energy-intensive processes like laser powder bed fusion or high reliance on specific materials can offset these gains. LCA provides a comprehensive framework to assess these trade-offs, guiding sustainable decision-making by identifying hotspots in energy use, material efficiency, and recyclability, ultimately driving innovation towards greener AM practices. This research conducted a cradle-to-gate study of a cylindrical dog-bone tensile specimen. The life-cycle inventory data were obtained from Ecoinvent for conventional manufacturing, while data from the literature review and our research were employed for laser-based powder bed fusion. The results obtained show that the additive manufacturing process is more environmentally friendly. Although the environmental impact is minor, this process consumes a large amount of energy, mainly due to the atomization process and the high laser power. Regarding the mechanical response, AM reduced the ductility but increased the yield strength and achieved the same fracture strength.
Article
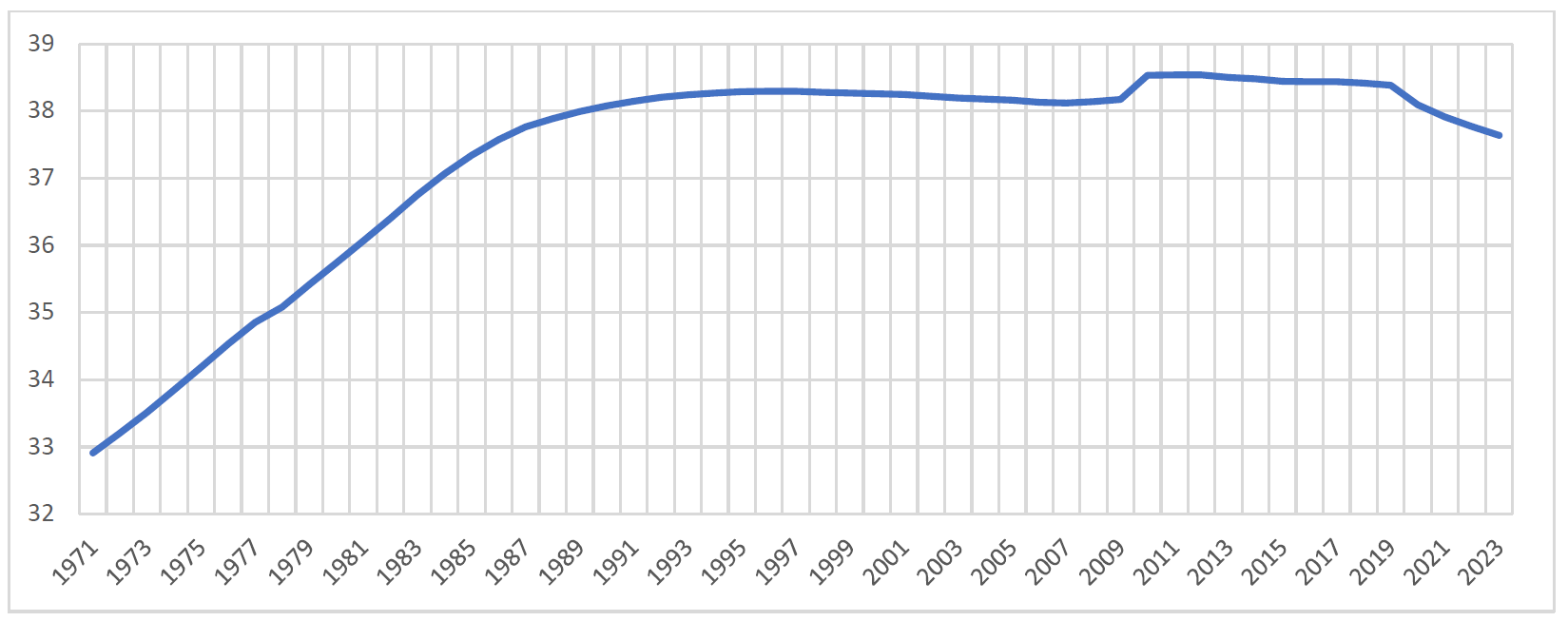
26 February 2025Autopsies in Poland 1971–2023
Autopsies, depending on their purpose, can be described as forensic or clinical. Both types are intended to determine the cause of death, but their goal is different. For forensic autopsies, this goal is to provide expertise with evidential value in various legal proceedings. For clinical autopsies, they have historically been seen as a tool in the development and investigation of disease processes. The aim of the study was to determine how the percentage of autopsies changed in Poland in the years 1971–2023. Research material was data obtained from the Polish Central Statistical Office. On the basis of this data, we showed changes in the population number, the number of deaths, and the number of autopsies in the indicated period. It was shown that in Poland, the percentage of autopsies in relation to all deaths in the period from 1971 to 2023 (53 years) fell about 4-fold from the initial level of approximately 16% to only approximately 4% now. This downward trend is consistent with the trends in other EU countries.
Article
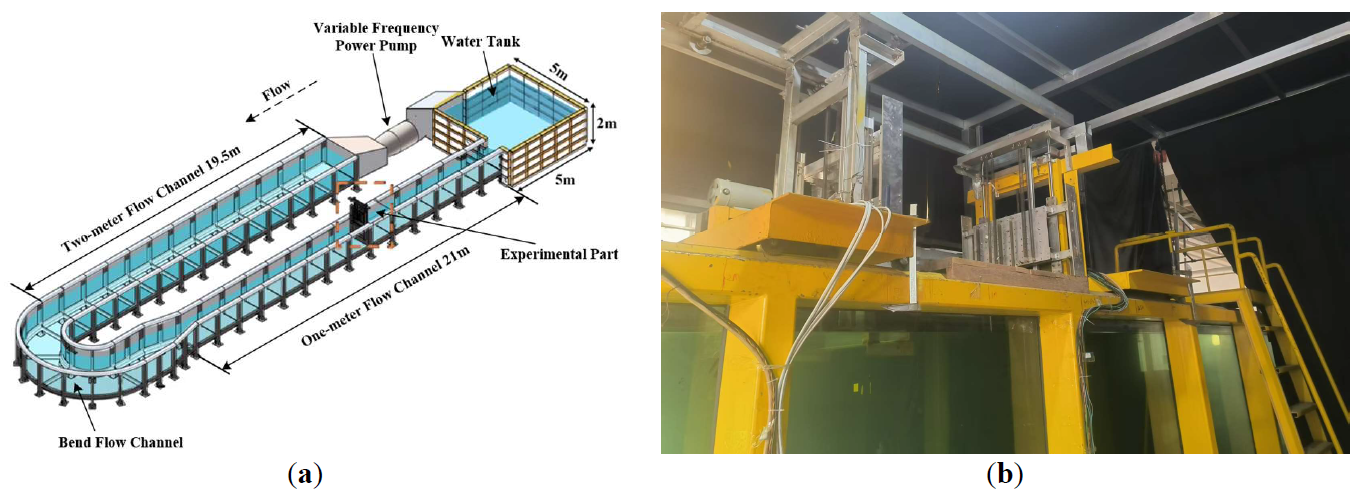
25 February 2025Energy Harness and Wake Structure of “Cir-Tri-Att” Oscillators for Flow-Induced Motion Tidal Energy Conversion System
The research focuses on the flow-induced motion (FIM) and energy harness of “Cir-Tri-Att” oscillators (CTAO). The wake was photographed by particle image velocimetry (PIV) to explore wake structures. With the increase of the aspect ratios: the ability of oscillators to galloping under self-excitation or external excitation is enhanced. When ζ = 0.033, Ur = 12.5, the maximum amplitude ratio A* = 2.408 for oscillators with α = 1:1. Moreover, oscillators with higher aspect ratios can bear larger loads, which is conducive to energy utilization and conversion. The maximum power output Pharn = 16.588 W and the optimal efficiency ηharn = 24.706% appear in oscillators with α = 1.5:1. Additionally, In the soft galloping (SG), the wake mode is 4P or 3P. The wake vortex is more broken and its scale increases, but the force effect of the oscillators is better and the oscillation is more stable. The pressure difference makes for a longer oscillation period. This paper summarizes the FIM, energy harness and wake structures of the CTAO under different working conditions, which provides theoretical and data support for the optimization oscillators of flow-induced motion tidal energy conversion system.
Article
25 February 2025Thermal Characterization Study of Double End Face Grinding Powder Metallurgy Stainless Steel 316L
Double end face grinding machining is a highly efficient surface grinding technique. And grinding temperature is an important factor affecting the surface quality of workpieces. However, it is difficult to monitor the surface temperature of the workpiece in real time because of the covered contact between the grinding wheel and the upper and lower surfaces of the workpiece during the machining process. This paper aims to conduct a mechanistic analysis and experimental investigation of the machining process to address this challenge. Initially, the paper conducts an analysis of the kinematic mechanism, modal analysis, and the grinding force mechanism specific to the double end face grinding process. Afterwards, the mechanisms leading to the generation of grinding heat and the associated heat transfer mechanisms are explored in depth. The paper then proceeds to solve the instantaneous temperature field during double end face grinding by the finite element method (FEM). Furthermore, the micro and macro profile heights of the machined workpiece surfaces are measured and analyzed. The results show that the machined workpiece surface shows a high center and low edge. This is due to the fact that the temperature at the edge of the workpiece is higher than the center during machining, resulting in more material removal. Through these investigations, the study is able to determine the optimal process parameters for the machining process. This in turn improves machining efficiency and product conformity. And these findings not only guide practical production processes but also provide a foundation for future theoretical research in this area.
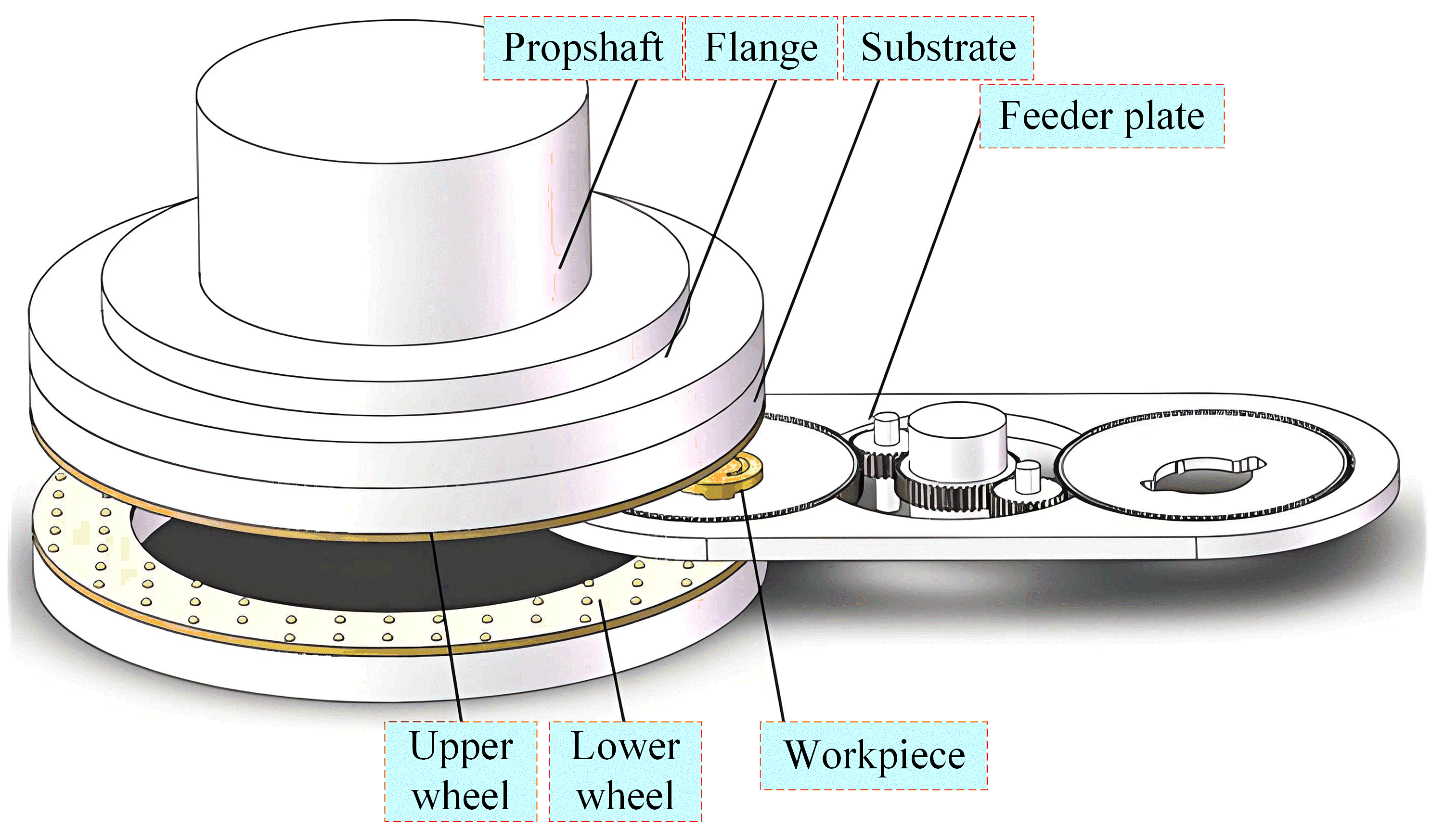
Review
25 February 2025Innovations in IN939: From Cast Alloy to Additive Manufacturing
Nickel-based superalloys are the most reliable material choice for the hot sections of turbines. These superalloys are mainly employed in aircraft engines, particularly in the combustor and turbine sections. In this scenario, the growing need for materials that can endure high temperatures while retaining their strength has driven the development of IN939. Although IN939 holds these significant important properties and applications, it has received less attention in recent literature than other superalloys. This review aims to comprehensively analyze the main research on IN939 over the past 50 years. From 1970 to 1980, research primarily focused on the development of IN939 through casting methods. Between 1980 and 1990, the emphasis shifted to studying its oxidation resistance and microstructural stability during service. The period from 1990 to 2000 focused on repairing components after long service time at high temperatures. In recent decades, advances in additive manufacturing techniques have led to growing interest in developing IN939 using methods like laser powder bed fusion (LPBF). Research in the area has demonstrated that the LPBF technique offers a promising approach to manufacturing high-performance IN939 components.
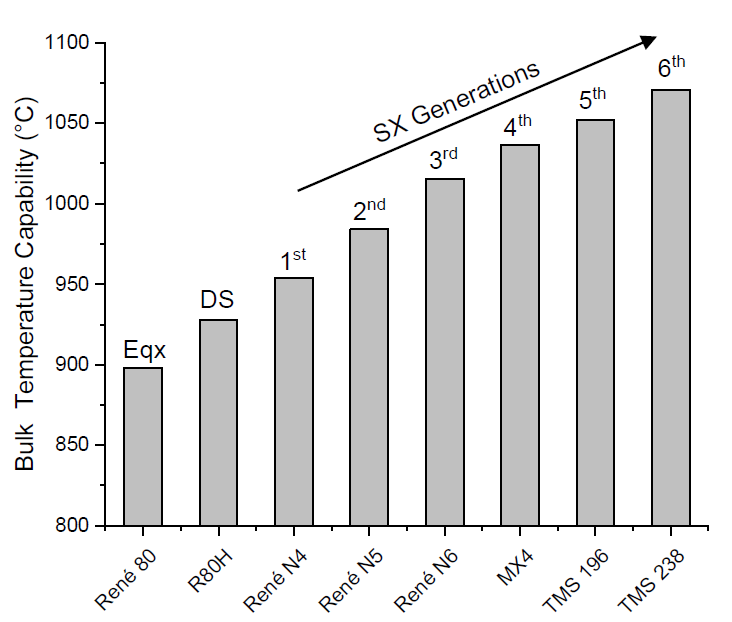
Article
24 February 2025Effect of Recycled High-Density Polyethylene on the Impact Strength of Polybutylene Terephthalate/Polyamide 6
Recycling high-density polyethylene (HDPE) is crucial to addressing plastic waste challenges. This study investigates the mechanical properties of blends composed of HDPE, polybutylene terephthalate (PBT), and polyamide 6 (PA6). Blends with varying HDPE content (0, 70, 80, 90, and 100%) were analyzed using injection molding to determine their impact toughness and structural characteristics. PBT and PA6 (blended in a 50:50 ratio) were combined with HDPE to create composites with enhanced properties. Testing included unnotched impact strength analysis and scanning electron microscopy (SEM). HDPE, a flexible thermoplastic, was paired with PBT and PA6, known for their strength and heat resistance, to produce a blend with superior mechanical performance. Results reveal that incorporating HDPE enhances the impact toughness of the composites compared to the pure PBT/PA6 blend, offering promising potential for many diverse applications in materials engineering in the automotive industry, household products, and protective casings of electronic products.

Article
21 February 2025Porous Cu(Mn)-Doped ZnO-MgO Nanocomposites for Photocatalytic and Antibacterial Applications
Porous Cu(Mn):ZnO-MgO composites synthesized by polymeric sol-gel method were characterized. The crystal structure, morphology, spectral properties, the ability of the photogeneration of chemically active singlet oxygen under external visible irradiation, photocatalytic and antibacterial properties of porous composites were studied. Obtained composites consist of small ZnO and MgO crystals having size less than 20 nm. It was found that Cu2+ and Mn2+ ions are embedded into the lattices of ZnO and MgO crystals, altering their crystal cell parameters. The band gap values of obtained composites are 3.41 ÷ 3.42 eV which are slightly higher than the band gap of pure ZnO. Prepared materials demonstrate a high ability of photogeneration of chemically active singlet oxygen under blue light (λ = 405 nm) irradiation. It was found that dependencies of the intensity of singlet oxygen photogeneration from the power density of visible irradiation are linear. Photocatalytic decomposition of the diazo dye Chicago Sky Blue in solutions under UV and blue light irradiation proceeds rapidly in the presence of the prepared composites (constants rate of photocatalytic dye decomposition under UV irradiation are 0.024 min−1 and 0.025 min−1 for ZnO-MgO composites doped with Cu and Mn, correspondingly). Porous composites demonstrate superior antibacterial activity against gram-positive bacteria. These materials are promising for practical application in medicine and photocatalytic technologies of air and water cleaning.
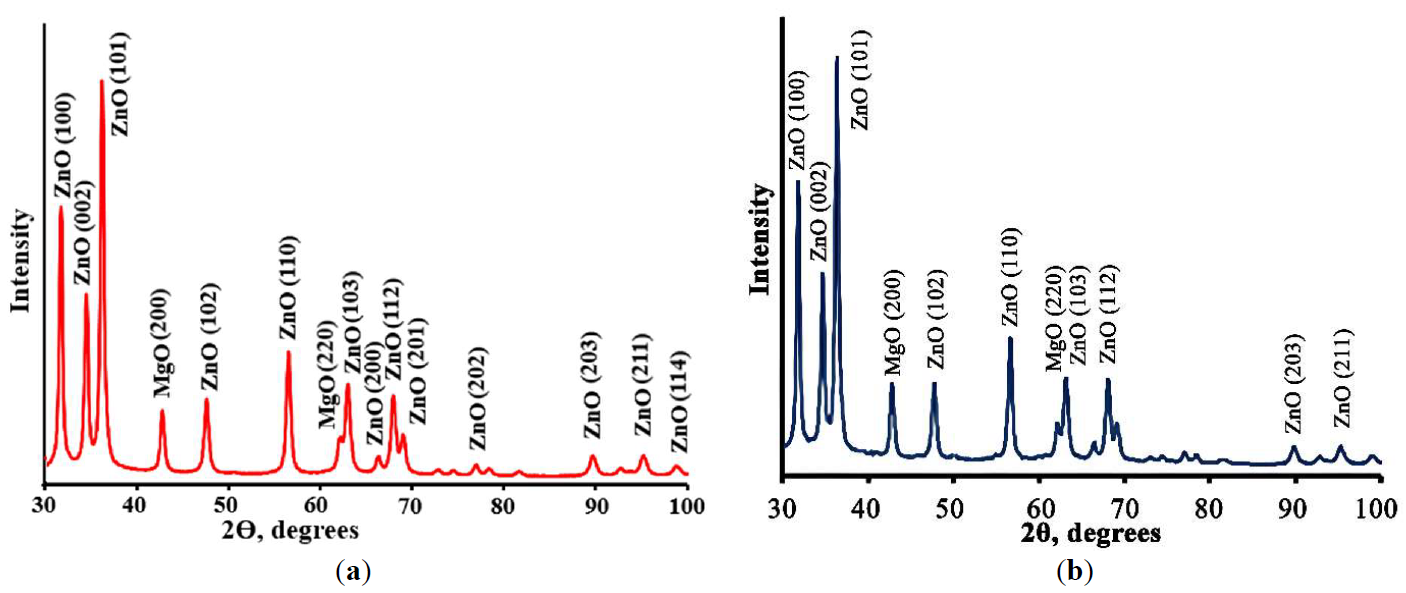
Review
21 February 2025Cement-Free Binders in Alumina-Magnesia Refractory Castables—A Review
To solve the problem of the accelerated deterioration of calcium aluminate (CAC)-bonded alumina-magnesia refractory castables during the secondary refining process, the development of cement-free binders has emerged as one significant research field of castables. The hydration behavior, curing mechanism, and properties of the most recent research on cement-free binders are compared in this paper. The problems and the modification of each binder of recent research are summarized. High-temperature performance of the castables bonded by traditional hydraulic cement-free binders (ρ-Al2O3 and activated MgO) is outstanding, explosive spalling resistance of the castables bonded by sol binders (silica sol, alumina sol) is good, and the properties of the castables bonded by novel organic hydratable binder (hydratable magnesium citrate) combine the advantages of these two binders above, but the mid-temperature mechanical strength is low. Furthermore, alumina-magnesia castables bonded by organic-composited inorganic cement-free binders are expected to be a future domain.
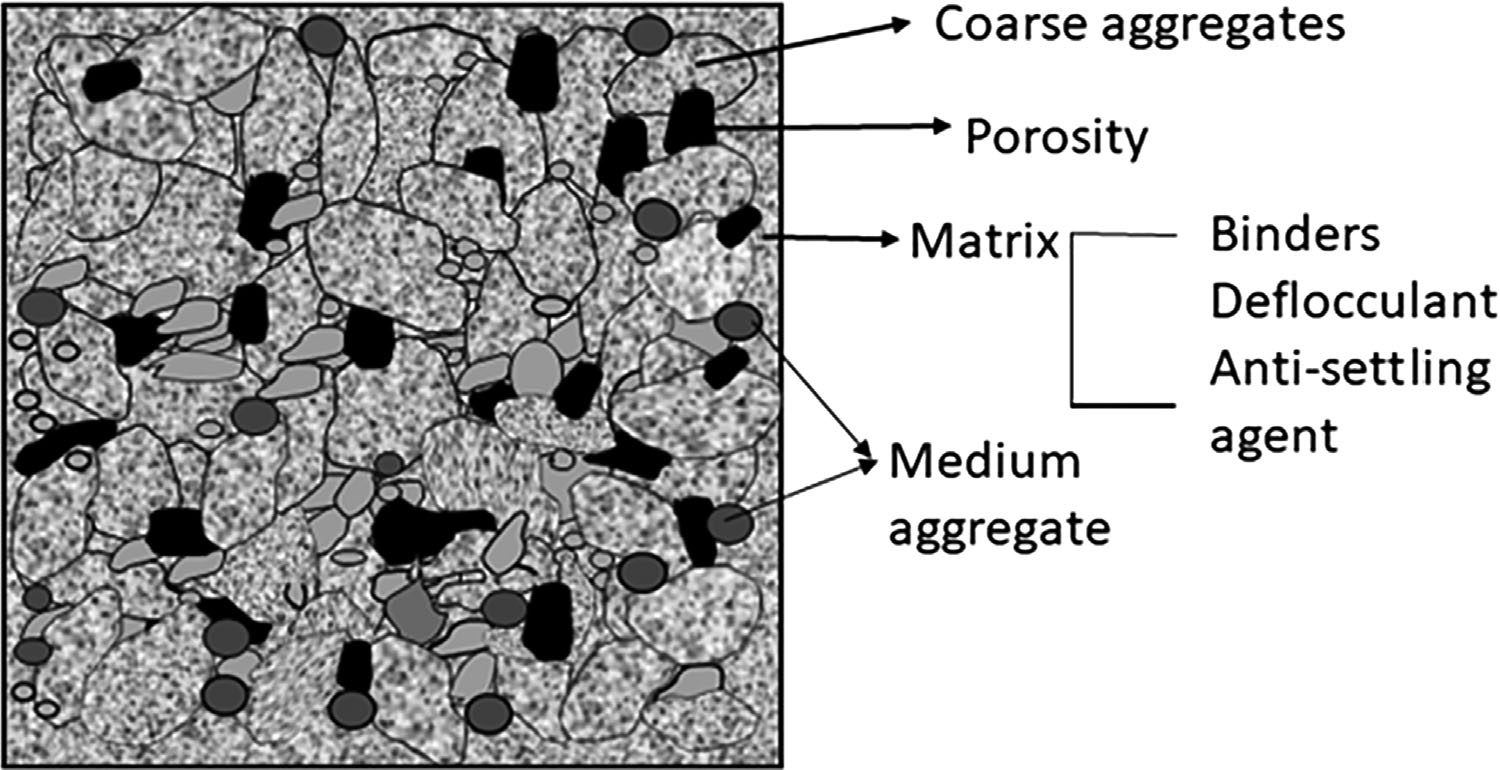
Article
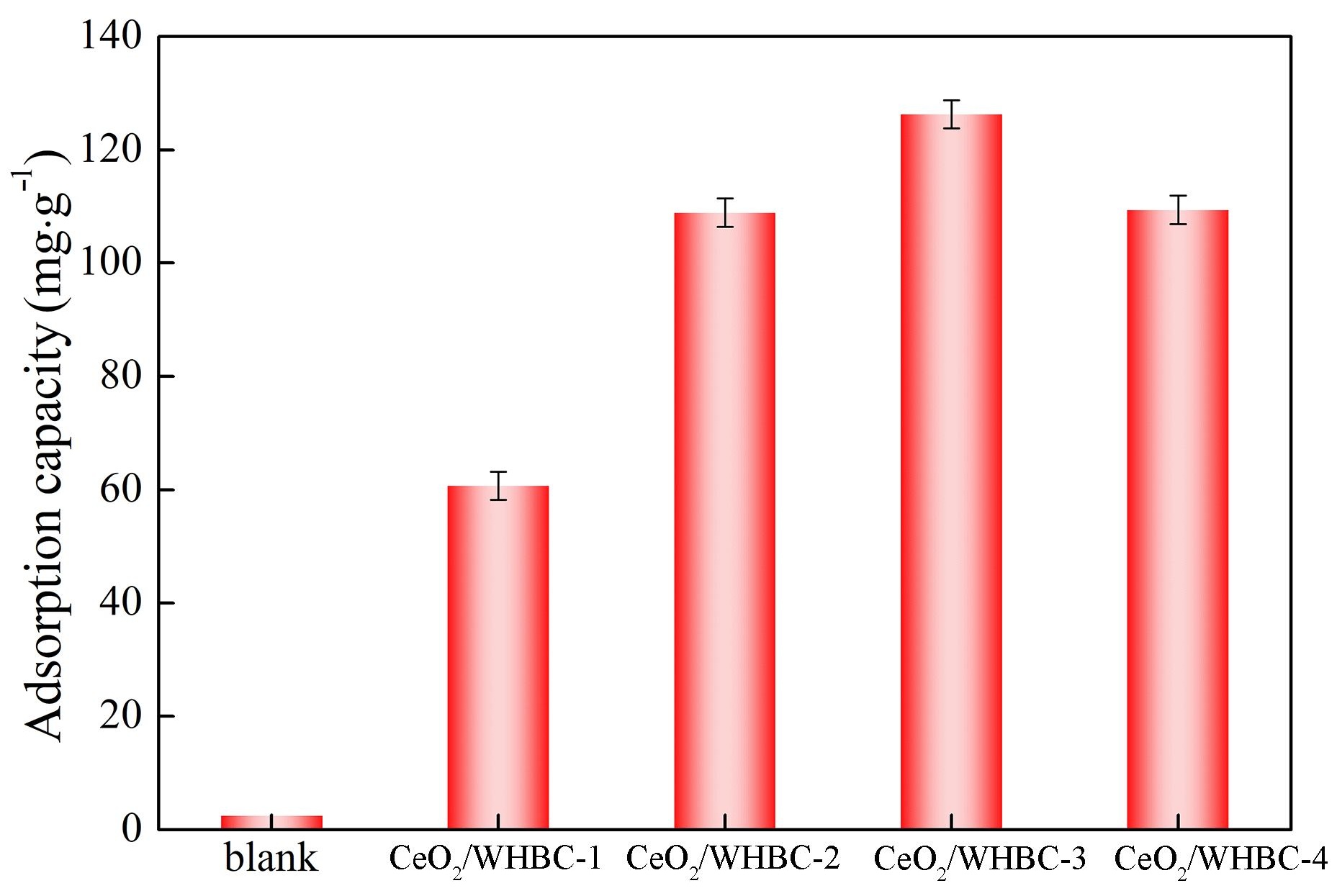
21 February 2025Efficient Removal of Glyphosate from Aqueous Solution by Cerium Dioxide Loaded Biochar
Glyphosate, which is one of the most widely used organophosphorus herbicides, poses a threat to the surrounding water environment. Traditional adsorbents were depicted to have poor capacities to eliminate it. CeO2 embraces the potential to adsorb glyphosate efficiently. However, suitable carbonaceous composites were necessary to be employed as its support. In this paper, water hyacinth was used as the precursor to prepare CeO2-loaded biochar (CeO2/WHBC), which was employed to remove glyphosate from the aqueous solution via adsorption. The results showed that CeO2/WHBC-3 illustrated the best adsorption performance for glyphosate with the capacity of 126.3 mg·g, which was prepared with per mmol CeO2 loaded of 0.2 g WHCB. Static adsorption experiments demonstrated that glyphosate adsorption at different solution pH values followed the Langmuir isotherm model and quasi-second order kinetic model, indicating that the adsorption was monolayer adsorption and that the adsorbent’s surface active sites primarily controlled the rate. Coexisting ion interference experiments showed that common cations (K+, Na+, Ca2+, Mg2+) and anions (Cl−, NO3−, SO42−) both promoted glyphosate adsorption on the CeO2/WHBC-3 surface. Moreover, the prepared sorbent maintained a high adsorption capacity after five adsorption-desorption cycles. Dynamic adsorption experiments showed that the CeO2/WHBC-3 packed column could efficiently remove glyphosate from aqueous solutions, even at high concentrations and fast flow rates. Zeta potentials and XPS analysis revealed that the adsorption mechanism of CeO2/WHBC-3 for glyphosate is mainly through electrostatic adsorption and metal complexation.
Article
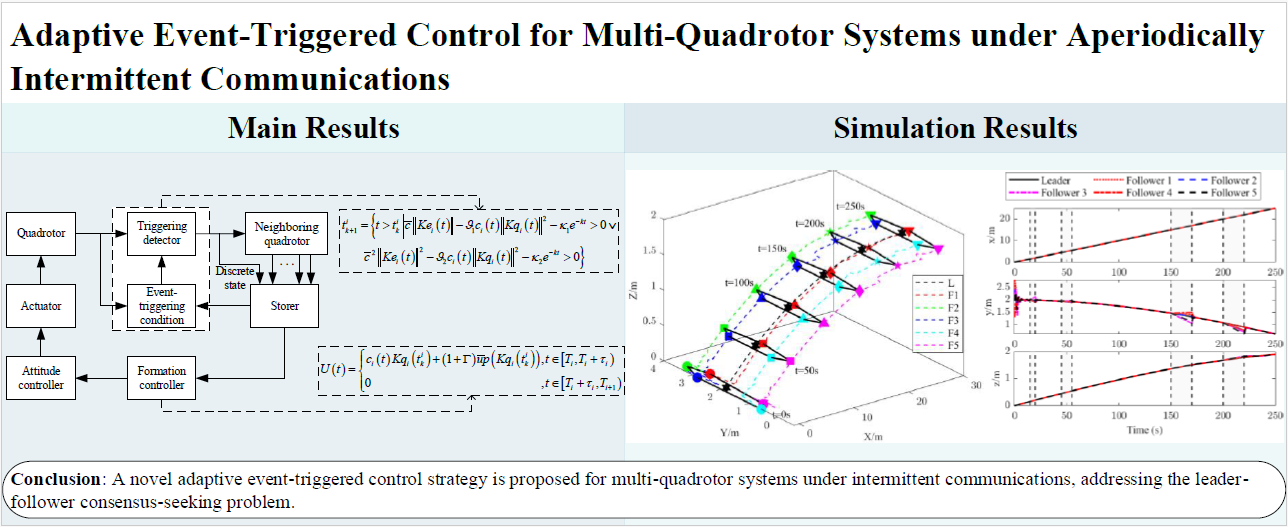
19 February 2025Adaptive Event-Triggered Control for Multi-Quadrotor Systems under Aperiodically Intermittent Communications
A novel adaptive event-triggered control strategy is proposed for multi-quadrotor systems under intermittent communications, addressing the leader-follower consensus-seeking problem where the leader has an unknown bounded input. Firstly, an activation time ratio condition is proposed, eliminating the reliance on the maximum time interval of intermittent communication. Secondly, a compensation term related to the leader’s unknown bounded input is designed in the controller to compensate for the error caused by intermittent communication in each period. Meanwhile, a prediction method is developed to eliminate the dependence on continuous information of neighboring quadrotors. Zeno behavior is strictly excluded, and communication among quadrotors is efficiently reduced with the designed event-triggering condition. Finally, numerical simulations verify the effectiveness and superiority of the proposed control strategy.