Articles (32)
Open Access
Communication
26 June 2025Production and Calibration of a Lambertian Surface Based on Barium Sulfate (BaSO4) for the Calibration of Multispectral Cameras
Drones, or unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs), are increasingly utilized across diverse fields such as agriculture, environmental analysis, and engineering due to their ability to capture high-quality multispectral imagery. To ensure the accuracy of these images, radiometric calibration of onboard multispectral cameras is essential. This study aimed to develop and calibrate a low-cost Lambertian surface using barium sulfate (BaSO4) for radiometric calibration of UAV-mounted multispectral cameras. A stainless steel mold was designed to compact BaSO4, and the resulting surface was calibrated using an ASD FieldSpec HandHeld UV/NIR spectroradiometer and a Spectralon plate as the reference standard. Results showed a strong correlation (Pearson’s r = 0.9988) between the BaSO4 surface and the Spectralon plate, confirming that the BaSO4-based surface is a cost-effective alternative for producing diffuse Lambertian surfaces with performance comparable to the standard.
Open Access
Article
12 May 2025Drone Operation with Human Natural Movement
This study proposes a method for operating drones using natural human movements. The operator simply wears virtual reality (VR) goggles. An image from the drone camera was displayed on the goggles. When the operator changes the direction of his or her face, the drone changes the direction to match that of the operator. When the operator moves their head up or down, the drone rises or falls accordingly. When the operator walks in place, rather than walking, the drone moves forward. This allows the operator to control the drone as if they were walking in the air. Each of these movements was detected by the values of the acceleration and magnetic field sensors of the smartphone mounted on the VR goggles. A machine learning method was adopted to distinguish between walking and non-walking movements. Compared with operation via conventional remote control, it was observed that the remote controller performed better than the proposed approach in the early stages. However, when the participants familiarized themselves with the natural operation, these differences became relatively small. This study combined drones, VR, and machine learning. VR provides drone pilots with a sense of realism and immersion, whereas machine learning enables the use of natural movements.
Open Access
Article
08 May 2025Nonlinear Optimal and Multi-Loop Flatness-Based Control for the 6-DOF Autonomous Bicopter
Bicopter UAVs can find use in several civilian and defence applications. In the present article a solution of the nonlinear optimal control problem of 6-DOF bicopters is first attempted using a novel nonlinear optimal control method. This method is characterized by computational simplicity, clear implementation stages and proven global stability properties. At a first stage, approximate linearization is performed on the dynamic model of the 6-DOF bicopter with the use of first-order Taylor series expansion and through the computation of the system’s Jacobian matrices. This linearization process is carried out at each sampling instance, around a temporary operating point. At a second stage, an H-infinity stabilizing controller is designed for the approximately linearized model of the 6-DOF bicopter. To find the feedback gains of the controller an algebraic Riccati equation is repetitively solved, at each time-step of the control method. Lyapunov stability analysis is used to prove the global stability properties of the control scheme. Next, the article examines a multi-loop flatness-based control method for the dynamic model of the 6-DOF bicopter. The drone’s dynamics is written in the form of two chained subsystems which are shown to be differentially flat. The state vector of the second subsystem becomes virtual control input to the first subsystem, while the control inputs of the first subsystem become setpoints for the second subsystem. Local controllers for the individual subsystems invert their dynamics. The global stability properties of the multi-loop flatness-based control scheme are also proven though Lyapunov analysis.
Open Access
Article
08 May 2025Evaluating Orthophoto Mosaic Accuracy Using RTK UAVs and AeroPoints 2 Ground Control Points: A User’s Perspective
With the growing use of Real Time Kinematics (RTK) Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs) and advancements in ground control points (GCPs), assessing positional accuracy of UAV derived orthophoto mosaics is crucial. This study aimed to improve UAV aerial image accuracy for more reliable orthophoto mosaics by examining the positional accuracy of orthophoto mosaics derived with (1) an RTK UAV; and (2) an RTK UAV combined with AeroPoints 2 GCPs. We tested two GPS base station methods for the RTK UAV: self-determined and manually assigned coordinates. The manually assigned coordinates resulted in significantly lower root mean square error (RMSE = 0.0729 m) compared to the self-determined method (RMSE = 1.9762 m), indicating improved accuracy. For the AeroPoints 2 GCPs, we recorded coordinates from a central GCP at a known location and four additional GCPs placed in each cardinal direction. The AeroPoints 2 system showed lower RMSE at all points compared to the RTK, with the central GCP at 0.0136 m, indicating high accuracy. These findings suggest that while RTK UAVs improve accuracy with manual base station assignment, incorporating AeroPoints 2 GCPs provides consistently higher precision across multiple locations. The study highlights the potential of AeroPoints 2 GCPs and suggests further research opportunities to enhance RTK UAV accuracy in areas lacking GPS correctional networks.
Open Access
Article
06 May 2025High-Efficiency Wireless Charging System for UAVs Based on PT-Symmetric Principle
To address the limited endurance of unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) and the efficiency degradation and instability in traditional wireless charging systems, this study proposes a high-efficiency UAV wireless charging system based on the parity-time (PT) symmetric principle. A non-Hermitian coupled resonator model is established, incorporating a dynamic gain-loss balancing mechanism and real-time parameter feedback control to adaptively compensate for coupling coefficient fluctuations caused by UAV positional deviations, thereby maintaining PT-symmetric phase stability. The receiver coil adopts a planar air-core spiral structure and is integrated beneath the UAV landing gear to minimize interference with aircraft operations. Experimental results show a transmission efficiency of 90.2% at 65 W output power, with both power and efficiency remaining stable in the strong coupling region. The system demonstrates strong robustness against horizontal misalignment and eliminates the need for complex relay structures or high-precision alignment. This work not only provides a theoretical foundation for the application of PT-symmetry in wireless power transfer but also offers a novel technical pathway for enhancing UAV endurance.
Open Access
Article
07 April 2025Evaluating a Motion-Based Region Proposal Approach with Background Subtraction Methods for Small Drone Detection
The detection of drones in complex and dynamic environments poses significant challenges due to their small size and background clutter. This study aims to address these challenges by developing a motion-based pipeline that integrates background subtraction and deep learning-based classification to detect drones in video sequences. Two background subtraction methods, Mixture of Gaussians 2 (MOG2) and Visual Background Extractor (ViBe), are assessed to isolate potential drone regions in highly complex and dynamic backgrounds. These regions are then classified using the ResNet18 architecture. The Drone-vs-Bird dataset is utilized to test the algorithm, focusing on distinguishing drones from other dynamic objects such as birds, trees, and clouds. By leveraging motion-based information, the method enhances the drone detection process by reducing computational demands. Results show that ViBe achieves a recall of 0.956 and a precision of 0.078, while MOG2 achieves a recall of 0.857 and a precision of 0.034, highlighting the comparative advantages of ViBe in detecting small drones in challenging scenarios. These findings demonstrate the robustness of the proposed pipeline and its potential contribution to enhancing surveillance and security measures.
Open Access
Article
10 March 2025
Leveraging Drone Technology for Precision Agriculture: A Comprehensive Case Study in Sidi Bouzid, Tunisia
The integration of drone technology in precision agriculture offers promising solutions for enhancing crop monitoring, optimizing resource management, and improving sustainability. This study investigates the application of UAV-based remote sensing in Sidi Bouzid, Tunisia, focusing on olive tree cultivation in a semi-arid environment. REMO-M professional drones equipped with RGB and multispectral sensors were deployed to collect high-resolution imagery, enabling advanced geospatial analysis. A comprehensive methodology was implemented, including precise flight planning, image processing, GIS-based mapping, and NDVI assessments to evaluate vegetation health. The results demonstrate the significant contribution of UAV imagery in generating accurate land use classifications, detecting plant health variations, and optimizing water resource distribution. NDVI analysis revealed clear distinctions in vegetation vigor, highlighting areas affected by water stress and nutrient deficiencies. Compared to traditional monitoring methods, drone-based assessments provided high spatial resolution and real-time data, facilitating early detection of agronomic issues. These findings underscore the pivotal role of UAV technology in advancing precision agriculture, particularly in semi-arid regions where climate variability poses challenges to sustainable farming. The study provides a replicable framework for integrating drone-based monitoring into agricultural decision-making, offering strategies to improve productivity, water efficiency, and environmental resilience. The research contributes to the growing body of knowledge on agricultural technology adoption in Tunisia and similar contexts, supporting data-driven approaches to climate-smart agriculture.
Open Access
Article
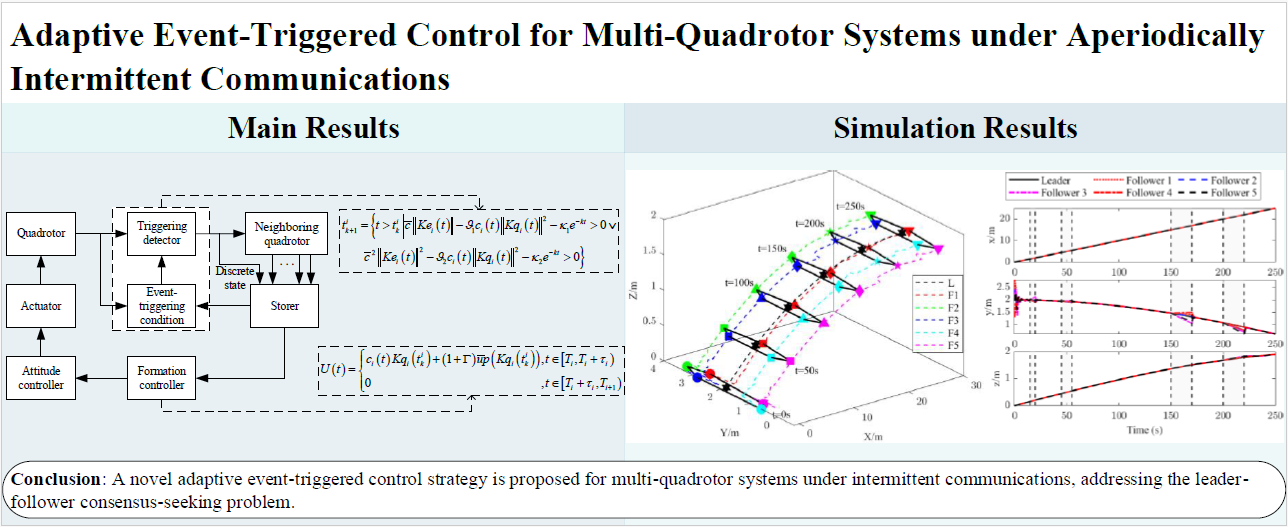
19 February 2025Adaptive Event-Triggered Control for Multi-Quadrotor Systems under Aperiodically Intermittent Communications
A novel adaptive event-triggered control strategy is proposed for multi-quadrotor systems under intermittent communications, addressing the leader-follower consensus-seeking problem where the leader has an unknown bounded input. Firstly, an activation time ratio condition is proposed, eliminating the reliance on the maximum time interval of intermittent communication. Secondly, a compensation term related to the leader’s unknown bounded input is designed in the controller to compensate for the error caused by intermittent communication in each period. Meanwhile, a prediction method is developed to eliminate the dependence on continuous information of neighboring quadrotors. Zeno behavior is strictly excluded, and communication among quadrotors is efficiently reduced with the designed event-triggering condition. Finally, numerical simulations verify the effectiveness and superiority of the proposed control strategy.
Open Access
Article
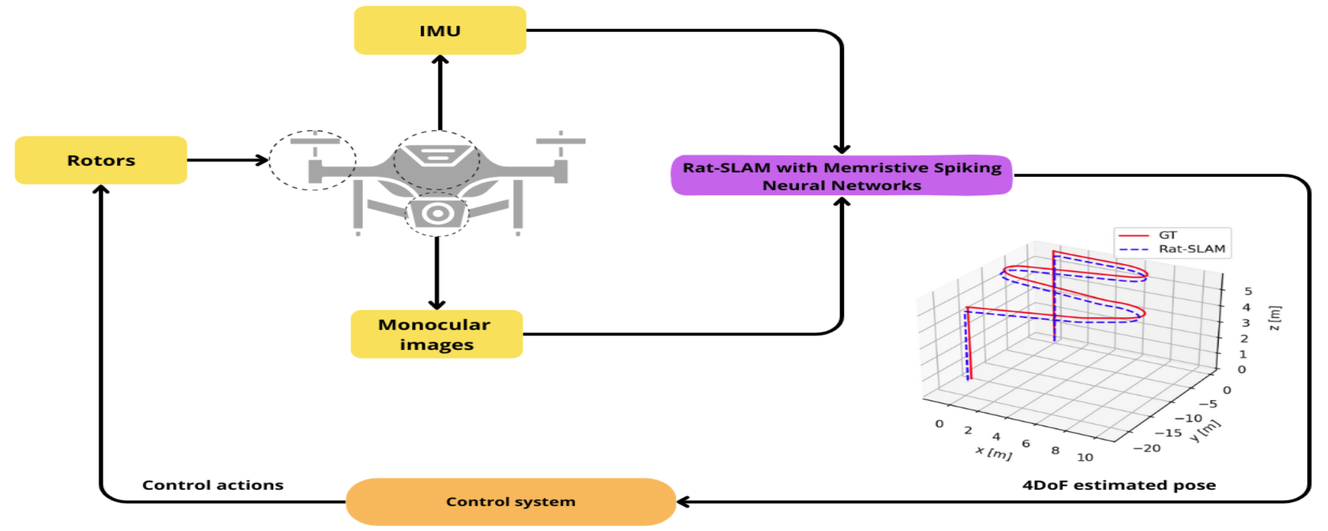
18 February 20254DoF Rat-SLAM with Memristive Spiking Neural Networks for UAVs Navigation System
Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs) are versatile platforms with potential applications in precision agriculture, disaster management, and more. A core need across these applications is a navigation system that accurately estimates location based on environmental perception. Commercial UAVs use multiple onboard sensors whose fused data improves localization accuracy. The bioinspired Rat-Simultaneous Localization and Mapping (Rat-SLAM) system, is a promising alternative to be explored to tackle the localization and mapping problem of UAVs. Its cognitive capabilities, semi-metric map construction, and loop closure make it attractive for localization in complex environments. This work presents an improved Rat-SLAM algorithm for UAVs, focusing on three innovations. First, Spiking Neural Networks (SNNs) are incorporated into Rat-SLAM’s core modules to emulate biological processing with greater efficiency. Second, Neuromorphic Computing models the neurons of the SNNs, assessing the feasibility of implementing SNNs on specialized hardware to reduce software processing, a key advantage for UAVs with limited onboard resources. Third, SNNs are developed based on the Memristive Leaky Integrate-and-Fire model, integrating memristors into artificial neurons to leverage their low power and memory properties. Our approach was evaluated through trajectory simulations using the Hector Quadrotor UAV in the Gazebo environment within the Robot Operating System, yielding valuable insights and guiding future research directions.
Open Access
Article
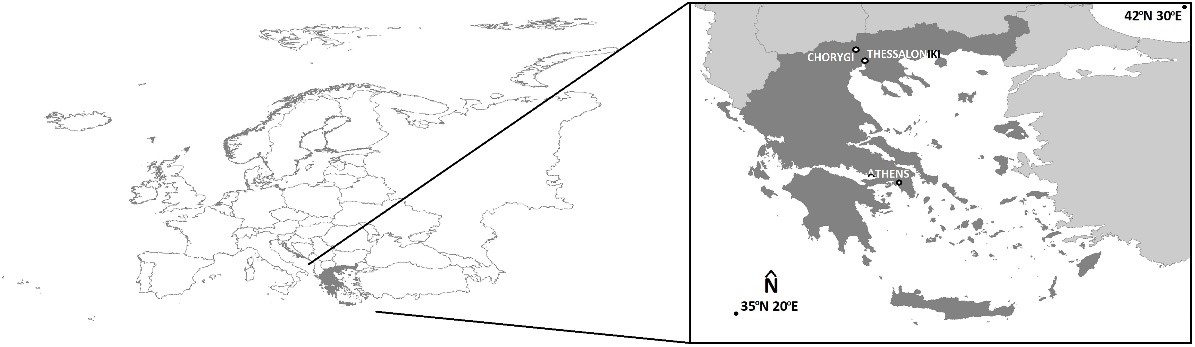
20 January 2025Visible Monuments above and below Ground Level, a Time-Honored Site from the Late Bronze Age to Modern Times
Due to the complex geometry of the monuments, it is often necessary to adapt the image collection process for their mapping. For the optimal mapping of the stronghold of Lazaritsa Chorygi (Greece) and its slopes, vertical, inclined, and horizontal images from different heights were collected using an Unmanned Aircraft System. Thus, for a monument of special archaeological/historical interest and natural beauty, a large set of high-spatial resolution data and final products (digital surface model and orthophotomosaic with spatial resolution 5.6 cm and 2.8 cm, respectively) is available. In addition, in the wider area of the fortified site, military structures (fire trenches, communication trenches, shelters, front and support trenches, and strong points) of the Great War length of 9 km were identified and mapped, which were identified in the 2003 or 2004 Google Earth Pro images, but worryingly are almost absent from the contemporary Google Earth Pro images.
Open Access
Article
10 January 2025Investigation of the Performance Characteristics of Unequal Co-Axial Rotors
The behaviour of co-axial rotors is well understood, and they are especially practical for large UAVs due to their increased thrust without changing the vehicle footprint. However, for co-axial systems with varying propeller diameters between the two disks, research is more limited. The goal of this paper was to determine an optimal configuration for several different unequal co-axial setups using numerous different propeller combinations and separation ratios. Propellers with diameters of 26 and 29 inches are tested at separation ratios of 0.05 to 0.35. Thrust and power were collected using an off-the-shelf FS15-TYTO thrust stand, with the upstream and downstream propellers running at equal throttles. From this, performance was assessed through efficiency, thrust, and power consumption, and comparisons were made to an ideal combination without losses. The results show that for unequal combinations, the user should place the smaller propeller upstream for greater efficiency, but for maximum thrust capacity, two equal propellers are preferred. When compared to two independent rotors of the same size, a 26″ upstream rotor and a 29″ downstream rotor minimised thrust loss to 16%, compared to 23% for the opposite arrangement. It was also found that the optimal separation ratio is always approximately 0.2.
Open Access
Article
06 January 2025A Bounded-Function-Based Scheme for Finite-Time Stabilization of a NWMR with Input Constraints
This paper addresses the finite-time stabilization problem for a nonholonomic wheeled mobile robot (NWMR) with input constraints. By utilizing the hyperbolic tangent function tanh(·), bounded finite-time stabilization controllers are developed. In addition, an explicit upper-bound estimate for the closed-loop settling time is given, and the level of input constraints is characterized by parameters that depend on the actuator’s capacity. A thorough finite-time stability analysis is carried out using appropriate Lyapunov functions. For a compact set contained in the domain of attraction, a guideline is presented to clarify how to construct it. Finally, simulation results show the effectiveness of the developed controllers.
Open Access
Article
07 November 2024Fully- and Partially- Distributed Adaptive Consensus of Second-Order Multi-Agent Systems Using Only Relative Position Measurements
In this paper, the distributed leader-follower consensus of a group of agents with second-order dynamics under the undirected graph communication topology is studied. The main objective of this study is to solve a major practical multi-agent problem in which the acceleration of the leader is not communicated to each follower. In contrast, the follower agents include some unknown dynamics in their intrinsic structure. By assuming a linear regression structure for leader acceleration and agent’s unknown dynamics, Lyapunov-based adaptive control algorithms are devised to control the network of agents in the presence of the communication loss and modeling uncertainties. The presented study describes two multi-agent control strategies called fully-distributed adaptive control (FDAC) and partially-distributed adaptive control (PDAC) systems in the first method, the followers do not have any a priori information about the communication graph, while in the second method, some information about the eigenvalues of the communication graph is available. The mathematical manipulations required to prove the stability of the FDAC and PDAC methods are presented. Finally, illustrative simulations are conducted to render the proposed algorithms’ merits and efficiencies.
Open Access
Perspective
10 October 2024Conceptual Design of Aerostat-Based Autonomous Docking and Battery Swapping System for Extended Airborne Operation
In response to the ever-growing global demand for Unmanned Aerial Vehicles, efficient battery solutions have become vital. This paper proposes a design and concept of an Autonomous Mid Air Battery Swapping System for Vertical Take-Off and Landing Unmanned Aerial Vehicles. The proposed design integrates Aerial Mechatronics, Lighter than Air Systems, and Digital Modelling by leveraging the innovative concept of aerostats for battery swapping. This adaptive and effective technology paves the way for the next generation of autonomous Vertical Take-Off and Landing, ensuring a longer flight time and range. Modern-day technologies have empowered Unmanned Aerial Vehicles to operate autonomously and be remotely controlled, expanding their utility across diverse industries. The enhanced Vertical Take-Off and Landing capabilities include the ability to dock on an aerostat-mounted system, facilitating seamless battery swapping without human intervention and ensuring extended flight duration and operational flexibility. These advancements promise to broaden the applications of Unmanned Aerial Vehicles across various industries.
Open Access
Article
02 September 2024Multi-Robot Cooperative Target Search Based on Distributed Reinforcement Learning Method in 3D Dynamic Environments
This paper proposes a distributed reinforcement learning method for multi-robot cooperative target search based on policy gradient in 3D dynamic environments. The objective is to find all hostile drones which are considered as targets with the minimal search time while avoiding obstacles. First, the motion model for unmanned aerial vehicles and obstacles in a dynamic 3D environments is presented. Then, a reward function is designed based on environmental feedback and obstacle avoidance. A loss function and its gradient are designed based on the expected cumulative reward and its differentiation. Next, the expected cumulative reward is optimized by a reinforcement learning algorithm that makes the loss function update in the direction of the gradient. When the variance of the expected cumulative reward is lower than a specified threshold, the unmanned aerial vehicle obtains the optimal search policy. Finally, simulation results demonstrate that the proposed method effectively enables unmanned aerial vehicles to identify all targets in the dynamic 3D airspace while avoiding obstacles.
Open Access
Opinion
22 August 2024Medical Drones for Public Health Emergency Preparedness, Response, and Resilience: Delivering Health for All
Amid a global metacrisis of health, environmental and economic challenges, medical delivery drones (or uncrewed aerial vehicles) offer a promising method to prepare for, and rapidly respond, to future emergencies. This opinion article summarizes the current medical delivery drone landscape, evidence base, and policy implications in the context of public health emergencies, such as pandemics, natural disasters, and humanitarian crises, with a particular emphasis on the region of sub-Saharan Africa. Using a multilateral, international health policy perspective, key challenges and opportunities, such as the development of sustainable funding mechanisms, robust regulatory frameworks, and capacity building, are identified.
Open Access
Review
06 August 2024Considerations for Unmanned Aerial System (UAS) Beyond Visual Line of Sight (BVLOS) Operations
This paper, intended for expert and non-expert audiences, evaluates the technical and regulatory requirements for Unmanned Aerial Systems (UAS) to operate beyond visual line of sight (BVLOS) services. UAS BVLOS operations have the potential to unlock value for the industry. However, the regulatory requirements and process can be complex and challenging for UAS operators. The work explored the BVLOS regulatory regime in the UK, Europe and the US and found similarities in process and requirements covering themes like Detect and Avoid (DAA), Remote identification and Reliable Connectivity. A unifying goal across these jurisdictions is to operate BVLOS safely and securely in non-segregated airspace. However, operating BVLOS in segregated airspace as the default or routine mode could accelerate approval and adoption. The paper reviewed existing challenges, highlighting Coverage, Capacity and Redundancy as critical for UAS BVLOS Operations. The work also highlighted the crucial role of Non-terrestrial Network (NTN) assets like Satellites and HAPS (High Altitude Platform Station) since terrestrial networks (not optimised for aerial platform coverage) may not be reliable for BVLOS connectivity.
Open Access
Article
25 July 2024A Distributed Framework for Persistent Wildfire Monitoring with Fixed Wing UAVs
Wildfires have proven to be a significantly exigent issue over the past decades. An increasing amount of research has recently been focused on the use of Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs) and multi-UAV systems for wildfire monitoring. This work focuses on the development of a decentralized framework for the purpose of monitoring active wildfires and their surrounding areas with fixed wing UAVs. It proposes a distributed fire data update methodology, a new formation algorithm based on virtual forces, fine-tuned by a Genetic Algorithm (GA), to arrange virtual agents into the monitoring area, and a control strategy to safely and efficiently guide fixed wing UAVs to loiter over the structured virtual agents. The system is tested in Software In The Loop (SITL) simulation with up to eight UAVs. The simulation results demonstrate the effectiveness of the system in monitoring the fire in a persistent manner and providing updated situational awareness data. The experiments show that the proposed framework is able to achieve and maintain coverage up to 100% over the area of interest, and very accurate fire representation. However, the performance is decreased for the experiments with low UAV numbers and large fire sizes.
Open Access
Article
24 June 2024An Integer Programming Approach to Multi-Trip Routing of Delivery Drones at Load-Dependent Flight Speed
In recent years, there has been a growing interest in utilizing drones for parcel delivery among companies, aiming to address logistical challenges. However, effective optimization of delivery routes is essential. A theoretical framework termed the Flight Speed-aware Vehicle Routing Problem (FSVRP) has emerged to address the variability in drone flight speed based on payload weight. Several approximate methods have been proposed to solve the FSVRP. Our research endeavors to optimize parcel delivery efficiency and reduce delivery times by introducing a novel delivery problem. This problem accounts for multiple deliveries while considering the variability in flight speed due to diverse payloads. Through experimentation, we evaluate the efficacy of our proposed method compared to existing approaches. Specifically, we assess total flight distance and flight time. Our findings indicate that even in cases where the payload exceeds maximum capacity, all parcels can be delivered through multiple trips. Furthermore, employing a multi-trip FSVRP approach results in an average reduction of 10% in total flight time, even when payload capacities are not exceeded.
Open Access
Article
12 June 2024Optimized Real Time Single-Drone Path Planning for Harvesting Information from a Wireless Sensor Network
We consider a remote sensing system in which fixed sensors are placed in a region, and a single drone flies over the region to collect information from cluster heads. We assume that the drone has a fixed maximum range and that the energy consumption for information transmission from the cluster heads increases with distance according to a power law. Given these assumptions, we derive local optimum conditions for a drone path that either minimizes the total or maximum energy required by the cluster heads to transmit information to the drone. We show how a homotopy approach can produce a family of solutions for different drone path lengths so that a locally optimal solution can be found for any drone range. We implement the homotopy solution in Python and demonstrate the tradeoff between drone range and cluster head power consumption for several geometries. Execution time is sufficiently rapid for the computation to be performed in real time so that the drone path can be recalculated on the fly. The solution is shown to be globally optimal for sufficiently long drone path lengths. A proof of concept implementation in Python is available on GitHub. For future work, we indicate how the solution can be modified to accommodate moving sensors.
Open Access
Article
05 June 2024An Architecture for Early Wildfire Detection and Spread Estimation Using Unmanned Aerial Vehicles, Base Stations, and Space Assets
This paper presents, an autonomous and scalable monitoring system for early detection and spread estimation of wildfires by leveraging low-cost UAVs, satellite data and ground sensors. An array of ground sensors, such as fixed towers equipped with infrared cameras and IoT sensors strategically placed in areas with a high probability of wildfire, will work in tandem with the space domain as well as the air domain to generate an accurate and comprehensive flow of information. This system-of-systems approach aims to take advantage of the key benefits across all systems while ensuring seamless cooperation. Having scalability and effectiveness in mind, the system is designed to work with low-cost COTS UAVs that leverage infrared and RGB sensors which will act as the primary situational awareness generator on demand. AI task allocation algorithms and swarming-oriented area coverage methods are at the heart of the system, effectively managing the aerial assets High-level mission planning takes place in the GCS, where information from all sensors is gathered and compiled into a user-understandable schema. In addition, the GCS issues warnings for events such as the detection of fire and hardware failures, live video feed and lower-level control of the swarm and IoT sensors when requested. By performing intelligent sensor fusion, this solution will offer unparalleled reaction times to wildfires while also being resilient and reconfigurable should any hardware failures arise by incorporating state of the art swarming capabilities.
Open Access
Article
08 May 2024Assessing Drone Return-to-Home Landing Accuracy in a Woodland Landscape
While aerial photography continues to play an integral role in forest management, its data acquisition can now be obtained through an unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV), commonly referred as a drone, instead of conventional manned aircraft. With its feasibility, a drone can be programed to take off, fly over an area following predefined paths and take images, then return to the home spot automatically. When flying over forests, it requires that there is an open space for a vertical takeoff drone to take off vertically and return safely. Hence, the automatic return-to-home feature on the drone is crucial when operating in a woodland landscape. In this project, we assessed the return-to-home landing accuracy based on a permanently marked launch pad nested in a wooded area on the campus of Stephen F. Austin State University in Nacogdoches, Texas. We compared four models of the DJI drone line, with each flown 30 missions over multiple days under different weather conditions. When each drone returned to the home launch spot and landed, the distance and direction from the launch spot to the landing position was measured. Results showed that both the Phantom 4 Advanced and the Spark had superior landing accuracy, whereas the Phantom 3 Advanced was the least accurate trailing behind the Phantom 4 Pro.
Open Access
Article
26 April 2024Exact and Heuristic Approaches to Surveillance Routing with a Minimum Number of Drones
The rising cost and scarcity of human labor pose challenges in security patrolling tasks, such as facility security. Drones offer a promising solution to replace human patrols. This paper proposes two methods for finding the minimum number of drones required for efficient surveillance routing: an ILP-based method and a greedy method. We evaluate these methods through experiments, comparing the minimum number of required drones and algorithm runtime. The findings indicate that the ILP-based method consistently yields the same or a lower number of drones needed for surveillance compared to the greedy method, with a 73.3% success rate in achieving better results. However, the greedy method consistently finishes within one second, whereas the ILP-based method sometimes significantly increases when dealing with 14 more locations. As a case study, we apply the greedy method to identify the minimum drone surveillance route for the Osaka-Ibaraki Campus of Ritsumeikan University.
Open Access
Article
19 March 2024Designing a Quadcopter for Fire and Temperature Detection with an Infrared Camera and PIR Sensor
In agriculture, medicine, and engineering, sudden fire outbreaks are prevalent. During such events, the ensuing fire spread is extensive and unpredictable, necessitating crucial data for effective response and control. To address this need, the current initiative focuses on utilizing an Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (UAV) with an Infrared (IR) sensor. This sensor detects and analyses temperature variations, accompanied by additional camera footage capturing thermal images to pinpoint the locations of the incidents precisely. The UAV’s programming is executed using Arduino-Nano and mission planner software, interfacing with the Pixhawk flight controller operating in a guided mode for autonomous navigation. The UAV configuration includes a radio module interfacing with Arduino-Nano, a flight controller, and remote-control functionality. The flight duration is approximately 10–15 min, contingent upon flight dynamics and environmental temperature. Throughout its airborne operation, the UAV transmits live telemetry and log feeds to the connected computer, displaying critical parameters such as altitude, temperature, battery status, vertical speed, and distance from the operator. The Pixhawk flight controller is specifically programmed to govern the UAV’s behavior, issuing warnings to the pilot in case of low voltage, prompting a timely landing to avert potential crashes. In case of in-flight instability or a crash, the mission planner can trace the UAV’s location, facilitating efficient recovery and minimizing costs and component availability losses. This integrated approach enhances situational awareness and mitigation strategies, offering a comprehensive solution for managing fire incidents in diverse fields.
Open Access
Article
26 January 2024A Lightweight Visual Navigation and Control Approach to the 2022 RoboMaster Intelligent UAV Championship
In this paper, an autonomous system is developed for drone racing. On account of their vast consumption of computing resources, the methods for visual navigation commonly employed are discarded, such as visual-inertial odometry (VIO) or simultaneous localization and mapping (SLAM). A series of navigation algorithms for autonomous drone racing, which can operate without the aid of the information on the external position, are proposed: one for lightweight gate detection, achieving gates detection with a frequency of 60 Hz; one for direct collision detection, seeking the maximum passability in-depth images. Besides, a velocity planner is adopted to generate velocity commands according to the results from visual navigation, which are enabled to perform a guidance role when the drone is approaching and passing through gates, assisting it in avoiding obstacles and searching for temporarily invisible gates. The approach proposed above has been demonstrated to successfully help our drone passing-through complex environments with a maximum speed of 2.5 m/s and ranked first at the 2022 RoboMaster Intelligent UAV Championship.
Open Access
Article
16 January 2024A Position-based Hybrid Routing Protocol for Clustered Flying Ad Hoc Networks
Unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) have been used to establish flying ad hoc networks (FANETs) to support wireless communication in various scenarios, from disaster situations to wireless coverage extensions. However, the operation of FANETs faces mobility, wireless network variations and topology challenges. Conventional mobile ad hoc network and vehicular ad hoc network routing concepts have rarely been applied to FANETs, and even then they have produced unsatisfactory performance due to additional challenges not found in such networks. For instance, position-based routing protocols have been applied in FANET, but have failed to achieve adequate performance in large networks. Clustering solutions have also been used in large networks, but with a significant overhead in keeping track of the complete topology. Hence, to solve this problem, we propose a hybrid position-based segment-by-segment routing mechanism for clustered FANETs. This approach facilitates traffic engineering across multiple wireless clusters by combining position-based inter-cluster routing with a rank-based intra-cluster routing approach capable of balancing traffic loads between alternative cluster heads. Simulation results show that our solution achieves, on average, a lower power consumption of 72.5 J, a higher throughput of 275 Mbps and a much lower routing overhead of 17.5% when compared to other state-of-the-art end-to-end routing approaches.
Open Access
Article
27 November 2023Enhancing the Monitoring Protocols of Intermittent Flow Rivers with UAV-Based Optical Methods to Estimate the River Flow and Evaluate Their Environmental Status
Temporary streams are a key component of the hydrological cycle in arid and semi-arid regions, but their flow is highly variable and difficult to measure. In this paper, we present a novel approach that could be used to assess the flow of temporary streams this allowing to characterize their environmental status. Specifically, we apply the Image Velocimetry (IV) method to estimate surface velocity in temporary streams using Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs) equipped with optical sensors (IV-UAV method). The IV-UAV method enables the easy, safe and quick estimation of the velocity on the water’s surface. This method was applied in different temporary streams in Lesvos Island, Greece. The results obtained indicate that the IV-UAV can be implemented at low discharges, temporary streams and small streams. Specifically, the water depth ranged from 0.02 m to 0.28 m, while the channel width ranged from 0.6 m to 4.0 m. The estimated surface velocity ranged from 0.0 to 5.5 m/s; thus, the maximum water discharge was 0.60 m3/s for the largest monitored stream of the island. However, there were many occasions that measurements were unable due to various reasons such as dense vegetation or archaeological sites. Despite of this, the proposed methodology could be incorporated in optical protocols which are used to assess the environmental status of temporary streams of Mediterranean conditions. Finally, this would become a valuable tool for understanding the dynamics of these ecosystems and monitoring changes over time.
Open Access
Review
08 November 2023Review on Drone-Assisted Air-Quality Monitoring Systems
Drone-aided systems have gained popularity in the last few decades due to their stability in various commercial sectors and military applications. The conventional ambient air quality monitoring stations (AAQMS) are immovable and big. This drawback has been significantly overcome by drone-aided low-cost sensor (LCS) modules. As a result, much research work, media information, and technical notes have been released on drone-aided air quality and ecological monitoring and mapping applications. This work is a sincere effort to provide a comprehensive and structured review of commercial drone applications for air quality and environmental monitoring. The collected scientific and non-scientific information was divided according to the different drone models, sensor types, and payload weights. The payload component is very critical in stablility of the multirotor drones. Most study projects installed inexpensive sensors on drones according to the avilibility of the space on drone frame. After reviewing of multiple environmental applications the common payload range was 0 gm to 4000 gm. The crucial elements are addressed, including their relation to meteorological factors, air isokinetics, propeller-induced downwash, sensor mounting location, ramifications etc. As a result, technical recommendations for AQ monitoring assisted by drones are addressed in the debate part. This work will help researchers and environmentalists choose sensor-specific payloads for drones and mounting locations. Also, it enables advanced methods of monitoring parameters that help policymakers to frame advanced protocols and sensor databases for the environment and ecology.
Open Access
Article
10 October 2023ℒ1 Adaptive Control of Quadrotor UAVs in Case of Inversion of the Torque Direction
This paper presents a method for fault tolerant control of quadrotor UAVs in case of inversion of the torque direction, a situation that might occur due to structural, hardware or software issues. The proposed design is based on multiple-model ℒ1 adaptive control. The controller is composed of a nominal reference model and a set of degraded reference models. The nominal model is that with desired dynamics that are optimal regarding some specific criteria. In a degraded model, the performance criteria are reduced. It is designed to ensure system robustness in the presence of critical failures. The controller is tested in simulations and it is shown that the multiple model ℒ1 adaptive controller stabilizes the system in case of inversion of the control input, while the ℒ1 adaptive controller with a single nominal model fails.
Open Access
Communication
03 March 2023Evaluating Different UAS Flight Methods for 3D Model Generation and Printing of a Tornado Destroyed Cultural Heritage: Caddo House in Texas
In recent years, the use of Unmanned Aerial Systems (UAS) to obtain imagery for photogrammetry has become commonplace. Using these data to develop 3D products has also grown significantly in both research and commercial applications. This study aims to find a relatively simple and low cost UAS flight method as a means to obtain data to produce a 3D model suitable for 3D printing. The study subject chosen to assess different flight methods was the Caddo House at Caddo Mounds State Historical Site located near Alto, Cherokee County, Texas, USA. To collect images for analysis, a DJI Phantom 4 Pro UAS was used with Pix4DCapture mission control app. Two main missions were carried out, one being a pre-defined double-grid flight, and the other being an orbital free-flight method. The findings of this study indicate that if the goal is to create a true-to-life 3D model of an object using UAS, the best method would be a curated orbital free-flight method. If there is time constraint and the subject is sufficiently large and not considerably irregular, a double-grid mission with sufficient forward and side overlap can produce desirable results, but with a slight loss of fine details. The 3D model developed from the curated orbital flight method was successfully printed with a customer grade FDM 3D printer.
Open Access
Article
22 December 2022Image Fusion Capability from Different Cameras for UAV in Cultural Heritage Applications
In this paper, image fusion is performed by utilizing images derived from different cameras for the unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV). By producing the fused image, the spatial resolution of the multispectral (MS) image is improved on the one hand and the classification accuracy on the other hand. First, however, the horizontal and vertical accuracy of the generated products, orthophoto mosaics, and digital surface models, is determined using checkpoints that do not participate in the processing of the image blocks. Also, the changes of these accuracies with a 50% increase (or decrease) of the UAV's flight height are determined. The study area is the Early Christian Basilica C and the flanking Roman buildings, at the archaeological site of Amphipolis (Eastern Macedonia, Greece).